Table of Contents
Introduction
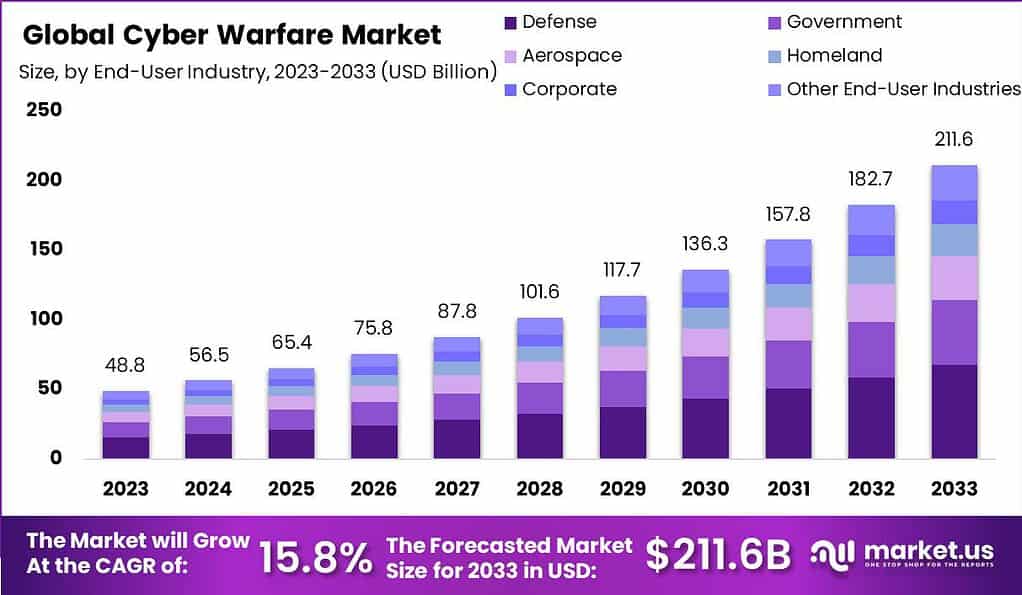
The global cyber warfare market is projected to reach a valuation of USD 56.5 billion by 2024, with a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.8% expected during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033. It is anticipated that the market will reach a valuation of USD 211.6 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increasing cyber threats, the digital transformation of industries, and stringent regulatory requirements. The market is characterized by substantial investments in cybersecurity solutions by governments and corporations aimed at protecting national security and sensitive data from sophisticated cyberattacks.
Key growth factors include the rising frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks, prompting defense and corporate sectors to strengthen their cyber defenses. Notably, the North American region has significantly increased its cyber defense budget, recognizing the critical importance of protecting digital infrastructure. This includes the establishment of specialized cybersecurity units and the implementation of advanced technologies and stringent regulations to enhance cyber resilience.
Recent developments underscore the dynamic nature of the market. For instance, the United States’ Department of Homeland Security allocated USD 374.9 million in grant funding for the State and Local Cybersecurity Grant Program in 2023, reflecting a substantial increase from the previous year. Additionally, partnerships and acquisitions among major players, such as the collaboration between Thales and 11 specialized cybersecurity organizations in France, aim to enhance cyber threat intelligence and resilience.
Key Takeaways
- The global cyber warfare market is projected to reach a valuation of USD 211.6 billion by 2033, with a noteworthy CAGR of 15.8% from 2024 to 2033.
- In 2024, the market is expected to be valued at USD 56.5 billion, showcasing a promising trajectory for growth over the forecast period.
- The Defense segment dominated the cyber warfare market in 2023, commanding a market share exceeding 32%.
- North America held a dominant market position in 2023, capturing over 41% of the global market share.
- The demand for cyber warfare solutions in North America was valued at USD 20.0 billion in 2023, indicating substantial market size.
- Europe maintained a notable presence in the cyber warfare market in 2023, contributing significantly to the global landscape.
- Asia-Pacific exhibited remarkable growth in the cyber warfare market in 2023, driven by increasing cybersecurity investments across countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea.
- The Department of Homeland Security announced the availability of USD 374.10 million in grant funding for the Fiscal Year 2023 State and Local Cybersecurity Grant Program (SLCGP).
- The cyber warfare market is characterized by key players such as BAE Systems, Cisco Systems Inc., DXC Technology Company, RTX, Booz Allen Hamilton Inc., General Dynamics Corporation, Intel Corporation, L3Harris Technologies Inc., IBM, and Airbus.
- Safe Security, a cybersecurity startup, secured USD 50.1 million in its Series B funding round, showcasing the market’s appetite for innovative solutions.
Key Cyber Warfare Statistics
- Global Hacking Incidents: 64% of companies globally have experienced hacking attacks.
- US as a Primary Target: 26.3% of all cyber warfare attacks are directed at the United States.
- Cyber Espionage: 20% of global organizations consider cyber espionage their top threat.
- Political Links: 35% of politically motivated cyberattacks are linked to China or Russia.
- Espionage-Related Attacks: 11% of all cyberattacks are related to espionage.
Notable Cases of Cyber Warfare
- 2013 FBI Notification: Over 3,000 companies were informed by the FBI about data breaches.
- US Government Breaches in 2013: 61,000 cybersecurity breaches were reported by the US federal government.
- Chinese Hack in 2015: Data of 4 million US government employees were accessed by Chinese hackers.
- 2017 Cybersecurity Incidents: More than 35,277 cybersecurity incidents were reported by the US federal government.
- Navy Personnel Records: 100,000 records were hacked in a notable cyberattack.
- Twitter Spear Phishing in 2017: 10,000 US Defense Department employees were targeted by Russian-backed hackers.
- Iranian Hackers in 2018: 144 US universities and 33 businesses were targeted, with $3.4 billion worth of data stolen.
- ISIS Funding via PayPal: In 2016, an ISIS operative received $8,700 via PayPal for terror activities.
- ISIS Twitter Accounts: In 2014, 46,000 Twitter accounts were used by ISIS supporters for propaganda.
Global Cyber Warfare Landscape
- Chinese Hackers’ Global Reach: In 2018, hackers stole data from 45 companies across multiple countries.
- External Breaches: In 2019, 69% of breaches and cyber attacks in the USA originated from outside the country.
- Cyber Warfare Proportion: 23% of breaches are acts of cyber warfare.
- Attack Surge: Cyber warfare attacks surged by 440% from 2009 to 2018.
- Chinese Cyber Activity: Since 2009, 31.6% of Chinese cyber warfare activity has targeted the US.
- Russian Election Interference: Russian hackers targeted election systems in all 50 states during the 2016 US election.
- Moscow’s Troll Army: Since 2015, Russia has supported a 400-strong troll army for cyberattacks.
- Frequency of Cyberattacks: A cyberattack occurs every 39 seconds.
- Human Error: Nearly 90% of breaches occur due to human error.
- Ransomware Incidents: 24% of cybersecurity incidents involving malware come with ransom notes.
- Law Firms’ Vulnerability: 64% of law firms globally faced hacking attacks.
- Data Breach Costs: Each major data breach in 2020 is expected to cause over $150 million in damage.
Recent Acquisitions and Megers
- Delinea Acquires Authomize: Delinea acquired Israeli startup Authomize, adding identity threat detection and response (IDTR) technologies to its portfolio. The deal was valued at several tens of millions of dollars.
- Dynatrace Acquires Runecast: Dynatrace, a firm specializing in observability and security, acquired UK-based Runecast to enhance its automated security posture management and compliance monitoring for hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) Acquires Juniper Networks: HPE acquired Juniper Networks for $14 billion in cash, expanding its network equipment capabilities.
- BlueVoyant Acquires Conquest Cyber: BlueVoyant acquired Conquest Cyber, integrating its advanced SaaS technologies with BlueVoyant’s cyber defense solutions. The acquisition was supported by $140 million in Series E funding led by Liberty Strategic Capital and ISTARI.
- Mimecast Acquires Elevate Security: Mimecast, a leader in email security, acquired Elevate Security to bolster its user education and awareness training offerings.
- SentinelOne Acquires PingSafe: SentinelOne acquired PingSafe for over $100 million in a cash-and-stock deal, adding cloud-native application protection platform (CNAPP) capabilities to its product lineup.
- Protect AI Acquires Laiyer AI: Protect AI, an AI/ML security firm, acquired Laiyer AI to extend its LLM Guard product for protecting large language models (LLMs) against security threats and misuse.
- HID Global Acquires ZeroSSL: HID Global, a provider of trusted identity solutions, acquired Austria-based SSL certificate provider ZeroSSL to enhance its website security capabilities.
- Option3 Acquires Onclave Networks: Option3 acquired Onclave Networks, specializing in zero-trust solutions for IoT and OT, as part of its strategy to build a unified cybersecurity platform.
- Link11 Acquires Reblaze Technologies: Germany-based Link11 acquired Israeli firm Reblaze Technologies to expand its presence in the network security and web application security sectors.
Notable Events
Espionage and Data Breaches
- U.S. Government Breaches: Chinese hackers targeted members of the Inter-Parliamentary Alliance on China and Italian MPs in March 2024, aiming to detect IP addresses and locations. This highlights the use of cyber warfare for political espionage and intelligence gathering.
- Corporate Espionage: Microsoft reported that Russian hackers stole source code and accessed internal systems in an ongoing campaign from November 2023 to February 2024. This demonstrates the use of cyberattacks to gain strategic advantage by accessing sensitive corporate data.
Disruption of Critical Infrastructure
- Energy Sector Attacks: Israeli-linked hackers disrupted approximately 70% of gas stations in Iran in December 2023 as retaliation for Iran’s aggressive actions. This showcases how cyber warfare can be employed to target and disrupt critical national infrastructure.
- Water Utility Sabotage: Ukrainian state hackers disabled Russia’s largest water utility plant by encrypting over 6,000 computers in December 2023. This attack illustrates the potential of cyber warfare to impact essential services and infrastructure during conflicts.
Military Operations and Coordination
- Russian Cyber Operations in Ukraine: During the ongoing conflict, Russian cyber operations aimed to support information warfare and propaganda efforts rather than direct military advantages. Cyberattacks were used to disrupt communications and gather intelligence, although they were not highly coordinated with conventional military actions.
- US Cyber Command Integration: The U.S. Cyber Command is working on consolidating its cyber warfare capabilities to better integrate with traditional military operations. This effort includes enhancing public-private partnerships and developing comprehensive strategies for defense and offense in cyberspace.
Political and Social Manipulation
- Information Warfare: Russian hackers have been involved in leaking sensitive communications, such as the intercepted conversation between German military officials discussing support for Ukraine. This type of cyber operation is used to create political instability and manipulate public opinion.
- Social Media Manipulation: Cyber warfare tactics also include the use of social media for misinformation campaigns, aiming to influence public perception and political outcomes. This was evident in Russia’s actions during the U.S. elections and ongoing propaganda efforts.
Key Players Analysis
BAE Systems Plc
BAE Systems plc is a global defense, aerospace, and security company headquartered in Camberley, United Kingdom. The company operates through five key segments: Electronic Systems, Platforms & Services, Air, Maritime, and Cyber & Intelligence. BAE Systems is renowned for its advanced technology solutions, including electronic warfare systems, cybersecurity services, and intelligence solutions that protect national security and critical infrastructure.
Recently, BAE Systems has been actively enhancing its capabilities in the cyber warfare sector. For instance, the company signed significant contracts such as maintaining and repairing light guns in Ukraine and developing next-generation airborne decoy countermeasures. Additionally, BAE Systems continues to expand its reach with new product developments and strategic partnerships, reflecting its commitment to strengthening global cyber defenses.
Cisco Systems Inc
Cisco Systems Inc., a global leader in networking and security technologies, plays a significant role in the cyber warfare sector. The company designs and sells a variety of products and services related to communications and information technology, with a strong focus on network security, cloud security, and advanced threat detection. Recently, Cisco introduced several new capabilities aimed at enhancing security and AI integration across its networking portfolio. These developments include new integrations with Cisco Secure Access for a unified approach to networking and security management, as well as enhanced security posture reporting for operational technology (OT) assets.
Cisco also continues to expand its cloud-managed solutions, such as the Catalyst 9300-M switches, which are now managed through the Meraki dashboard. Additionally, Cisco’s acquisition of companies like Splunk Inc. for $28.13 billion highlights its commitment to strengthening its cybersecurity offerings and addressing the complex needs of modern IT environments.
DXC Technology Company
DXC Technology Company, headquartered in Ashburn, Virginia, is a leading provider of IT services and solutions with a significant presence in the cyber warfare sector. The company operates through two main segments: Global Business Services (GBS) and Global Infrastructure Services (GIS), offering a range of services including cybersecurity, cloud infrastructure, and IT outsourcing. DXC has been recognized as a leader in NelsonHall’s 2024 Cyber Resiliency Services NEAT evaluation for its robust cybersecurity capabilities, which include end-to-end IT service solutions aimed at enhancing cyber resiliency across entire IT estates.
Recent developments at DXC include their focus on strengthening mainframe services, as highlighted in Everest Group’s Mainframe Services PEAK Matrix® Assessment 2024, and their advancements in AI-driven enterprise intelligence services. Additionally, DXC continues to build strong customer relationships and improve business continuity plans, further solidifying its role in the cybersecurity landscape.
RTX
RTX, formerly Raytheon Technologies, is a major player in the aerospace and defense industry, with a significant presence in the cyber warfare sector. The company has recently undergone notable changes, including the sale of its cybersecurity and intelligence business for $1.3 billion, which has since been rebranded as Nightwing. This strategic move aims to focus more on core defense capabilities.
RTX continues to advance in the cyber warfare domain by collaborating with L3Harris Technologies to update the electronic warfare systems on the U.S. Navy’s F/A-18 Super Hornet fleet, with $80 million in prototyping contracts awarded in 2023. The company reported a 6% increase in sales for Q1 2024, driven by higher volumes in land and air defense systems. These developments underline RTX’s commitment to maintaining and enhancing its capabilities in cyber and electronic warfare.
Booz Allen Hamilton Inc.
Booz Allen Hamilton Inc. is a prominent player in the cyber warfare sector, leveraging its extensive expertise in cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and digital solutions to support both government and commercial clients. The company is renowned for its ability to integrate and defend critical networks, data, and weapon systems, enhancing the operational capabilities of the U.S. military and other entities. Recent developments include the hiring of strategic defense talent, such as Retired Vice Admiral Roy Kitchener and Retired Major General David Gaedecke, to strengthen their global defense business.
Booz Allen also opened a new Mission Systems Integration Facility in California, Maryland, aimed at addressing growing challenges for the Department of Defense. Additionally, the firm has been actively involved in deploying AI and electronic warfare capabilities to maintain air superiority and secure national infrastructure against advanced cyber threats.
General Dynamics Corporation
General Dynamics Corporation is a key player in the cyber warfare sector, offering advanced electronic and cyber warfare capabilities. The company provides integrated solutions that enhance cybersecurity across land, sea, air, and space domains. Recently, General Dynamics secured a significant $980 million contract from the U.S. Army to deliver advanced cyber warfare capabilities, including new cyber systems, upgrades, training, and support.
Additionally, the company won a $171 million contract to support the Air Force in securing industrial control systems. General Dynamics continues to invest heavily in its cyber and electronic warfare capabilities, reinforcing its position as a leading provider of critical defense technologies.
Intel Corporation
Intel Corporation, headquartered in Santa Clara, California, is a global leader in the design and manufacturing of semiconductor products, including CPUs, GPUs, and other hardware critical for both consumer and enterprise markets. In the cyber warfare sector, Intel plays a pivotal role by providing advanced processors and system-on-chips (SoCs) that power various defense and cybersecurity applications. The company’s focus on artificial intelligence (AI), cryptography, and secure networking technologies enhances the cybersecurity posture of numerous organizations and governmental entities worldwide.
Recent developments in Intel’s operations include a strategic partnership with Synopsys and ARM to develop optimized compute SoCs on the Intel 18A process, which significantly enhances their cybersecurity capabilities. Additionally, Intel has launched several new products, such as the Mobileye EyeQ6 Lite to advance autonomous driving technologies, and the world’s largest neuromorphic system to support sustainable AI development. These innovations underscore Intel’s commitment to leading in technological advancements that support both commercial and defense sectors.
Furthermore, Intel continues to invest in expanding its manufacturing capabilities with Intel Foundry Services (IFS), which offers advanced packaging technologies and aims to meet the growing demand for semiconductor fabrication in the U.S. and Europe. This initiative is crucial for national security and cyber defense, ensuring a reliable supply of critical technology components.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the global cyber warfare market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the escalating cyber threat landscape and the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures across various sectors. However, the market must address challenges such as the evolving nature of cyber threats and the shortage of skilled professionals to sustain its growth trajectory.


