Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Editor’s Choice
- History of Thin Clients
- Thin Client Market Statistics
- Global Desktop Virtualization Market Size Forecast
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) Thin-client Statistics
- HP Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- Dell Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- Lenovo Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- Samsung Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- HCL Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- ClearCube Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- VXL Technology Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- Perceptions of Thin Clients Among Teachers and Students Statistics
- User Preferences for Thin vs. Fat Clients
- Thin Client Vulnerabilities Statistics
- Environmental Impact
- Innovations and Developments in Thin Client Statistics
- Recent Developments
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Thin Client Statistics: Thin clients are lightweight computing devices that rely on centralized servers for processing and storage, providing users access to applications and data remotely.
Operating on a client-server model, they utilize protocols like Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) for connectivity.
With minimal hardware requirements and simplified operating systems, thin clients offer cost efficiency, centralized management, enhanced security, and scalability. Making them ideal for corporate environments, educational institutions, and remote work scenarios.
However, they may face performance limitations, dependency on reliable network connectivity, and limited offline capabilities. Which organizations must consider when implementing these solutions?

Editor’s Choice
- The term “thin client” was officially coined in 1993, marking a shift towards lighter computing endpoints that offloaded heavy tasks to centralized servers.
- The global thin client market revenue reached $1.43 billion in 2023.
- By 2032, the market is anticipated to reach a total size of $1.70 billion. With standalone units accounting for $0.68 billion. Mobile units are $0.53 billion, and units with monitors are $0.49 billion.
- The global thin client market is segmented by application. Displaying varied market shares across different sectors. As of the latest data, the retail sector holds the largest share at 30%. Indicating a robust utilization of thin clients in this industry.
- In 2015, the Japanese thin-client virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) market generated sales of 42.5 billion Japanese Yen.
- In exploring student perceptions of using thin clients. Survey results reveal that issues related to saving and retrieving work are relatively infrequent. Specifically, about 11% of students reported having trouble keeping track of revisions to their computer work when using thin clients.
- A UK study by Winmark, modeled after the Pepsi Challenge. Surveyed 110 users on their preferences between thin and fat client computing. The findings showed that 72% of participants believed thin clients booted up faster than desktop PCs. 23.6% preferred the boot-up speed of desktop PCs, and 4.5% were undecided.
History of Thin Clients
- The history of thin clients traces back to the era of mainframe computers in the 1960s. Whereas basic terminals relied on central servers for processing power.
- Thin clients evolved significantly during the 1990s, driven by companies like Oracle and Sun Microsystems. Which promoted the use of network-based computing to reduce the need for powerful local devices.
- The term “thin client” was officially coined in 1993. Marking a shift towards lighter computing endpoints that offloaded heavy tasks to centralized servers.
- Key developments over the years include Microsoft’s introduction of Windows-based terminals in the late 1990s. Advancements in networking in the 2000s, and the rise of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and cloud computing in the 2010s.
- Modern thin clients, such as those from companies like Dell and HP. Now supports complex applications, high-resolution graphics, and enhanced security. Making them integral to many businesses, particularly in education, healthcare, and enterprise environments.
- Thin clients continue to adapt, with future growth driven by trends in cloud computing, edge computing, and 5G technology.
(Sources: Bright Hub, Hackernoon)
Thin Client Market Statistics
Global Thin Client Market Size Statistics
- The global thin client market revenue is projected to experience steady growth over the next decade at a CAGR of 2.0%.
- In 2022, the market generated revenue of $1.40 billion.
- This figure is expected to slightly increase to $1.43 billion in 2023. Followed by a gradual rise to $1.45 billion in 2024.
- By 2025, revenue is anticipated to grow to $1.49 billion.
- The upward trajectory continues, with revenues reaching $1.52 billion in 2026, $1.55 billion in 2027, and $1.57 billion in 2028.
- The market is expected to achieve $1.60 billion by 2029, and further growth is projected for the subsequent years. With revenues of $1.63 billion in 2030, $1.66 billion in 2031, and reaching $1.70 billion by 2032.
- This consistent increase reflects the sustained demand and expanding applications of thin client solutions in various sectors.
(Source: market.us)

Thin Client Market Size – By Form Factor Statistics
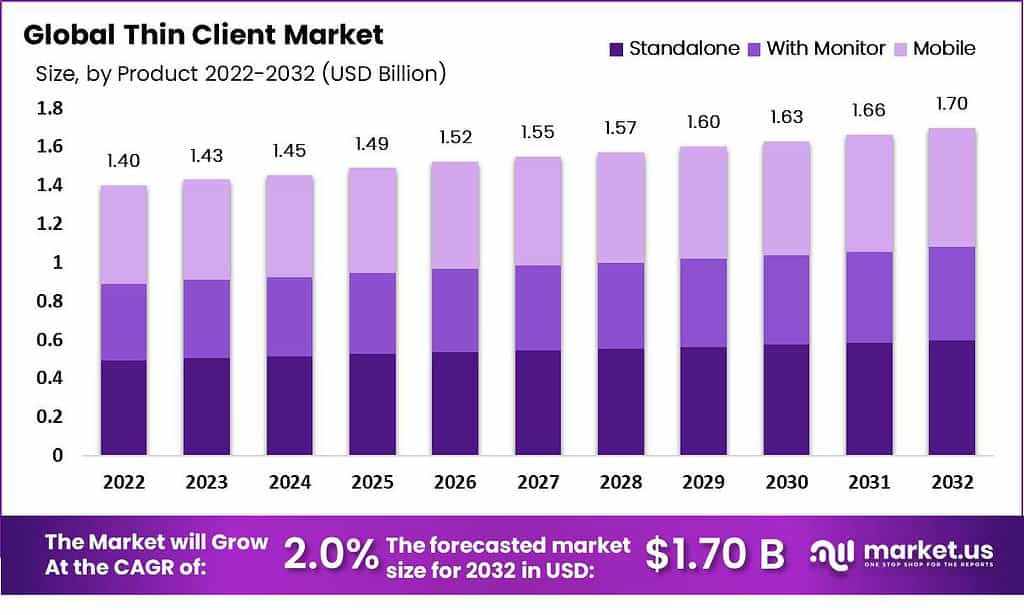
- The global thin client market is segmented by form factor. It is forecasted to see incremental growth from 2022 to 2032.
- In 2022, the market’s total revenue was $1.40 billion. Divided among standalone units ($0.56 billion), mobile units ($0.43 billion), and units with monitors ($0.41 billion). Over the forecast period, all segments are expected to experience growth.
- By 2023, revenue figures are projected at $1.43 billion overall. With standalone units contributing $0.57 billion, mobile units $0.44 billion, and units with monitors $0.41 billion.
- This pattern of growth will persist through 2024 and beyond. Reaching total market revenues of $1.45 billion in 2024 and $1.49 billion in 2025 and continuing to rise each year.
- Notably, by 2032, the market is anticipated to reach a total size of $1.70 billion. With standalone units accounting for $0.68 billion, mobile units $0.53 billion, and units with monitors $0.49 billion.
- This data underscores the steady demand across different thin client form factors. Reflecting diverse usage scenarios and consumer preferences in the sector.
(Source: market.us)

Global Thin Client Market Share – By Application Statistics
- The global thin client market is segmented by application, displaying varied market shares across different sectors.
- As of the latest data, the retail sector holds the largest share at 30%. Indicating a robust utilization of thin clients in this industry.
- The Information Technology Services (ITS) sector follows with a 21% market share, reflecting significant adoption in technology-driven operations.
- Education accounts for 15%, showing the relevance of thin clients in academic settings.
- The government sector also represents a substantial portion of the market at 14%, underscoring its strategic importance in public administration.
- Additionally, the industrial sector commands a 9% market share. Pointing to the growing penetration of thin clients in manufacturing and production environments.
- The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector contributes 7%. Which highlights the adoption of thin clients in financial institutions aiming for enhanced security and efficiency.
- Lastly, the healthcare sector, although holding the smallest share at 4%. Indicates focused usage where data security and reliability are crucial.
- These distributions illustrate the diverse applications and strategic importance of thin clients across various sectors.
(Source: market.us)

Global Desktop Virtualization Market Size Forecast
- Various research firms have analyzed the global desktop virtualization market. Offering diverse forecasts for the period from 2020 to 2027.
- In 2020, estimates of the market size varied significantly: 360 Research Reports projected the market at $7.8 billion. Slightly lower at $6.7 billion, and Global Industry Analysts at a higher $10.6 billion.
- By 2022, a company projected the market size to rise to $12.3 billion, indicating a growth trend.
- Forecasts for 2026 showed an even broader divergence: 360 Research Reports estimated the market size to be $8.4 billion. They predicted a substantial increase to $12.3 billion, and Global Industry Analysts projected the highest growth to $18.9 billion.
- Looking ahead to 2027, it anticipates the market to reach $20.1 billion. Reflecting expectations of sustained expansion and increasing adoption of desktop virtualization technologies across various sectors.
- These projections highlight differing perspectives on the pace and extent of growth within the desktop virtualization industry over these years.
(Source: Statista)

Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) Thin-client Statistics
Thin-client VDI Market Size in Japan
- The thin-client virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) market in Japan has demonstrated consistent growth from fiscal year 2015 through 2020.
- In 2015, the market generated sales of 42.5 billion Japanese Yen.
- This figure rose steadily in subsequent years, reaching 45.85 billion Yen in 2016 and further increasing to 48.9 billion Yen in 2017.
- The growth trajectory continued, with sales climbing to 52.9 billion Yen in 2018 and 57.15 billion Yen in 2019.
- By 2020, the market’s sales were forecasted to achieve a significant mark of 62 billion Yen. Reflecting a robust expansion and increasing adoption of thin-client VDI solutions in Japan over these six years.
(Source: Statista)

Thin-client VDI Annual Sales Growth in Japan
- The year-on-year change in the thin-client virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) market in Japan from fiscal year 2015 to 2020 reflects a generally positive growth trend.
- In 2015, the market experienced a year-on-year increase of 6.8%.
- This growth accelerated in 2016, reaching 7.9%, before slightly declining to 6.7% in 2017.
- The market rebounded in 2018 with a year-on-year change of 8.2% and maintained a strong growth rate of 8.0% in 2019.
- Forecasts for 2020 indicated an increase to 8.5%, suggesting continued robust expansion within the VDI sector.
- These figures underscore the market’s resilience and the increasing adoption of thin-client technologies in Japan over these five years.
(Source: Statista)

HP Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- The HP t630 Thin Client is equipped with a robust set of specifications designed for performance and versatility.
- It features an AMD GX-420GI SOC, which is a quad-core APU with a processing speed ranging from 2.0 to 2.2 GHz and integrated Radeon R7E graphics.
- The device offers various memory options, including flash storage capacities of 8GB, 16GB, 32GB, 64GB, and 128GB, alongside RAM options of 4GB, 8GB, 16GB, or 32 GB.
- Connectivity is facilitated through a variety of ports. Including a 10/100/1000 network interface, four USB 2.0 ports (two at the front and two at the rear), three USB 3.0 ports (two at the front and one internal), one serial port, and one parallel port.
- Additionally, it supports two Display Port video outputs with a resolution of 3840 x 2160 at 60Hz and one VGA port with a resolution of 1920 x 1200 at 60Hz. Power requirements include a supply of 19.5V at 3.33A, with a coax male plug measuring 7.4mm/5.0mm at the center pin.
- The device consumes approximately 0.5W when off, around 12W during idle operation, and about 28W while running.
- The dimensions of the HP t630 Thin Client are 240 mm in height, 42 mm in width, and 220 mm in depth. Excluding the stand, it is a compact solution for various computing needs.
(Source: HP)
Dell Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- The Dell Wyse 3040 Thin Client is designed for efficiency and performance. Featuring an Intel Atom x5-Z8350 quad-core processor with a base speed of 1.44 GHz and the capability to boost up to 1.92 GHz.
- It is equipped with integrated Intel HD Graphics and offers flexible memory options. Including 8GB or 16GB eMMC flash storage and 2GB or 4GB DDR3L RAM.
- For connectivity, the device includes a 10/100/1000 Ethernet port. Four USB 2.0 ports (two front and two rear), and two USB 3.0 ports (one front and one rear).
- Additionally, it supports dual DisplayPort outputs with resolutions up to 3840 x 2160 at 60Hz, along with a VGA port for resolutions up to 1920 x 1200 at 60Hz, and features a headphone/microphone combo jack for audio.
- Power requirements consist of a 19V, 3.42A power supply, with power consumption figures of less than 0.5W when off, approximately 6W while idle, and around 12W during operation.
- The compact dimensions of the Wyse 3040 measure 197 mm in height, 25 mm in width, and 205 mm in depth, weighing approximately 1.1 kg.
- It supports various operating systems, including Windows 10 IoT Enterprise and a Linux-based OS, and offers optional wireless connectivity through Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. With integrated security features, the Dell Wyse 3040 Thin Client presents itself as an effective solution for diverse virtual desktop environments.
(Source: Dell)
Lenovo Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- The ThinkCentre M625q Thin Client is built for efficient performance. Powered by an AMD 7th Gen E2-9000e processor, and equipped with a single DDR4 memory slot that supports a maximum of 8GB at 1866MHz.
- It utilizes a 65W power supply with an efficiency rating of 88%. Connectivity options are extensive, featuring front ports that include two USB 3.0 ports (one designed for FastCharge) and two audio jacks (one combo). In contrast, the rear ports offer one USB 3.0 port, three USB 2.0 ports, dual DisplayPort outputs, and various punch-out options (Type-C/VGA/Serial and Serial).
- Additionally, it includes one LAN port and expansion capabilities with an M.2 slot for PCIe/SATA SSD and another M.2 2230 slot for Wi-Fi. The device supports NFA344 QCA6174A 2x2ac + BT4.2 M.2 Combo Wi-Fi.
- In terms of design, the ThinkCentre M625q features a compact 1L Tiny4 form factor with hardware TPM 2.0 for enhanced security. An open chassis for easy upgrades to HDD and memory, and a fanless design for quieter operation. It complies with various green certifications, including Energy Star 6.1, EPEAT® Gold, and UL Green Guard®.
- The device is complemented by the ThinkVision T22i-10 Monitor. Which boasts a 1920×1080 resolution near-edgeless IPS-type screen for vibrant images from wide viewing angles.
- This monitor features built-in power and rich connectivity options. Including VGA, HDMI, and DisplayPort, and four USB 3.0 ports for quick charging. Its full-function stand allows for versatile adjustments, including height, tilt, pivot, and swivel, enhancing user experience.
(Source: Lenovo)
Samsung Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- Samsung’s TC Series Thin Clients are engineered to provide a streamlined virtual desktop experience that is ideal for business environments.
- These thin clients are typically equipped with Intel or AMD processors. Integrated graphics suitable for handling standard office applications and multimedia, and support dual monitor setups.
- Memory configurations often include 2GB to 8GB of DDR3 or DDR4 RAM and flash storage ranging from 8GB to 64 GB. Tailored for environments where data is primarily stored remotely.
- Connectivity options feature Gigabit Ethernet and, in some models, optional Wi-Fi capabilities. Along with multiple USB ports, including USB 2.0 and USB 3.0, plus DisplayPort and HDMI or DVI outputs for multi-display setups.
- Depending on the model, the operating system choices include Windows Embedded Standard or IGEL OS, optimized for virtual desktop infrastructures. The design of the TC Series is compact and sleek, offering VESA mounting options to maximize space efficiency.
- Energy efficiency is paramount, with models often adhering to Energy Star certification standards. Ensuring low operational costs through power consumption as low as 5-15 watts. Security features might include TPM chips and software safeguards to protect data integrity and prevent unauthorized access.
- Additionally, Samsung’s management software facilitates easy deployment, configuration, and maintenance. Making these thin clients a versatile choice for various business needs and budget constraints.
(Source: Samsung)
HCL Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- The HCL WINBee 5000-WES VX is a thin client model featuring the Genuine Windows Embedded Standard 2009 operating system. It is built around the VIA CN896 chipset with a VIA C7 processor clocked at 1.6 GHz.
- The system supports a single DDR slot with a starting 512MB of DDR2 RAM, which is upgradeable up to 2GB. For graphics, it includes 32 MB of shared VRAM. Storage capabilities feature 2 IDE 40 Pin channels, each supporting a 4 GB IDE, with a 1 GB IDE Flash drive standard, expandable up to 4 GB.
- It offers robust protocol support, including RDP, ICA, Telnet, and various network protocols such as TCP/IP, DNS, DHCP, and SNMP, among others. The network interface provides 10/100/1000Mbps BaseT Fast Ethernet.
- The device’s I/O ports include connections for PS/2 keyboard and mouse, one RJ-45 LAN port, one VGA and one DVI port, four USB 2.0 ports, two serial ports, and one parallel port. Optional features include an emulation suite and either internal or external wireless LAN support.
- The WINBee 5000-WES VX is compatible with various operating systems, including versions of Microsoft Windows Server, UNIX, and LINUX, and comes equipped with Internet Explorer 7.0 or 8.0.
- It includes one PCI expansion slot and an external power supply, and it supports 5.1 speaker output and local microphone input. The system offers a selection of HCL TFT-LCD monitors starting at 15.6 inches.
- Manageability is enhanced with HCL Embedded Device Management Software and multi-level security. Allowing admin/user password changes and the enabling/disabling of serial, parallel, and USB ports, including USB mass storage devices.
- The device complies with PCI, ACPI, and RoHS standards, reflecting its adherence to industry regulations and environmental standards.
(Source: RSSING)
ClearCube Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- The ClearCube CD8805 Thin Client is equipped with an Intel Celeron J4125 CPU featuring four cores and four threads, with a base clock of 2.0 GHz and a boost up to 2.5 GHz.
- It supports dual 4K video output, making it ideal for high-resolution applications.
- This device includes a variety of external ports: two HDMI ports for video output, one 3.5mm speaker jack, four USB 3.0 ports for high-speed data transfer, and one RJ45 port that supports 1 GHz 2.4G/5G dual-band Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 4.0 for versatile connectivity. Internally, it offers a SATA port for additional storage options.
- The CD8805’s memory system uses DDR4 RAM, with a recommended capacity of 8GB, to ensure smooth operation.
- For storage, it comes with a 128GB M.2 SSD and provides an option for adding a SATA 2.5-inch drive, offering flexibility in storage expansion.
- This thin client can run various operating systems, including Windows 10 IoT, Windows 10 Pro, Windows 11 Pro, and StratoDesk, with optional SIPR token support for enhanced security, along with IGEL OS.
- In terms of physical dimensions, the device is compact, measuring only 1.7 inches in height, 4.5 inches in length, and 4 inches in width. Making it an excellent choice for setups where space is at a premium.
- This blend of performance, connectivity, and compact size makes the ClearCube CD8805 an efficient solution for diverse computing environments.
(Source: ClearCube)
VXL Technology Thin Client Specifications Statistics
- The VXL Thin Client is categorized under thin clients or diskless workstations. Designed primarily for network-based computing with no monitor included.
- This desktop form factor device is equipped with Gigabit Ethernet connectivity, supporting Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, and Gigabit Ethernet protocols to ensure robust and versatile network connections.
- It adheres to several compliance standards, including TUV GS and RoHS. Which reflects its safety and environmental considerations.
- In terms of physical dimensions, the VXL Thin Client measures 4.12 inches in height, 14.12 inches in length, and 10.87 inches in width, with a UPC of 0506011089855.
- It does not come with an optical drive, emphasizing its role as a diskless workstation that relies on networked resources rather than local storage.
- The device includes a power adapter and supports a single CPU, with no capacity for additional CPUs, highlighting its design for straightforward, single-user operations.
- This model is ideal for environments where high efficiency and minimal local computing resources are preferred. Making it a suitable choice for various professional settings.
(Source: SHI Government Solutions)
Perceptions of Thin Clients Among Teachers and Students Statistics
Teacher Perceptions of Problems Saving and Retrieving Individual Student Work While Using Thin Client Statistics
- In a survey assessing teachers’ perceptions of thin clients regarding student issues with saving and retrieving work. The results indicate relatively few problems.
- According to the survey, only 5% of teachers observed students frequently having trouble saving their work.
- A slightly higher percentage, 10%, reported that students often struggle with keeping track of revisions.
- Meanwhile, the loss of work appears to be a minimal issue. With only 2% of teachers noting that students’ work gets lost.
- These findings suggest that there are some challenges associated with using thin clients in educational settings. Significant issues such as losing work are not commonly reported by teachers.
(Source: EDC’s Center for Children and Technology)

Student Perceptions of Problems Saving and Retrieving Their Work While Using Thin Client Statistics
- In exploring student perceptions of using thin clients, survey results reveal that issues related to saving and retrieving work are relatively infrequent.
- Specifically, about 11% of students reported having trouble keeping track of revisions to their computer work when using thin clients.
- Additionally, the incidence of work getting lost is quite low. Only 2% of students experience this problem.
- These findings suggest that while there are some navigational challenges in managing revisions. The overall stability and reliability of thin clients in educational settings allow most work to be saved and retrieved effectively.
(Source: EDC’s Center for Children and Technology)

User Preferences for Thin vs. Fat Clients
- A study by UK market research firm Winmark resembled a Pepsi Challenge format. Investigated preferences between thin and fat client computing among 110 users.
- The results indicated a significant preference for thin clients.
- Approximately 72% of participants noted that thin clients booted up faster than desktop PCs. While about 23.6% felt the opposite, and 4.5% were undecided.
- In terms of overall performance, 54.5% believed that thin clients operated more efficiently. Compared to 26.4% who favored desktop PCs, and 19.1% found no difference between the two.
- Overall, 60.9% of users preferred thin clients, 26.4% opted for desktop PCs, and 12.7% expressed no strong preference for either.
- The findings suggest general favoritism towards thin clients due to perceived efficiency and speed.
(Source: IT News)

Thin Client Vulnerabilities Statistics
Impact of Thin Client on Computing Vulnerabilities Statistics
- The survey on the impact of vulnerabilities in thin client computing revealed several significant effects on users.
- A majority of respondents, 75%, reported a loss of productivity as the most common consequence.
- This was followed by 69% of users experiencing unavailability of their PCs.
- Corrupted files were also a major issue, affecting 62% of respondents.
- Nearly half, 49%, reported loss of access to data, while 47% actually lost data. Loss of user confidence was noted by 33% of the participants.
- Other effects included interference or lockups cited by 19%, unreliable applications by 13%, and trouble reading files by 12%.
- Issues with saving files, system crashes, and trouble with printing were reported by 9% and 7% of users, respectively.
- Lastly, a small percentage, 2%, felt threatened by potential job loss due to these computing vulnerabilities.
- These findings underscore the wide range of challenges faced by users due to vulnerabilities in thin client computing environments.
(Source: HP)

Vulnerability Exposure Between Personal Computers and Thin Client Statistics
- In a comparative study on the response to vulnerabilities between HP personal computers (PCs) and thin clients (TCs) spanning 2002 and 2003. Distinct differences were observed in the exposure to various security threats.
- In 2002, email was identified as a significant vulnerability for PCs. With 86% encountering issues, whereas thin clients reported zero exposure.
- By 2003, the perceived vulnerability via email for PCs decreased to 49.9% but remained at zero for thin clients.
- Operating systems showed no initial vulnerabilities in 2002 for PCs, but by 2003, this figure rose to 13.5%, a rate that matched thin clients if the component was present.
- Instant messaging and web browsers also showed vulnerabilities in PCs (10.1% and 8.1% respectively in 2003) but none for thin clients.
- Similarly, peer-to-peer applications, office applications, and multimedia viewers reported vulnerabilities ranging from 3.6% to 11% for PCs in 2003, again with no issues reported for thin clients.
- Other lesser-known vectors and third-party software presented a 4% vulnerability for PCs in 2002, dropping to 2.9% in 2003, with thin clients unaffected.
- Overall, PCs showed a total vulnerability exposure of 105% in 2002, which normalized to 100% in 2003. While thin clients demonstrated a total exposure of zero in 2002 and only 13.5% in 2003 if specific components were installed.
- This data highlights the robust security profile of thin clients compared to traditional PCs over the studied period.
(Source: HP)

Environmental Impact
- The comparison of annual CO2 emissions between PCs and thin clients for a scenario involving 5,000 users highlights significant differences in environmental impact.
- Specifically, PCs are responsible for generating approximately 237,930 kilograms of CO2 annually.
- In contrast, thin clients produce significantly lower emissions, totaling around 183,408 kilograms per year.
- This data underscores the environmental benefits of opting for thin clients over traditional PCs, as they offer a more sustainable solution by reducing carbon emissions.
(Source: Forrester Research, Inc.)

Innovations and Developments in Thin Client Statistics
- Thin client technology has seen notable innovations and developments in recent years, particularly driven by advancements in cloud computing, edge computing, and cybersecurity.
- Companies like Dell, HP, and Fujitsu have made significant strides by integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into their thin clients, enhancing processing capabilities and security features.
- These devices are now pivotal in industries such as healthcare, education, and finance, offering efficient remote access and centralized management. Thin clients have also evolved to support 5G and Wi-Fi 7, which enable faster, low-latency connections for data-heavy tasks.
- Product innovations include the development of highly energy-efficient models that reduce power consumption by up to 85% compared to traditional PCs, a key sustainability focus for enterprises.
- In healthcare, for example, thin clients facilitate secure access to telemedicine and e-clinics, enhancing patient care while reducing operational costs.
- This trend of innovation, alongside the growing adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart city infrastructure, positions thin clients as essential tools for modern digital workplaces and sustainable IT environments.
(Sources: Bluewayz Blog, IoT Marketing)
Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- HP acquires Teradici: In 2023, HP Inc. acquired Teradici, a cloud-based desktop virtualization solutions provider, for $300 million. This acquisition strengthens HP’s portfolio in the thin client and remote computing market. Particularly in cloud-based work environments where security and remote access are crucial.
- Dell merges with Wyse Technology: In 2023, Dell Technologies announced a merger with Wyse Technology, a major player in the thin client market. The $1 billion deal aims to enhance Dell’s offering of thin client solutions. Targeting healthcare, education, and enterprise sectors that require secure, lightweight computing systems.
New Product Launches:
- IGEL launches IGEL UD3 Thin Client: In mid-2023, IGEL launched the IGEL UD3 Thin Client, designed for secure, high-performance remote work. The new model features built-in Wi-Fi and enhanced security protocols, targeting industries like healthcare and finance. Where data security and reliability are critical.
- HP introduces HP Elite t655 Thin Client: In late 2023, HP introduced the Elite t655 Thin Client, aimed at hybrid work environments. The device supports 4K multi-display setups and offers cloud-based management solutions. Designed to improve productivity and reduce IT maintenance costs.
Funding:
- NComputing secures $50 million for expanding thin client solutions: In early 2023, NComputing, a global leader in thin client computing. Raised $50 million to develop more powerful and cost-effective thin client solutions for cloud-based virtual environments. This funding will support expansion into emerging markets and education sectors.
- VXL Instruments secures $40 million for global expansion: In late 2023, VXL Instruments, a thin client manufacturer. Raised $40 million to enhance its thin client solutions for remote desktop environments. This funding is targeted at scaling operations in Europe and Asia. Where demand for thin client devices is growing due to increased remote work.
Technological Advancements:
- Cloud-based thin clients: By 2025, it is projected that 50% of thin client devices will be cloud-managed. With enhanced security features and AI-based diagnostics. Reducing the need for onsite IT support.
- Integration of AI in thin client environments: AI is becoming more prominent in managing thin client ecosystems. By 2026, 40% of enterprises using thin clients are expected to adopt AI-driven systems to improve data security, monitor performance, and optimize resources.
Conclusion
Thin clients provide a practical alternative to traditional PCs, especially in environments where security, cost-efficiency, and sustainability are key concerns.
They offer reduced power consumption, lower operational costs, and a smaller environmental footprint. By centralizing data and applications, thin clients also enhance security and simplify IT management, although their performance depends on network stability and server capacity.
Particularly suitable for sectors like education, healthcare, and corporate settings. Thin clients align well with the modern IT demands for increased efficiency and reduced costs, making them an effective choice for enhancing organizational functionality.
FAQs
A thin client is a lightweight computer that depends on a connection to a central server for processing activities. It generally hosts minimal hardware and software and primarily serves to connect to the server where the actual computing is done.
Thin clients work by connecting over a network to a powerful central server. This server runs applications and processes data. While the thin client provides a portal through which users can interact with these applications and data virtually.
Thin clients are ideal for organizations with high-security needs, such as governmental organizations, financial institutions, and educational facilities. They are also well-suited for organizations looking to streamline IT management and reduce hardware costs.
Generally, thin clients are not suitable for high-end gaming or intensive multimedia tasks due to their limited local processing power and graphics capabilities. They are best used for general office applications, web browsing, and data entry tasks.
Software on thin clients typically includes a minimal operating system and a set of applications designed for remote access. The actual applications are run on the server. So the range of software is not limited by the hardware of the thin client but by what the server can handle.


