Table of Contents
Introduction
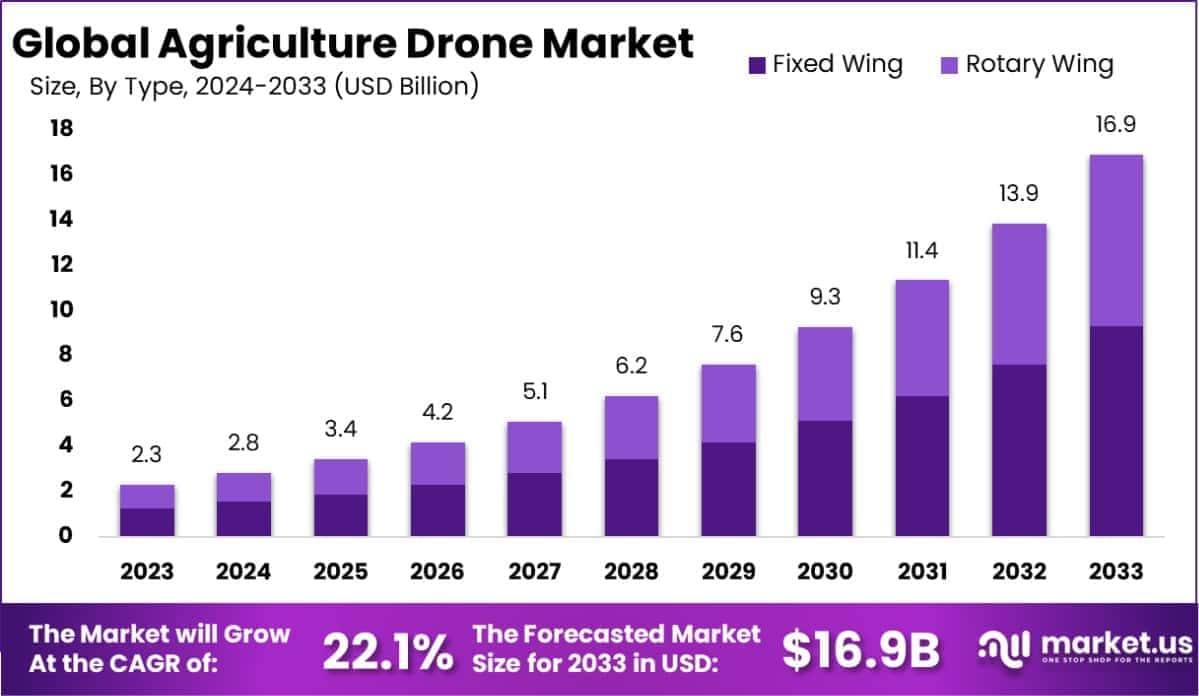
The Global Agriculture Drone Market is projected to grow significantly, with an estimated value of USD 16.9 billion by 2033, up from USD 2.3 billion in 2023. This reflects a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.1% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
Agriculture drones are unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) designed specifically for use in agricultural applications. These devices are equipped with advanced sensors, imaging cameras, and GPS technology, enabling farmers to gather precise data on crop health, soil conditions, and irrigation needs. They are also used for seeding, spraying, and monitoring livestock, offering a significant advantage in terms of efficiency, precision, and sustainability. By providing real-time insights, agriculture drones help optimize farming practices, reduce resource wastage, and increase overall agricultural productivity.
The agriculture drone market refers to the global ecosystem of manufacturers, software providers, and service operators involved in the production, deployment, and application of drones for agricultural purposes. This market encompasses various segments, including fixed-wing drones, rotary-wing drones, and hybrid drones, as well as ancillary technologies such as data analytics software, AI-driven platforms, and IoT integrations. It serves a wide range of stakeholders, from small-scale farmers to large agribusinesses, aiming to modernize and enhance agricultural practices through cutting-edge technology.
The growth of the agriculture drone market is driven by several key factors. Increasing global food demand, coupled with the need for sustainable farming practices, has accelerated the adoption of precision agriculture technologies, including drones. Government initiatives and subsidies promoting smart farming methods further bolster market growth.
Additionally, advancements in drone technology, such as AI-based analytics and autonomous operation, are making these devices more accessible and efficient. The declining costs of drones and related software have also contributed to their growing popularity across emerging markets.
The demand for agriculture drones is on a strong upward trajectory, fueled by their ability to improve crop yields, reduce operational costs, and address labor shortages in the agricultural sector. Opportunities abound in regions with large agricultural economies, such as Asia-Pacific and South America, where drone adoption is still in its nascent stages.
Furthermore, the integration of drones with other technologies, such as IoT and machine learning, presents lucrative prospects for innovation. Customizable solutions catering to specific farming needs, such as targeted pesticide application or nutrient management, are likely to expand the scope of drone applications and drive future growth in the market.
Key Takeaways
- The global agriculture drone market is projected to grow significantly, with an estimated value of USD 16.9 billion by 2033, up from USD 2.3 billion in 2023, reflecting a robust CAGR of 22.1% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
- Fixed-wing drones commanded the market with a leading 55% share, demonstrating their efficiency and versatility in agricultural applications.
- The hardware segment dominated with a 52.4% share, driven by advancements in drone manufacturing and technology integration.
- Outdoor farming remained the largest segment, capturing an 81.6% share, highlighting its widespread adoption for large-scale agricultural activities.
- Crop spraying emerged as the leading application, underscoring the growing demand for precision agriculture solutions.
- North America held the largest regional market share at 35.3%, contributing USD 0.8 billion in revenue.
Agriculture Drone Statistics
- By late 2022, over 200,000 DJI agricultural drones were in use globally, covering more than 200 million hectares.
- By June 2024, agricultural drones treated over 500 million hectares worldwide.
- Multispectral drone sensors detect crop health issues up to 10 days before visible to the naked eye.
- Drones increase crop yields by up to 25%.
- Targeted spraying with drones reduces chemical use by 30%.
- Drone-based spraying is 40-60% more efficient than traditional ground methods.
- Advanced agricultural drones process field data 10-15 times faster than ground surveys.
- Current agricultural drones carry 20-25 kg payloads for extensive spraying.
- Improved battery technology enables 45-60 minutes of flight time.
- Drone use in agriculture saved 210 million metric tons of water and reduced pesticide use by 47,000 metric tons.
- Drones plant up to 100 trees per minute, achieving up to 1 million trees annually in some projects.
- Thermal imaging drones reduce heat loss in buildings, cutting energy consumption by 40%.
- Drone inspections in the energy sector lower costs by 70%.
- Drones reduce surveying time in construction by 90%.
- Drones in search and rescue operations reduce search time by 70%.
- DJI holds 54% of the global drone market share and 80% in the U.S.
- Drone ownership in the U.S. is at 8%, with the largest demographic being 45-54 years old.
- Agricultural drone prices range from $500 for basic models to $30,000 for advanced systems.
- Fixed-wing drones fly over 45 minutes due to continuous forward motion.
- LiDAR-equipped drones map fields in 3D with 2-3 inch accuracy.
- Drones are expected to create 100,000 U.S. jobs by 2025.
- Businesses using drones save up to 30% in costs and 25% in time.
- Drone-related injuries most commonly involve lacerations (72%) and affect fingers (56%) and the head (24%).
- Drones can fly up to 400 feet, requiring compliance with local regulations.
Emerging Trends
- Integration of Multispectral Imaging for Enhanced Crop Monitoring: The adoption of multispectral imaging technology in agricultural drones is revolutionizing crop monitoring. By capturing data across various light wavelengths, drones can detect crop health issues, such as nutrient deficiencies and water stress, that are not visible to the naked eye. This capability enables farmers to implement precise interventions, optimizing crop yields and resource utilization.
- Expansion of Autonomous Drone Operations: Advancements in autonomous flight technology are leading to the development of drones capable of operating without human intervention. Companies like Rotor Technologies have introduced unmanned helicopters for agricultural applications, such as crop spraying, enhancing efficiency and safety in farming operations
- Regulatory Developments Influencing Drone Adoption: Evolving regulations are shaping the adoption of agricultural drones. In the United States, lawmakers have expressed concerns over the use of Chinese-manufactured drones, citing national security risks. Proposed legislation aims to increase tariffs on Chinese-made drones and ban imports of drones with critical components made in China by 2030, potentially impacting market dynamics and encouraging domestic production.
- Advancements in Drone: Payload Capacities Recent developments have led to drones with increased payload capacities, enabling them to carry larger quantities of fertilizers or pesticides. For instance, Guardian Agriculture’s SC1, an electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, can carry up to 200 pounds of agricultural inputs, covering approximately 60 acres per hour. This advancement enhances the efficiency of crop spraying operations.
- Emergence of AI and Machine Learning in Data Analytics : Drones integrated with AI are enabling smarter agricultural management. They can analyze data in real-time, predicting crop diseases or estimating yields with higher accuracy. These insights are crucial for optimizing resource allocation and improving decision-making processes.
Top Use Cases
- Precision Spraying of Pesticides and Fertilizers: Drones equipped with advanced spraying systems enable targeted application of pesticides and fertilizers, reducing chemical usage and minimizing environmental impact. For instance, in Mexico, the use of drones for herbicide application over agave farms resulted in an 88% reduction in water usage and cost savings exceeding $60 USD per hectare.
- Crop Health Monitoring and Analysis: Utilizing multispectral imaging, drones can assess crop health by capturing data across various light wavelengths. This technology allows for early detection of issues such as nutrient deficiencies and pest infestations, enabling timely interventions. In Japan, a rice producer increased yield and saved on fertilizer costs, gaining an additional $5,425 USD per hectare through drone-assisted monitoring.
- Field Mapping and Soil Analysis : Drones facilitate the creation of detailed field maps, providing insights into soil conditions, moisture levels, and topography. This information supports informed decision-making regarding irrigation and planting strategies, leading to optimized resource utilization and improved crop yields.
- Planting and Seeding Operations: Some drones are designed to assist in planting by dispersing seeds over prepared fields. This method can cover up to 40 acres per day, significantly accelerating the planting process compared to traditional methods. Additionally, drone planting can reduce labor costs and increase planting efficiency.
- Livestock Monitoring and Management: Equipped with thermal imaging cameras, drones can monitor livestock health and movement across large pastures. This capability allows farmers to quickly identify sick or injured animals, ensuring prompt care. Drones can cover extensive areas, monitoring up to 1,000 acres in a single flight, thereby enhancing the efficiency of livestock management.
Major Challenges
- Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance: Navigating the complex regulatory landscape is a primary challenge for agricultural drone adoption. In the United States, for instance, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) mandates that commercial drone operators obtain specific certifications and adhere to operational restrictions, such as maintaining visual line-of-sight and altitude limitations. These regulations can limit the scalability of drone operations in large agricultural settings.
- High Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs: The financial barrier associated with acquiring and maintaining advanced agricultural drones is substantial. High-end drones equipped with multispectral sensors and autonomous capabilities can cost upwards of $25,000. Additionally, ongoing expenses for software updates, battery replacements, and repairs can strain the budgets of small to medium-sized farms, hindering widespread adoption.
- Technical Complexity and Skill Requirements: Operating sophisticated drones necessitates specialized knowledge in areas such as flight planning, data analysis, and equipment maintenance. A survey indicated that 65% of farmers feel inadequately trained to utilize drone technology effectively, highlighting a significant skills gap that could impede the technology’s effective deployment.
- Data Management and Interpretation Challenges: Drones generate vast amounts of data that require proper management and interpretation to be useful. Farmers often lack access to user-friendly analytical tools, making it difficult to convert raw data into actionable insights. This complexity can lead to underutilization of the technology’s full capabilities.
- Limited Battery Life and Flight Range: The operational efficiency of drones is constrained by their battery life and flight range. Many agricultural drones have flight times limited to 20-30 minutes, covering approximately 50-100 acres per flight. This limitation necessitates multiple flights to survey large fields, increasing labor and time requirements
Top Opportunities
- Government Initiatives and Subsidies: Governments worldwide are recognizing the potential of drone technology in agriculture and are implementing supportive policies. For instance, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) announced up to USD 7.7 billion in aid for fiscal year 2025 to support agricultural and forestry producers in implementing conservation practices on working lands. This funding aims to maximize climate benefits nationwide while offering significant conservation and operational advantages, including economic opportunities for producers, improved soil productivity, cleaner water and air, healthier wildlife habitats, enhanced connectivity, and the preservation of natural resources for future generations.
- Technological Advancements in Drone Capabilities: Ongoing innovations are enhancing drone functionalities, such as increased payload capacities and extended flight durations. For example, the SC1, an electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, can carry up to 200 pounds of agricultural inputs, covering approximately 60 acres per hour. These advancements enable more efficient crop spraying operations, reducing labor costs and increasing productivity.
- Integration with Precision Agriculture Practices: The synergy between drones and precision agriculture is creating new avenues for growth. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras, multispectral sensors, and GPS technology enable farmers to gather detailed data on crop health, soil conditions, and moisture levels. This data-driven approach allows for optimized resource utilization, leading to higher yields and cost savings.
- Expansion into Emerging Markets: Emerging economies, particularly in Asia and Africa, present substantial growth opportunities for agricultural drones. The adoption of drone technology in these regions can address labor shortages and enhance productivity. For instance, in India, the government’s strategic investment of Rs. 129.19 crores (approximately $15.5 million) to promote Kisan Drones underlines a strong commitment to integrating advanced technologies in agriculture. This initiative includes comprehensive financial assistance schemes, providing up to 100% funding for drone acquisitions by agricultural institutions and up to 75% cost coverage for farmer demonstrations.
- Environmental Monitoring and Sustainable Farming: Drones are increasingly utilized for environmental monitoring, such as detecting invasive species and assessing crop health, which supports sustainable farming practices. For example, in Sydney’s west, drones are deployed to locate and eradicate invasive aquatic weeds in the Hawkesbury and Nepean river systems, protecting local agriculture and ecosystems.
Key Player Analysis
- DJI: DJI, headquartered in Shenzhen, China, is a leading manufacturer of drones and aerial imaging technology. The company offers a range of drones tailored for agricultural applications, such as the Agras series, which are designed for crop spraying and monitoring. DJI’s dominance in the consumer drone market extends to agriculture, with a significant share attributed to its innovative products and extensive distribution network.
- Trimble Inc: Based in Sunnyvale, California, Trimble Inc. specializes in advanced positioning solutions. In agriculture, Trimble provides drone-based technologies for field mapping, crop health monitoring, and precision farming. Their solutions integrate hardware and software to deliver actionable insights, enhancing farm productivity and efficiency.
- AeroVironment Inc: AeroVironment, located in Arlington, Virginia, is known for its unmanned aircraft systems. In the agricultural sector, the company offers drones equipped with advanced sensors for crop monitoring and data collection. Their Quantix Recon drone, for example, provides high-resolution imagery to assist farmers in making informed decisions.
- Parrot Drone: Parrot Drone, a French company, develops drones for various applications, including agriculture. Their ANAFI USA drone is designed for precision agriculture, offering features like 32x zoom and thermal imaging to monitor crop health and optimize farming practices.
- AgEagle Aerial Systems Inc: AgEagle, headquartered in Wichita, Kansas, focuses on drone solutions for precision agriculture. The company provides drones and data analytics platforms that enable farmers to monitor crop health, assess field conditions, and improve yield outcomes.
Recent Developments
- In 2023, Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative (IFFCO) committed to procuring 2,500 agricultural drones for spraying nano urea and nano DAP. The initiative, under “IFFCO Kisan Drones,” aims to train 5,000 rural entrepreneurs to operate these drones, along with 2,500 electric three-wheelers for transporting drones and related materials to farms.
- In 2024, AGCO Corporation and Trimble finalized their joint venture, PTx Trimble, combining expertise in precision agriculture to deliver advanced solutions for mixed-fleet farming systems.
- In 2024, DJI Agriculture reported a surge in the global agricultural drone industry, with over 300,000 drones treating more than 500 million hectares of farmland. The report highlighted significant growth and innovation in agricultural drone technology.
- In 2024, AgEagle Aerial Systems secured a $2 million contract to deliver 20 eBee VISION systems to a UAE distributor. The package includes advanced drones, control systems, and accessories, marking a key international expansion.
- In 2024, Airbus completed the acquisition of Aerovel, adding the Flexrotor unmanned aerial system to its tactical portfolio for advanced intelligence and reconnaissance capabilities.
Conclusion
The agriculture drone market is poised for substantial growth, driven by the increasing adoption of precision farming techniques and advancements in drone technology. These unmanned aerial vehicles offer farmers enhanced capabilities in crop monitoring, field mapping, and resource management, leading to improved yields and operational efficiency. The integration of multispectral imaging and real-time data analytics further empowers farmers to make informed decisions, optimizing inputs and reducing environmental impact. As regulatory frameworks evolve to support drone usage in agriculture, and as costs continue to decline, the accessibility of this technology is expected to expand, benefiting a broader range of agricultural operations. This trajectory underscores the pivotal role of drones in modernizing agriculture and meeting the growing global food demand sustainably.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



