Table of Contents
Introduction
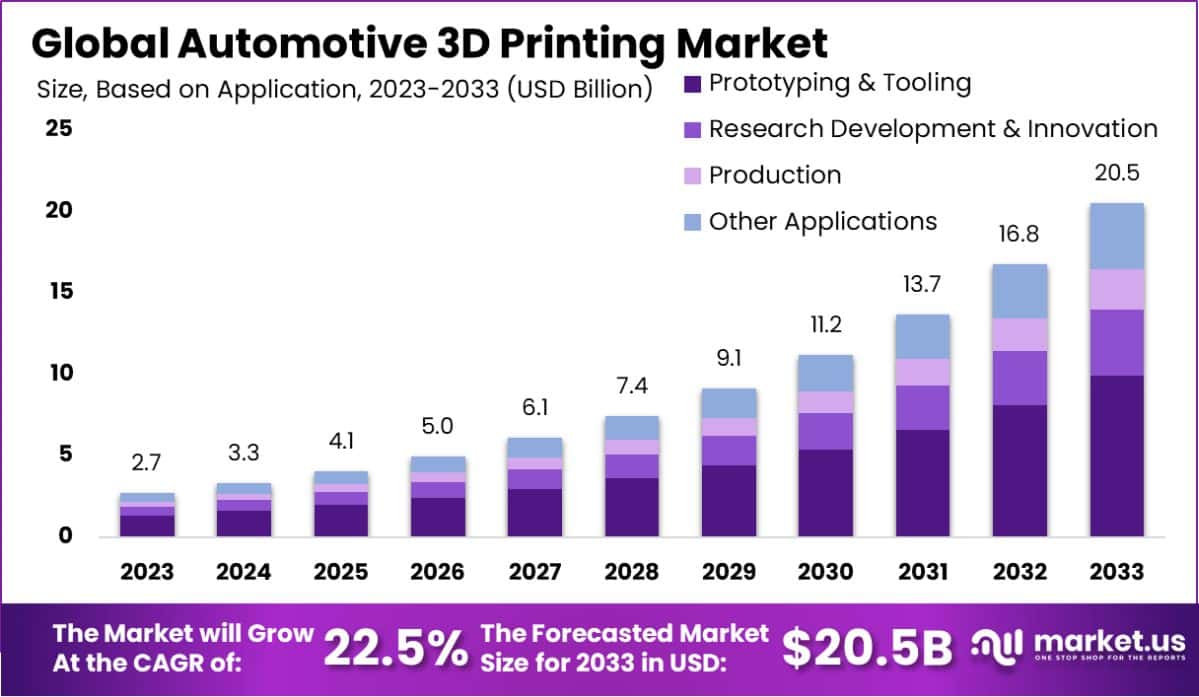
The Global Automotive 3D printing market is projected to grow from USD 2.7 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 20.5 billion by 2033, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.5% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The Automotive 3D Printing Market refers to the use of additive manufacturing technologies in the production, prototyping, and design of automotive components and parts. This market encompasses a range of 3D printing methods, including Stereolithography (SLA), Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), among others, which enable manufacturers to produce complex geometries, lightweight structures, and custom components with greater speed and precision.
Initially used primarily for prototyping, 3D printing has now expanded into producing end-use parts, spare parts, and even tooling within the automotive sector, driving significant transformation in manufacturing processes.
Several factors are propelling the growth of the Automotive 3D Printing Market. A key driver is the automotive industry’s increasing focus on reducing weight to improve fuel efficiency and meet stringent environmental regulations. 3D printing allows for the creation of lightweight, high-strength components, which is crucial in the development of electric and hybrid vehicles.
Furthermore, the push for mass customization and rapid prototyping capabilities enables automakers to shorten development cycles and bring new models to market faster, offering a competitive edge. Advances in material sciences, particularly with polymers and metal powders, are also expanding the range of parts that can be effectively printed, further bolstering market growth.
The demand for 3D printing in the automotive sector is shaped by several trends. There is a rising need for faster turnaround times in prototyping and production, allowing automakers to innovate rapidly and respond to changing consumer preferences. As automotive design becomes increasingly complex, with more intricate geometries and integrated functionalities, 3D printing offers the flexibility required to produce such designs without the constraints of traditional manufacturing.
Moreover, supply chain disruptions have highlighted the value of on-demand manufacturing, where 3D printing allows for localized production of parts, reducing dependency on global supply chains and minimizing lead times.
The market presents significant opportunities for innovation and investment. As the technology matures, there is potential for increased adoption of 3D printing in high-volume production, especially for custom components and small batch manufacturing. The growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) presents a particularly lucrative opportunity, as manufacturers explore new ways to produce lightweight components and battery-related parts.
Additionally, there is an emerging trend towards using 3D printing for aftermarket parts and spare parts production, which can simplify inventory management and reduce costs for automakers. As the industry moves towards more sustainable manufacturing practices, 3D printing’s ability to reduce material waste and energy consumption can also provide a competitive advantage in the evolving market landscape.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Automotive 3D Printing Market is projected to reach approximately USD 20.5 billion by 2033, growing from USD 2.7 billion in 2023, with an estimated CAGR of 22.5% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
- In 2023, Prototyping & Tooling was the leading application segment in the Automotive 3D Printing Market, accounting for a 48.2% share.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) held a dominant position in the technology segment of the Automotive 3D Printing Market in 2023, capturing a 29.3% share.
- Plastic materials led the market in 2023 within the materials segment of the Automotive 3D Printing Market, comprising a 44.2% share.
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles dominated the market based on vehicle type in 2023, representing a 56.1% share.
- The Hardware segment was the largest in terms of offerings within the Automotive 3D Printing Market in 2023, with a 57.2% share.
- Exterior Components emerged as the leading component segment in 2023, holding a 61.2% share of the Automotive 3D Printing Market.
- North America was the leading region in the Automotive 3D Printing Market in 2023, accounting for a 39.2% market share and generating USD 1.05 billion in revenue.
Automotive 3D Printing Statistics
- Metal 3D printing made up 45% of the automotive 3D printing market in 2023.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) held a 35% share in the automotive sector.
- Prototyping dominated, accounting for 55% of 3D printing use in 2023.
- 3D printers range from $200 to $10,000 based on quality and specs.
- The 3D-printed prosthetics, orthotics, and audiology market aims for $509 million in revenue by 2026 and $996 million by 2030.
- Use of 3D printing for end-use vehicle parts grew by 25% from 2022 to 2023.
- Industrial-grade 3D printers generally cost around $10,000.
- Boeing achieved $3 million in savings by using 3D printing for titanium parts.
- General Electric expects $5 million in savings over a decade through 3D printing.
- AutoDesk is the largest 3D printer manufacturer, valued at $68.22 billion.
- Entry-level 3D printers are priced between $400 and $1,000.
- As of 2023, 90% of automotive companies utilize 3D printing.
- 3D printing can cut automotive product development time by up to 70%.
- Average cost savings from 3D-printed tooling in 2023 were 70-90%.
- By early 2024, over 50% of automotive 3D printing is used for interior components.
- Spare parts production using 3D printing grew by 30% in 2023.
- 3D printing reduced some automotive part weights by up to 70%.
- Electric vehicle 3D printing adoption increased by 40% from 2022 to 2023.
- Functional prototypes accounted for 25% of automotive 3D printing in 2023.
- Use of recyclable materials in 3D printing rose by 35% in 2023.
- 3D printing helped reduce automotive inventory costs by up to 90%.
- The automotive 3D printing software market reached $650 million in 2023.
- By 2024, over 60% of major automakers invested in in-house 3D printing.
- Customization using 3D printing grew by 45% from 2022 to 2023.
- Lead times for certain parts reduced by up to 90% through 3D printing.
- AI-driven design optimization for 3D printed parts increased by 50% in 2023.
- In early 2024, 15% of 3D printed parts were used in final vehicle assembly.
- Formula 1’s use of 3D printing rose by 30% from 2022 to 2023.
- Tooling costs in automotive manufacturing dropped by up to 80% in 2023 due to 3D printing.
- Adoption of composite materials for 3D printing in the automotive industry grew by 40% in 2023.
- By early 2024, 20% of 3D printing in automotive was for assembly tools and fixtures.
- On-demand spare parts production using 3D printing increased by 35% from 2022 to 2023.
- 3D printing reduced the number of parts in some automotive assemblies by up to 30%.
- Large-format 3D printer adoption for automotive uses grew by 25% in 2023.
Emerging Trends
- Shift from Prototyping to Production: The use of 3D printing in the automotive industry has evolved significantly from just prototyping to actual production of end-use parts. Manufacturers increasingly employ additive manufacturing (AM) for small-batch production of components, enabling faster time-to-market and reducing the need for large-scale tooling. This shift allows automakers to adapt quickly to changes in design and demand, thus improving production flexibility
- Adoption of High-Performance Materials: A notable trend is the integration of advanced materials like carbon fiber-reinforced polymers and high-performance thermoplastics in 3D printing. These materials allow for the creation of lightweight, durable components, which are critical for electric vehicles (EVs) aiming to maximize energy efficiency. The ability to use such materials in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and metal printing processes makes them particularly attractive for automotive applications.
- Sustainability and Circular Manufacturing: The automotive sector is increasingly leveraging 3D printing to enhance sustainability through waste reduction and the use of recycled materials. Additive manufacturing allows for more efficient material use and supports circular business models like “right to repair,” where components can be locally produced and replaced, reducing transportation emissions and extending the life cycle of parts.
- Integration with AI and Automation: AI and machine learning are becoming critical in refining 3D printing processes, especially in automotive production. AI aids in optimizing design through generative modeling, improving precision and reducing errors. Coupled with automation, these advancements enable faster, more efficient production, supporting mass customization—a significant benefit for automakers seeking to meet diverse customer preferences.
- Expansion into Large-Format Printing: There is growing interest in large-format 3D printing capabilities within the automotive industry. This trend supports the production of larger components, including body parts and structural elements, directly through 3D printing. This approach can drastically cut production times and costs for certain vehicle parts, making it an increasingly viable alternative to traditional manufacturing methods
Top Use Cases
- Rapid Prototyping: One of the most significant benefits of 3D printing is its ability to accelerate the prototyping phase. Traditional methods like CNC machining or injection molding can take weeks and involve high costs, whereas 3D printing allows automakers to produce prototypes within hours. This enables faster design iterations and testing, cutting down development cycles by up to 50% compared to conventional methods. For example, Ford uses 3D printing to rapidly iterate on design changes for models like the Shelby Mustang GT500, significantly reducing time-to-market.
- Production of End-Use Parts: Beyond prototyping, 3D printing is increasingly being used for manufacturing low-volume, end-use components. Companies such as Lamborghini use 3D printing for complex parts in their high-performance cars, including aerodynamic elements and interior components. This approach allows manufacturers to bypass the need for expensive tooling, making it ideal for producing specialized parts for limited-edition models. The adoption of 3D printing for end-use parts helps reduce production costs by up to 30%, especially for parts with intricate geometries.
- Custom Tooling and Fixtures: Automotive manufacturers leverage 3D printing to produce custom tools, jigs, and fixtures used in the assembly process. For instance, Volkswagen has been able to reduce tooling costs by 90% by printing specialized tools in-house, cutting the production time from 35 days to just 4 days. Such applications are particularly beneficial for improving efficiency on the production line, enabling adjustments without the lengthy wait times associated with outsourced tool manufacturing.
- On-Demand Spare Parts Production: 3D printing is transforming how automakers handle spare parts, especially for legacy or out-of-production models. Companies like Porsche have adopted 3D printing to produce rare spare parts for classic models, allowing them to maintain a supply chain for vehicles that are no longer mass-produced. This on-demand manufacturing approach reduces the need for maintaining large inventories and can cut storage costs by up to 50%, while ensuring the availability of components that would otherwise be discontinued.
- Lightweighting with Advanced Materials: 3D printing allows the use of lightweight, high-performance materials such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers and engineering-grade thermoplastics. This capability is particularly critical in the era of electric vehicles (EVs), where reducing weight translates directly to better range and efficiency. By incorporating 3D printed lightweight parts into EV designs, manufacturers can reduce the overall weight of a vehicle by up to 10%, improving both performance and energy efficiency. For example, Stratasys has worked with automotive companies to create lighter, yet durable, components that can withstand high stress conditions.
Major Challenges
- Scaling Production for Mass Manufacturing: While 3D printing is highly effective for prototyping and small-batch production, scaling it up to mass manufacturing remains difficult. The challenge lies in maintaining consistent quality and speed when shifting from low-volume runs to large-scale production. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, 3D printing struggles with economies of scale, making it more costly for high-volume applications. This limits its widespread adoption for mass-produced automotive components, where precision and speed are crucial.
- High Material Costs: The costs associated with materials for 3D printing, especially high-performance polymers and metal powders, remain a significant barrier. While some advances have been made in using recycled and lower-cost materials, the overall expense of specialized materials remains about 30% higher than those used in conventional manufacturing processes. This cost factor can deter automakers from adopting 3D printing for standard parts, where minimizing input costs is critical for maintaining competitive pricing.
- Quality Control and Part Reliability: Ensuring the quality and consistency of 3D-printed parts is a persistent challenge. Variability in print outputs, such as differences in layer adhesion or surface finish, can affect the structural integrity of parts. For automotive components, especially those used in safety-critical areas like braking systems or structural frames, such variability is unacceptable. The need for rigorous testing and validation processes adds to production time and costs, making 3D printing less attractive for critical automotive applications.
- Integration with Existing Manufacturing Systems: Integrating 3D printing into traditional automotive production lines requires significant changes in workflows and systems. Many existing production facilities are optimized for conventional methods like injection molding or CNC machining. Shifting to 3D printing means adapting processes for design, part assembly, and post-processing, which can be complex and costly. This challenge is especially pronounced in older factories where retrofitting for additive manufacturing capabilities can involve high upfront investments.
- Cybersecurity and Intellectual Property Concerns: As 3D printing involves the digital transfer of design files, there are heightened concerns about cybersecurity and intellectual property protection. The risk of unauthorized access to digital blueprints poses a serious threat, particularly in an industry where design innovation is a key differentiator. Automakers must invest in secure data transmission and encryption technologies to protect their designs, adding to the operational complexity and costs of adopting 3D printing
Top Opportunities
- Customization and Personalization: 3D printing offers significant potential for customization in the automotive industry, particularly as consumer demand for personalized vehicles increases. Using 3D printing, automakers can produce unique parts tailored to specific customer needs, such as interior components and custom trim. This capability supports premium and luxury vehicle segments, where customization is a major value driver. The market for such customized parts is projected to grow, contributing to a larger adoption of 3D printing technologies.
- On-Demand Spare Parts Production: 3D printing enables automotive manufacturers to produce spare parts on demand, reducing the need for extensive physical inventories. This is especially beneficial for older models or low-volume production vehicles, where traditional manufacturing methods may not be cost-effective. By utilizing 3D printing for spare parts, companies can minimize warehousing costs and reduce lead times, which is projected to save up to 30% on logistics and inventory management expenses.
- Lightweighting and Enhanced Performance: The drive for fuel efficiency and the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) have increased the focus on reducing vehicle weight. 3D printing allows for the creation of complex, lightweight structures using advanced materials like carbon fiber composites. This can result in up to a 10% reduction in vehicle weight, directly improving range and energy efficiency in EVs. As automakers continue to adopt 3D-printed components for chassis parts and structural elements, this focus on lightweighting represents a significant market opportunity.
- Advancements in Multi-Material Printing: The development of multi-material 3D printing technologies is expanding the range of applications in automotive manufacturing. This allows for parts that combine different properties—such as flexible and rigid sections—in a single print. These advancements make it possible to produce more sophisticated and integrated components, offering automakers greater design flexibility and potentially reducing the need for assembly. This segment is expected to grow as automotive manufacturers look for ways to innovate with materials and component designs.
- Integration into Digital Manufacturing Ecosystems: The automotive industry is increasingly embracing Industry 4.0, where 3D printing plays a crucial role in digital manufacturing ecosystems. This involves integrating 3D printing with digital design software, simulation tools, and automation, which streamlines the entire production process. Such digital integration enhances efficiency and precision, reducing time-to-market for new vehicle models. As companies invest in smarter manufacturing systems, the role of 3D printing in digital factories is set to grow, particularly in markets like North America and Europe, which have seen strong adoption of these technologies
Key Player Analysis
- Stratasys Ltd. : Stratasys Ltd. is a leader in polymer-based 3D printing, offering advanced solutions such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and PolyJet technologies, which are widely used in automotive prototyping and small-batch production. With over $630 million in revenue as of 2023, the company plays a critical role in helping automakers accelerate design iterations and streamline the production of complex components. Stratasys has further expanded its materials portfolio through strategic acquisitions, such as its purchase of Covestro’s additive manufacturing division, enhancing its capabilities to meet automotive industry demands.
- 3D Systems Corporation: 3D Systems Corporation is a pioneer in the additive manufacturing industry, providing a comprehensive range of 3D printing solutions, including hardware, software, and materials. With a reported revenue of approximately $538 million in 2022, 3D Systems supports automotive applications from prototyping to end-use parts production. The company’s focus on developing advanced materials, like the DuraForm PAx, and expanding industry partnerships, makes it a key player in addressing the automotive sector’s need for high-performance, cost-efficient components.
- Desktop Metal Inc.: Desktop Metal Inc. specializes in high-speed metal 3D printing, particularly through its binder jetting technology, making it suitable for mass production of automotive parts such as powertrain components. In 2022, the company secured a $9 million contract from a major German automaker, highlighting its capability to scale additive manufacturing for automotive needs. Desktop Metal’s focus on speed, scalability, and reducing the costs of producing complex metal parts makes it a vital partner for automotive companies transitioning to advanced manufacturing methods.
- Materialise NV : Materialise NV, based in Belgium, provides 3D printing software and services that support both prototyping and production in the automotive industry. In 2022, it generated about $232 million in revenue, driven largely by its robust software solutions that enhance the efficiency and reliability of additive manufacturing processes. The company has also partnered with major players like Renishaw to integrate secure data transfer technologies, ensuring high standards in digital manufacturing for automotive applications.
- EOS GmbH: EOS GmbH is renowned for its expertise in Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), a technology that allows for the production of lightweight and complex metal parts. With revenues exceeding $400 million in 2023, EOS is a key provider of industrial 3D printing solutions tailored for high-precision automotive components. The company is also committed to sustainability, investing in innovations that reduce waste and energy consumption, making it a valuable partner as the automotive industry moves towards greener manufacturing practices
Recent Developments
- In 2023, Nano Dimension Ltd. based in Waltham, Massachusetts, announced a preliminary cash proposal to acquire all remaining shares of Stratasys Ltd. (Nasdaq: SSYS) that it does not already own. The offer is priced at $16.50 per share, reflecting a 40% premium compared to Stratasys’ average share price since September 28, 2023. This proposal came after Stratasys disclosed that its Board of Directors was considering strategic alternatives, including a potential sale.
- In 2023, HP Inc., during the RAPID+TCT event held in Chicago and Palo Alto, introduced new automation solutions alongside expanded materials, software, and services aimed at scaling 3D printed parts production. HP also elevated several members of its Digital Manufacturing Network to the elite group of HP Digital Manufacturing Partners. Notably, Endeavor 3D, a leading contract manufacturer, added Metal Jet capabilities to its portfolio, enhancing its existing polymer-based Multi Jet Fusion services.
- In 2023, 3D Systems, headquartered in Rock Hill, South Carolina, submitted a proposal for a merger with Stratasys Ltd. (Nasdaq: SSYS). The merger plan includes a combination of cash and stock, offering Stratasys shareholders $7.50 per share in cash plus 1.2507 shares of 3D Systems’ stock for each Stratasys share. This merger would position the combined entity as a leader in the additive manufacturing sector, with Stratasys shareholders owning about 40% of the new entity and receiving approximately $540 million in cash.
Conclusion
The automotive 3D printing market is set to grow significantly, driven by its potential to transform manufacturing processes. Key advantages like rapid prototyping, the ability to produce complex geometries, and customization are making 3D printing an integral part of the automotive industry. As the sector embraces sustainable manufacturing practices and looks for ways to optimize supply chains, 3D printing enables manufacturers to produce lighter, more efficient components with reduced waste. Additionally, the technology supports the production of spare parts on demand, offering greater flexibility and cost savings. With these benefits, automotive 3D printing is becoming a critical tool for innovation and efficiency in vehicle production.


