Table of Contents
Introduction
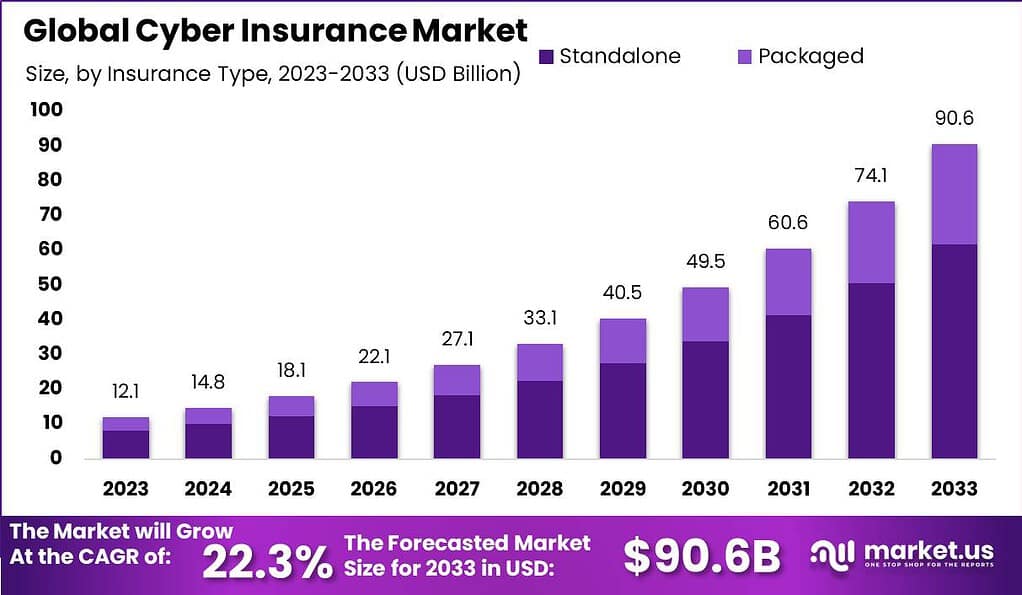
The cyber insurance market is growing rapidly and is expected to reach USD 90.6 billion by 2033, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 22.3% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033. This growth reflects the increasing reliance on digital technologies and the growing awareness of cyber risks among businesses of all sizes.
North America is expected to maintain its dominance in the market due to strict government regulations on cybersecurity, a high incidence of cyberattacks, and the presence of leading cyber insurance providers. The Asia Pacific region is also expected to witness remarkable growth due to escalating ransomware attacks, increased government investment in cyber insurance, and rapid digital transformation, which exposes organizations to cyber vulnerabilities. There has been a significant increase in demand for cyber insurance in the Asia Pacific region, with an 87% increase attributed to the growing connectivity and digital transformation efforts across the region.
However, the dynamic nature of cyber threats poses significant challenges in the cyber insurance market. Such threats are becoming more sophisticated and capable of causing extensive financial damage. For example, the average cost of a cyberattack in the U.S. rose by 29% from $21.2 million in 2017 to $27.4 million in 2018. The scalable nature of cyberattacks also poses a significant challenge, as they can impact numerous companies simultaneously, leading to large interconnected losses for insurers. The complexities of underwriting and pricing cyber insurance policies are underscored by incidents like NotPetya, which resulted in cascading failures.
Key Takeaways
- The global cyber insurance market is projected to reach USD 90.6 billion by 2033, with a steady CAGR of 22.3% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
- In 2023, the market was valued at USD 12.1 billion.
- Standalone cyber insurance policies held a dominant market share of over 68.2% in 2023.
- Third-Party Coverage accounted for more than 62.1% of the cyber insurance market in 2023.
- Large Enterprises constituted a significant segment with a share of over 72.4% in 2023.
- The BFSI sector led the market with a share of over 28.3% in 2023.
- North America commanded a substantial revenue share of 37.6% in 2023, followed by Europe and the Asia-Pacific region.
- The demand for cyber insurance in North America was valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2023.
Cyber Insurance Statistics
- Chubb Ltd Grp’s Market Presence: Chubb Ltd Grp is a leading insurer, writing $404 million in premiums and holding a 14.7% market share.
- Ransomware Claims: Ransomware attacks are a major issue, accounting for 81% of claims related to recovery expenses.
- Claim Payouts:
- 27% of data breach claims and 24% of first-party claims were affected by exclusions, leading to no or partial payouts.
- Business email compromise scams resulted in 1,153 claims in 2022.
- Insurance Coverage and Claims:
- Only 55% of organizations have some form of cyber insurance.
- A mere 19% are covered for cyber events costing more than $600,000.
- Claim Frequency and Costs:
- Claims have surged by 100% over the past three years, with payouts increasing by 200%.
- The peak number of claims reached 8,100 in 2021.
- SMEs, with annual revenues under $2 billion, are the most affected, making up 99% of claims.
- The average claim cost for an SME is $345,000, which rises to $485,000 for ransomware events. Across all types of organizations, the average claim cost is $812,360.
Cyber Insurance Claims Statistics
Awareness and Coverage:
- About 66% of Americans know what cyber insurance is.
- Only 55% of organizations have any cyber insurance, and just 19% are covered for incidents costing over $600,000.
Claims and Costs:
- Cyber insurance claims doubled in the last three years, with payouts increasing by 200%. The highest number of claims in a year was 8,100 in 2021.
- Small to Medium Enterprises (SMEs), with revenues under $2 billion, submitted 99% of these claims.
- The average cost for a cyber insurance claim for SMEs is $345,000, but this rises to $485,000 for ransomware attacks. Across all organizations, the average claim is $812,360.
Reasons for Claims:
- Ransomware attacks are the main reason for claims, causing about 81% of recovery expense losses.
- Business email compromise scams resulted in 1,153 claims in 2022.
Claim Denials:
- 27% of data breach claims and 24% of first-party claims had exclusions that led to denied or partially denied payouts.
Sector-specific Insights:
- The healthcare sector had claims mainly due to accidental data breaches (29%) and stolen/lost devices (16%).
- In the IT and communications sector, malicious data breaches (24%) and ransomware (11%) were significant reasons for claims.
- The retail and wholesale sector saw claims mostly due to malicious data breaches (30%) and social engineering (11%).
- Manufacturing faced claims primarily from social engineering (30%) and malicious data breaches (22%).
Growth in Premiums and Claims:
- Cyber insurance premiums grew by 74% in 2021, reaching over $4.8 billion.
- Small businesses experienced a 40% increase in ransomware attacks and a 56% increase in fund transfer fraud incidents from 2020 to 2021.
Purchase Triggers:
- 40% of companies bought cyber insurance after witnessing an attack on a similar organization, while another 40% were influenced by recommendations following a cybersecurity risk assessment.
Use Cases of Cyber Insurance
- Ransomware Dominates Claims: Ransomware remains the primary cause of cyber insurance losses, with a prediction that by 2031, ransomware could cost victims about $265 billion annually. The trend is shifting towards data destruction rather than encryption, making ransomware even more threatening.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: The supply chain is increasingly targeted by cybercriminals, with a projected 45% of organizations worldwide experiencing attacks on their software supply chains by 2025. This highlights the critical need for companies to have transparent risk assessments and cybersecurity measures in place.
- Data Breaches and Liability: With data creation expected to reach 463 exabytes daily by 2025, the risk of data breaches and subsequent liability is skyrocketing. Companies are anticipated to face significant challenges, especially with the increasing focus on biometric data.
- Increasing Cyber Claims: The frequency of cyber claims has picked up in the first half of 2023, though improvements in cybersecurity measures have helped control losses to some extent. However, undetected breaches can be exponentially more costly.
- Critical Cybersecurity Hygiene: The lack of adequate cybersecurity measures can significantly increase the vulnerability of an organization to cyberattacks. This includes the importance of early detection of breaches and maintaining good data management practices to mitigate the impact of data exfiltration attacks.
- Phishing and Credit Fraud: Phishing attacks continue to be a common form of cybercrime, with a significant number of phishing victims reported. Credit fraud also remains a concern, with a large number of cases reported annually.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) Scams: BEC attacks are a notable cause of cyber insurance claims, with an increasing number of claims reported in recent years. This underscores the importance of awareness and preventive measures against such scams.
Recent Developments
- Pfizer’s Acquisition of Seagen – In a significant move within the biotechnology industry, Pfizer acquired Seagen for $43 billion, emphasizing the growing focus on oncology and the development of transformative cancer medicines.
- Tapestry’s Acquisition of Capri Holdings – Tapestry Inc acquired Capri Holdings for $8.5 billion, stepping into the luxury fashion segment and aiming to boost e-commerce sales by integrating renowned brands like Michael Kors, Jimmy Choo, and Versace.
- Databrick’s Acquisition of Mosaic ML – This $1.3 billion deal marks a significant milestone in the artificial intelligence sector, promising to enhance enterprise data applications through the integration of generative AI models.
- Thales’ Acquisition of Imperva – Thales strengthened its cybersecurity offerings with a $3.6 billion acquisition of Imperva, highlighting the importance of application and data security in today’s digital landscape.
- Clearlake Capital’s Acquisition of Alteryx – Alteryx, a leader in data science and analytics, was acquired by Clearlake Capital for $4.4 billion, reflecting the increasing value placed on data analytics and science in business strategies.
- IBM’s Acquisition of Apptio – IBM expanded its portfolio of automated software solutions through the acquisition of Apptio for $4.6 billion, emphasizing the strategic importance of financial and operational insights in enterprise IT.
- Silver Lake Acquisition of Qualtrics – In a deal valued at $12.5 billion, Silver Lake acquired Qualtrics, showcasing the growing interest in AI and data-driven decision-making processes in the technology sector.
- Cisco’s Acquisition of Splunk – Cisco’s largest transaction to date, the $28 billion acquisition of Splunk, underscores the increasing focus on cybersecurity and observability in the tech community.
Conclusion
The cyber insurance market is characterized by robust growth driven by the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, digital transformation, and regulatory pressures. However, it faces challenges related to the evolving nature of cyber risks, requiring ongoing innovation and strategic collaborations among insurers to mitigate these risks effectively and protect businesses from potential financial losses due to cyber incidents.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



