Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Editor’s Choice
- Cyber Insurance Market Size Statistics
- Cyber Insurance Claims
- Leading Causes of Claims
- Claims by Industry
- Cyber Crime Categories
- Factors Affecting Claims
- Leading Causes of Claims:
- Benefits of Cyber Insurance
- Cybercrime Statistics
- Why Cyber Insurance Is Growing:
- Key Financial Figures
- Cyber Insurance Trends in Companies Statistics
- Claim Costs For SMEs in Cyber Insurance Statistics
- Cyber Insurance Claims Statistics
- Recent Developments
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Cyber Insurance Statistics: Cyber insurance is a form of coverage that safeguards individuals and businesses against financial losses from cyberattacks and data breaches.
In today’s interconnected digital world, where cyber threats like hacking, malware, and ransomware are ever-present, having cyber insurance is crucial.
This insurance protects data breach expenses, ransomware incidents, and business interruption. Cyber extortion, data restoration, liability claims, regulatory fines, and crisis management.
The specifics of coverage and costs can vary, but cyber insurance is an essential component of a comprehensive risk management strategy in an era where cybersecurity threats evolve.
Helping organizations recover faster and minimize the financial and reputational damage caused by cyber incidents.

Editor’s Choice
- The Cybersecurity Insurance Market witnessed steady growth over the years, starting at $3.5 billion in 2017, and then increasing to $4.5 billion in 2018.
- Finally, in 2025, the market is expected to expand, with a projected size of $22.5 billion. Reinforcing its position as a robust and thriving sector.
- Phishing: 83% of companies experienced phishing attacks in 2021.
- 19% of companies have cyber insurance that covers incidents costing more than $600,000.
- For SMEs, the average cost of crisis services related to cyber insurance claims from 2017 to 2023 amounts to $111,000.
- Claims grew by 100% in the past three years.
- Over 56% of claims came from small businesses with revenue under $25 million.
Cyber Insurance Market Size Statistics
- The market witnessed steady growth over the years, starting at $3.5 billion in 2017, and then increasing to $4.5 billion in 2018.
- Continuing this upward trajectory, the market grew to $5.5 billion in 2019, reflecting a consistent annual growth pattern.
- In 2020, there was a notable increase in market size, reaching $6.9 billion. Indicating a significant surge compared to previous years.
- The year 2021 marked a pivotal moment in the market. As it reached a remarkable size of $10 billion, signifying a substantial leap in market value.
- Building on this momentum, the market continued to thrive in 2022. With a size of $13 billion, showcasing sustained growth.
- Looking ahead to 2023, there are high expectations. With a projected market size of $15.6 billion, underscoring the industry’s resilience and potential.
- As we move into 2024, further growth is anticipated. The market size is forecasted to reach $18.7 billion, highlighting its promising outlook.
- Finally, in 2025, the market is expected to expand. With a projected size of $22.5 billion, reinforcing its position as a robust and thriving sector.
- The top cause of cyber insurance claims is ransomware. Accounting for 29% of all reported incidents, highlighting the prevalence and impact of ransomware attacks.
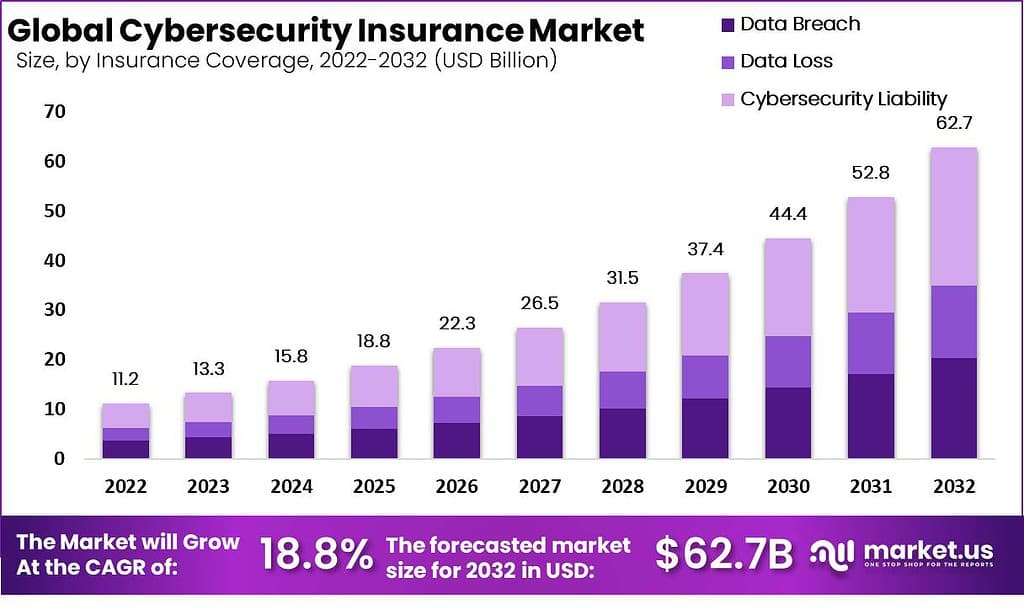
Cyber Insurance Claims
- Claims grew by 100% in the past three years.
- 200% increase in claims closed with payments in 2021, totaling around 8100 claims paid.
- Chubb Ltd Grp, a major insurer, had $404,144,104 in premiums written and a 14.7% market share.
Leading Causes of Claims
- Ransomware accounted for 81% of claims involving recovery expenses.
- About 27% of data breach claims and 24% of first-party claims had exclusions in insurance packages, resulting in non-payouts or partial payouts.
- Business email compromise scams led to 1,153 claims in 2022.
Claims by Industry
- Over 56% of claims came from small businesses with revenue under $25 million.
- Only 19% of organizations had insurance coverage beyond $600,000.
Cyber Crime Categories
- Data breaches, incident response, and crisis management caused 73% of cyber insurance claims.
- Healthcare, IT, and communications industries faced the highest frequency of claims.
Factors Affecting Claims
- Cost of Response: Higher costs in responding to cyberattacks impact claims.
- Weak Cybersecurity: Lack of security measures can diminish claims.
- Business Interruption: Lost business operations expenses are part of cyber claims.
- Types of Attacks: Malware and ransomware attacks are costly.
- Response Plans: Preparedness affects the efficiency of response.
Leading Causes of Claims:
- Phishing: 83% of companies experienced phishing attacks in 2021.
- Credit Fraud: Identity thefts, bank frauds, and credit fraud increased in 2021.
- Scams: Business email compromise scams led to cyber insurance claims.
- Malware: Malware attacks cost over $2.5 million on average.
Benefits of Cyber Insurance
- Financial Protection: Covers data restoration costs, system repairs, and investigations.
- Legal Support: Assists with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Risk Assessment: Helps identify vulnerabilities and prevent attacks.
- Forensic Support: Aids in investigating the source of the attack.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing your business is protected.
Cybercrime Statistics
- Cybercrime cases increased by 69% in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Individuals under 20 saw a 100% increase in cybercrimes during the pandemic.
- SMEs faced an 83% increase in cyber claims from 2018 to 2020.
Why Cyber Insurance Is Growing:
- Organizations seek protection in the digital world.
- Cyber insurance grew from 26% in 2016 to 47% in 2020.
- The global cyber insurance market is projected to reach $28 billion by 2026.
Key Financial Figures
- The average cost of cybercrime in the U.S. is $27.37 million.
- Over 817 data breaches have been reported in the U.S. since H1 2022.
Cyber Insurance Trends in Companies Statistics
- 19% of companies have cyber insurance that covers incidents costing more than $600,000.
- 55% of companies have some form of cyber insurance coverage.
- 28% of companies intend to acquire cyber insurance shortly, indicating a growing awareness of the importance of such coverage in the face of cyber threats.

Claim Costs For SMEs in Cyber Insurance Statistics
- For SMEs, the average cost of crisis services related to cyber insurance claims from 2017 to 2023 amounts to $111,000.
- Legal expenses associated with cyber insurance claims for SMEs over the same period average around $98,000.
- The cost attributed directly to the cyber incident for SMEs averages approximately $145,000.
- Combining all these expenses, the average total claim for cyber incidents for SMEs during this period is $345,000.
- Considering the various components of cyber insurance claims, the total average claim for SMEs is $485,000, reflecting the comprehensive financial impact of cyber incidents on small and medium-sized enterprises.

Cyber Insurance Claims Statistics
- The top cause of cyber insurance claims is ransomware, accounting for 29% of all reported incidents, highlighting the prevalence and impact of ransomware attacks.
- Other unspecified factors contribute to 17% of cyber insurance claims. Showcasing the diversity of issues that can lead to insurance claims.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a significant contributor, responsible for 15% of cyber insurance claims, indicating the risks associated with email-based attacks on businesses.
- Hackers, comprising various types of cyberattacks, contribute 12% of cyber insurance claims, illustrating the persistent threat malicious actors pose.
- Unspecified events, which may include various unforeseen cyber incidents, make up 7% of cyber insurance claims, underscoring the complexity of cyber risk.
- Staff mistakes and human error are responsible for 4% of cyber insurance claims, emphasizing the importance of employee training and awareness in cybersecurity efforts.
- Phishing attacks account for another 4% of claims, emphasizing the continued relevance of this common cyber threat.
- Theft of money, driven by financial cybercrimes, represents 3% of cyber insurance claims.
- Malware and viruses are responsible for another 3% of claims, indicating the persistence of these types of cyber threats.
- Legal actions resulting from cyber incidents contribute to 2% of claims, highlighting the legal consequences and liabilities that can arise from cyber events.
- Privacy breaches, which can have significant regulatory implications, account for 2% of cyber insurance claims.
- Finally, rogue employee actions represent another 2% of claims, emphasizing the need for internal controls and monitoring to mitigate insider threats.

Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- Aon acquires Cytelligence: In 2023, global insurance broker Aon acquired Cytelligence, a Canadian-based cyber risk consultancy firm, to strengthen its cyber insurance offerings. The acquisition, valued at $100 million, allows Aon to enhance its risk assessment capabilities and provide more comprehensive cybersecurity solutions to its clients.
- Allianz partners with Coalition: In 2024, Allianz entered into a strategic partnership with Coalition, a leading cyber insurance provider, to co-develop cyber insurance products aimed at small and medium-sized businesses. The collaboration is expected to provide enhanced cyber risk management solutions, combining insurance coverage with cybersecurity tools.
New Product Launches:
- AXA introduces an AI-driven cyber insurance platform: In late 2023, AXA launched an AI-powered platform to help businesses assess their cyber risk in real time and automatically tailor cyber insurance policies based on those risks. This platform aims to provide flexible and more customized cyber insurance coverage.
- Zurich launches comprehensive cyber insurance for SMEs: In 2024, Zurich Insurance introduced a cyber insurance product specifically designed for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The new product includes 24/7 cybersecurity assistance and response services to help businesses manage breaches effectively.
Funding:
- Coalition raises $250 million in Series F funding: In 2023, Coalition, one of the fastest-growing cyber insurance companies, raised $250 million in Series F funding, boosting its valuation to $5 billion. The funds are aimed at expanding the Coalition’s reach in the U.S. and international markets and investing in AI-driven cybersecurity tools.
- At-Bay secures $185 million for global expansion: In early 2024, At-Bay, a cyber insurance provider focused on proactive risk management, raised $185 million in Series D funding. The funds will support global expansion and the development of its risk monitoring platform, designed to reduce claims by identifying vulnerabilities before they lead to cyberattacks.
Technological Advancements:
- AI and machine learning in cyber risk assessment: AI and machine learning technologies are becoming integral to cyber insurance. By 2025, over 40% of cyber insurance policies are expected to be underwritten using AI-powered risk assessments, enabling insurers to offer more tailored coverage based on real-time data and trends.
- Proactive cyber defense integration: Cyber insurance providers are increasingly incorporating proactive defense mechanisms, such as vulnerability scanning and real-time alerts, into their policies. By 2026, 35% of cyber insurance policies are expected to include built-in cybersecurity services as a way to reduce the likelihood of claims.
Conclusion
Cyber Insurance Statistics – In conclusion, cyber insurance emerges as an indispensable necessity for businesses in our digitally-driven world, serving as a crucial safeguard against the pervasive and evolving landscape of cyber threats.
This report highlights the imperative for organizations, regardless of size or industry, to embrace cyber insurance as a vital risk mitigation tool.
However, businesses need to recognize that not all policies are created equal; careful policy selection tailored to specific cybersecurity needs is paramount.
Complementing cyber insurance with proactive cybersecurity measures, compliance with evolving regulations, and staying attuned to emerging technologies are key to a holistic defense strategy. Challenges persist, including policy exclusions and waiting periods, demanding ongoing attention.
In this dynamic landscape, the collaboration, adaptation, and innovation of both businesses and insurers are paramount to fortify our collective resilience against cyber threats and safeguard operations, finances, and reputation in the digital age.
FAQs
Cyber insurance is a type of coverage that helps organizations mitigate financial losses resulting from cyberattacks, data breaches, and other cybersecurity incidents.
Businesses need cyber insurance to protect themselves against the financial and reputational risks associated with data breaches and cyberattacks, which can lead to significant financial losses and damage to their brand.
Cyber insurance can cover various expenses, including data breach response costs, legal fees, public relations efforts, and business interruption losses. It may also cover third-party claims against the insured.
No, cyber insurance policies can vary widely in terms of coverage and cost. It’s essential for businesses to carefully review policies and select the coverage that aligns with their specific needs and risk profile.
The cost of cyber insurance depends on various factors, including the size and industry of the business, the level of coverage required, the cybersecurity measures in place, and the business’s past claims history.
Cyber insurance policies typically cover many cyber threats, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, social engineering fraud, etc. However, specific coverage may vary, so reviewing policy details is essential.


