Table of Contents
Introduction
The global digital remittance market is expected to experience significant growth in the coming years, with a valuation predicted to increase from USD 22.1 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 77.7 billion by 2032, resulting in a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.0%. This growth is largely attributed to the widespread adoption of mobile-based remittance solutions that are revolutionizing the way funds are transferred across borders.
Several factors are contributing to the vibrancy of this market. The increased use of smartphones and the internet has democratized access to digital remittance platforms, making it easier for users to perform financial transactions conveniently. The rise in global migration has also escalated the demand for efficient cross-border money transfers, as migrants seek reliable ways to support their families back home. Furthermore, advancements in financial technology, such as blockchain and digital payment technologies, have enhanced the speed, security, and cost-effectiveness of these services.
In 2023, the digital remittance sector saw a flurry of mergers and acquisitions that underscored the industry’s dynamic nature and its attractiveness to investors. Among the significant transactions, FIS divested a majority stake in its Worldpay Merchant Solutions business to GTCR for USD 18.5 billion, a move aimed at simplifying operations and boosting capital flexibility. Additionally, Nasdaq’s acquisition of Adenza for USD 10.5 billion marked a substantial step towards expanding Nasdaq’s FinTech footprint beyond traditional exchange operations.
In another notable deal, Deutsche Börse acquired SimCorp for €3.9 billion. It integrated SimCorp’s investment management software into its data and analytics businesses to create a comprehensive investment management solutions platform. This acquisition is part of Deutsche Börse’s strategy to capitalize on industry trends and enhance its recurring revenue streams.
Moreover, Duck Creek Technologies’ acquisition of Vista for $2.6 billion represented the largest FinTech M&A deal in the first quarter of the year, highlighting the sector’s robust activity even amid market volatility and economic uncertainties. These transactions reflect the sector’s strategic realignments and the pursuit of innovation within the digital remittance and broader financial technology sectors.
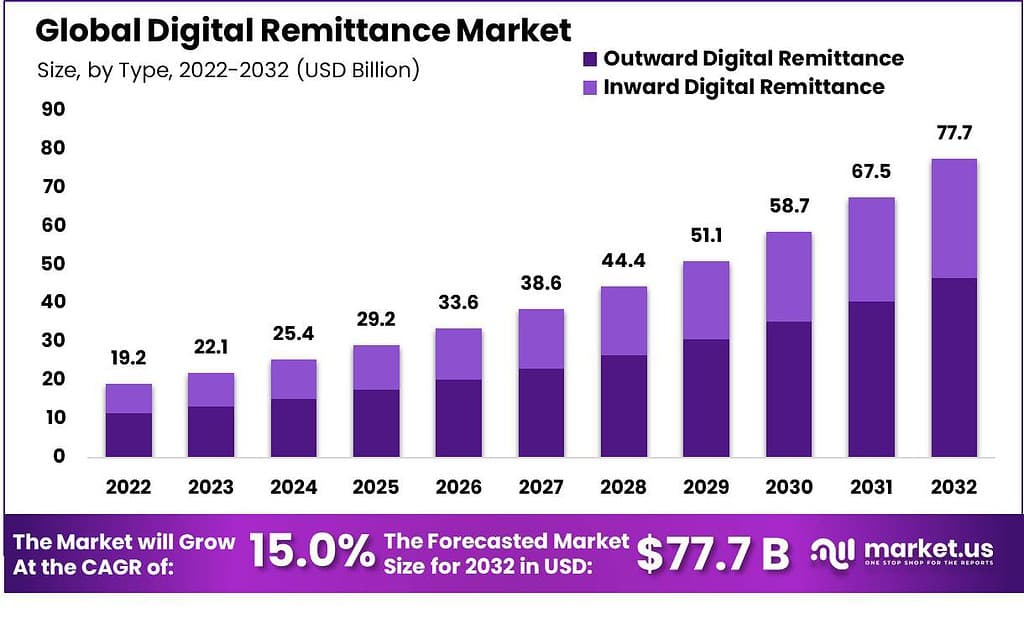
Key Takeaways
- By 2032, the market for digital remittances is expected to grow to USD 77.7 billion, with an annual growth rate of 15% from 2023 to 2032.
- In 2022, more than 60% of the digital remittance market was from outward remittances, influenced by people moving globally.
- Money Transfer Operators were the largest group handling these transactions in 2022, making up nearly 40% of the market.
- The personal segment, which includes remittances sent by individuals for reasons like work abroad or tourism, made up over 58% of the market in 2023.
- North America was the leader in digital remittance revenue in 2022, holding a 30.2% share, with Asia-Pacific also being a major player.
- Blockchain technology is likely to lead to more growth in the market by making transactions quicker, safer, and more open.
- The five biggest companies in the digital remittance market made up about 45% of the total market in 2022.
- Countries considered lower to middle income received USD 626 billion in remittances in 2022, according to the World Bank.
- Over the years, the cost of sending money has decreased from 8.9% in 2008 to 6.3% in 2022, thanks to more digital options and competition.
- Annual growth of money sent across borders is expected to be 2.9% from 2022 to 2035.
Digital Remittance Statistics
2023 Visa Digital Remittances Adoption Report
- In 2021, global remittance inflows hit a new record of $733 billion, with $605 billion going to low and middle-income countries.
- The survey included over 14,000 remittance senders and receivers across 10 countries.
- 53% of consumers surveyed use digital apps to send and receive funds globally.
- 34% of consumers still go to a physical bank or branch to manage remittances.
- 12% of consumers send cash, checks, or money orders by mail.
- In the U.S., 63% send and 57% receive remittances at least once per year.
- In Canada, 64% of people send and 52% receive money at least once per year.
- 33% of U.S. survey respondents sent money internationally in December 2022.
- In North America, the adoption of app-based digital payments for remittances is around 60-61%.
- High fees and issues with exchange rates are common pain points for digital remittance users in the U.S. and Canada.
- In the Philippines, 70% of those surveyed receive remittances from abroad, driven by about 1.83 million Overseas Filipino Workers.
- Digital payment adoption among remittance users in the Philippines and Singapore is extremely high, ranging from 70-80%.
- In Europe, 62-67% of remittance users in France and Poland use digital methods to send and receive international remittances.
- Residents of Mexico and Peru who were surveyed receive money from abroad more often than they send it, with adoption rates of digital payment methods among senders as high as 75%.
- In the Middle East, 69% of surveyed users in Saudi Arabia and 65% in the UAE prefer sending money through digital apps.
According To WorldBank
- Remittances to low- and middle-income countries grew by an estimated 5% in 2022, reaching $626 billion.
- This 5% growth is much lower than the 10.2% increase seen in 2021.
- Remittances are very important for household income in developing nations. They help reduce poverty and improve nutrition and education.
- In 2022, remittance growth was 10.3% for Europe and Central Asia, aided by rising oil prices and demand for migrant workers in Russia.
- Latin America and the Caribbean saw 9.3% growth in remittances in 2022.
- Remittances to South Asia grew 3.5% in 2022, with India set to receive over $100 billion, a first for any single country.
- Sub-Saharan Africa’s remittances grew 5.2% in 2022, down from 16.4% growth in 2021.
- The cost of sending $200 remained high at 6% on average in Q2 2022 for low- and middle-income countries.
- Sending via mobile operators was cheapest at 3.5% but made up less than 1% of total transactions.
- Remittances as a share of GDP exceeded 20% in several countries like Tonga (50%), Samoa (34%), El Salvador, Honduras, Jamaica and Haiti.
- Nicaragua saw a 45% increase in remittances in the first 9 months of 2022.
- Guatemala’s remittances grew 20% during this period, while Mexico and Colombia saw 15% and 9% growth respectively.
- Lebanon (38%) and West Bank & Gaza (19%) had significant remittance inflows as a percentage of GDP.
- Nepal’s remittance growth was just 4% in 2022, while the remaining South Asian nations saw an aggregate 10% decline.
- The Gambia (28%), Lesotho (21%) and Comoros (20%) were highly dependent on remittances as a share of GDP.
- The costliest remittance corridors averaged 25.2%, while the cheapest were just 3.4% on average.
- Digital channels account for less than 1% of total remittance transaction volume currently.
- Compliance costs related to anti-money laundering restrict new remittance service providers’ access to banks.
Case Study of BRAC Bank in Bangladesh
- In 2020, inbound remittances to Bangladesh increased by 18%, primarily due to a shift from cash to digital channels driven by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- At BRAC Bank, the proportion of remittance transactions received digitally (in a bank account or mobile wallet) rose from 37% in 2019 to 75% in 2020.
- 86% of remittance transactions received through bKash mobile wallets were under $200, compared to 30% of those received in a bank account and 19% received in cash.
- Remittance recipients in Bangladesh had a financial inclusion rate of 55% in 2018, higher than the overall population at 47%.
- Only 25% of remittance recipients in Bangladesh saved money in 2018, often through informal means rather than banks.
- Women comprise 60% of remittance recipients in Bangladesh, but as of the project start, only 37% of BRAC Bank’s digital remittance customers are women.
Can Fintech Help Reduce Remittance Costs?
Digital remittance could significantly lower the costs of sending money, especially in the world’s poorest areas. In 2022, the average fee for sending $200 was over 6%, twice as high as the United Nations’ goal for 2030. The most expensive way to send money is through banks, which charged about 11.8% at the end of 2022. Money transfer operators like Western Union and MoneyGram had lower fees at 5.4%. The cheapest option was mobile money providers, charging just 4.5%. Despite these options, many people still use cash for most money transfers. High transfer fees sometimes force people to use unofficial methods, like unlicensed operators or local traders, to send money across borders. These methods can be risky and less secure.

During the COVID-19 pandemic, lockdowns made it hard for people to carry money in person to other places. This led to more people using official and digital ways to send money, such as through mobile phones. In fact, in 2020, the amount of money sent by mobile phones increased by 65%. From 2014 to 2021, the number of adults in developing countries who used digital methods to send or receive money rose from 35% to 57%. Changes in laws and rules in different countries have also helped increase digital payments by making it easier to use digital IDs and remote methods for sending money. These changes often allowed people to send more money at lower costs.

Use Cases
- Frequent Small Transactions: Digital remittance platforms are increasingly used for sending small amounts more frequently. This use case is prominent among migrants who prefer to send money home regularly rather than in large sums. For example, the adoption of mobile wallets and online platforms has enabled such transaction patterns, particularly in countries with significant migrant populations.
- Bank Account and Mobile Wallet Transfers: A significant portion of digital remittances now directly goes to bank accounts or mobile wallets, bypassing traditional cash pickup methods. This shift not only speeds up the transfer process but also reduces costs associated with physical cash transactions. Such methods have become particularly prevalent, reflecting a broader shift towards financial digitization.
- Cross-Border Payments: Digital remittance services facilitate cross-border payments by enabling users to send money across different countries and regions without the need for physical banking infrastructure. This is especially useful in regions like Sub-Saharan Africa, where digital remittance services are integrated with local mobile money systems, allowing users to send and receive money across borders with greater ease and lower costs.
- Supporting Migrant Workers and Families: Digital remittances play a critical role in supporting the financial inclusion of migrant workers and their families. By using digital channels, migrants can support their families back home more effectively, contributing to their daily needs and emergencies without the delays and high fees associated with traditional remittance methods.
- Blockchain Applications: Blockchain technology is emerging as a powerful tool in the remittance industry, offering faster transaction speeds and reduced costs by eliminating intermediaries. Companies are using blockchain to facilitate remittances across various countries, improving the efficiency of these transactions and offering enhanced security features.
Key Players Analysis
PayPal Holdings Inc.
PayPal Holdings Inc. plays a significant role in the digital remittance sector, leveraging its platform to facilitate global money transfers with a focus on accessibility, speed, and reduced costs. A key highlight in their recent developments is the acquisition of Xoom in 2015, a digital money transfer service that enhances PayPal’s capacity to provide remittances across national borders efficiently. Xoom allows users to send money quickly to over 53 countries, using either a bank card or account, which underscores PayPal’s commitment to reducing the costs and increasing the convenience of sending money internationally.
Moreover, PayPal continues to innovate in the digital payments space. In 2021, they launched a new version of their PayPal app, which integrates numerous financial services including high-yield savings accounts, in-app shopping, direct deposits, bill payments, and a new rewards program. These features are designed to consolidate financial management into a single platform, making it easier for users to handle their finances effectively. Additionally, PayPal introduced Fastlane, a streamlined checkout solution, and Smart Receipts, an AI-driven tool for enhancing customer loyalty with personalized deals and cashback offers, in 2024. These innovations are aimed at improving user experience and expanding PayPal’s influence in digital commerce and remittances.
Digital Wallet Corporation
Digital Wallet Corporation (DWC) has made significant strides in the digital remittance sector, particularly in Japan, where it has become the top service with access to over 77,000 ATMs nationwide. A notable development for DWC was the acquisition of Seven Global Remit from Seven Bank in February 2024, which has significantly broadened its market presence and service capabilities, making DWC a leader in Japan’s remittance services. This move not only expanded DWC’s ATM network but also enhanced its service offerings to foreign residents in Japan, promoting financial inclusion and improving the international money transfer landscape.
Additionally, DWC has formed strategic partnerships to advance digital remittance services. For instance, it joined hands with MoneyGram in 2022 to enhance real-time payment capabilities for customers in Japan, allowing them to send money globally through the Smiles Mobile Remittance app. This partnership reflects a shared commitment to leveraging fintech to facilitate efficient and secure cross-border transactions. Furthermore, a collaboration with Rizal Commercial Banking Corporation (RCBC) aims to redefine digital banking services in the Philippines, reflecting DWC’s commitment to advancing fintech adoption and improving financial services for Filipino families.
InstaReM Pvt. Ltd.
InstaReM Pvt. Ltd., now known as Nium, has significantly evolved within the digital remittance sector, transitioning from a remittance service provider to a broader global payments platform. Founded in 2014, InstaReM initially focused on simplifying cross-border payments for individuals but has expanded its services to cater to businesses as well. In 2019, it rebranded to Nium, reflecting its broader capabilities beyond remittances, including payment solutions for businesses and the ability to develop custom financial products on its platform.
Recent developments for Nium include significant expansions and partnerships aimed at enhancing its digital payment solutions. For instance, Nium has been actively participating in Visa’s Fintech Fast-track program, collaborating with major financial institutions to develop innovative payment solutions. The company’s commitment to creating an open financial ecosystem is evident in its launch of the ‘Open Money Network’, which allows various financial entities to build and integrate new financial services using Nium’s infrastructure.
MoneyGram International, Inc
MoneyGram International, Inc. is a major player in the digital remittance sector, continuously adapting to the evolving financial technology landscape. Recently, MoneyGram has been focusing on expanding its digital services. In 2023, MoneyGram announced plans to launch a non-custodial digital wallet which allows users to transition seamlessly between fiat and digital currencies using stablecoin technology. This wallet is set to debut in the first quarter of 2024, emphasizing MoneyGram’s commitment to integrating blockchain technologies into its services.
Further demonstrating its dedication to digital transformation, MoneyGram has also been enhancing its digital transaction capabilities. In partnership with Visa Direct, MoneyGram has focused on improving payments through its app and website, aiming for 50% of its transactions to be digital by 2024. Additionally, MoneyGram has engaged in strategic partnerships to broaden its digital reach and service offerings, such as its collaboration with Stellar in 2021 to facilitate cross-border transactions using blockchain technology.
Azimo B.V.
Azimo B.V., a prominent player in the digital remittance sector, has recently made significant changes to its business model and operations. Originally established in 2012 in London, Azimo gained recognition for enabling users to send money to over 195 countries in a variety of currencies through its user-friendly platform. However, in March 2022, Azimo was acquired by Papaya Global, a New York-based payroll and payments solutions provider. Following this acquisition, Azimo announced in August 2023 that it would cease processing transfers via its service and shift its focus towards providing salary payments to business customers, signaling a significant pivot in its business strategy. This transition marks Azimo’s move away from general consumer remittance services to a more business-focused offering, aligning more with corporate payroll solutions.
Western Union Holdings Inc.
Western Union Holdings Inc. is actively enhancing its position in the digital remittance sector through a series of strategic initiatives aimed at expanding its digital services and broadening its customer engagement. Known for its longstanding history in financial services, Western Union is emphasizing digital growth, as evidenced by the significant increase in digital transactions and revenues. For instance, digital money transfer revenues saw a notable rise, underscoring the company’s successful pivot towards digital-first solutions.
Recent developments include the introduction of the “Evolve 2025” strategy, where Western Union aims to further integrate and expand its digital and retail services globally. This strategy is focused on providing comprehensive financial services that meet the evolving needs of consumers worldwide, including new digital banking services in selected markets like Germany and Romania. Additionally, Western Union has been strengthening its global footprint through partnerships, such as with Google Pay in the U.S., enhancing the ease and reach of its cross-border payments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the digital remittance market is confronted with regulatory and security challenges, the ongoing technological innovations and growing global need for fast and reliable cross-border money transfers continue to drive substantial market growth. The potential to reach underserved populations in emerging markets presents additional growth opportunities, promising a broader impact on global financial inclusion and economic empowerment.


