Table of Contents
- Editor’s Choice
- Global Facial Recognition Market Statistics
- Facial Recognition Statistics by Key Players
- Country-Wise Facial Recognition Statistics
- Breakdown of Industries Using Facial Recognition Statistics
- Facial Recognition Accuracy Statistics
- Facial Recognition Prominent Examples of Inaccuracy Statistics
- Public Views of Facial Recognition Technology Statistics
- Recent Developments
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Facial Recognition Statistics: Facial recognition technology is an advanced system employing algorithms and AI to authenticate and validate individuals by analyzing distinct facial attributes.
These attributes include eye spacing, nose shape, and jawline contours. This analysis generates a facial profile matched against databases or images to establish identity.
The technology’s versatility and impact on diverse fields have garnered substantial interest. For example, facial recognition is commonly used for security purposes, such as access control to buildings, airports, and restricted areas.
It can help identify and track individuals on watchlists, alert authorities to potential threats, and aid investigations.

Editor’s Choice
- The facial recognition technology market stood at 5 billion USD in 2022 and is expected to grow to 19 billion USD in 2032 at a CAGR of 14%.
- The accuracy of facial recognition technology varies widely depending on conditions and use cases. In ideal scenarios, some algorithms achieve accuracy rates above 99%. Real-world deployments often have lower accuracy due to environmental factors and diversity in subjects’ appearances.
- Approximately 70% of governments globally employ facial recognition technology (FRT) on a significant scale.
- The likelihood of a random individual successfully unlocking your iPhone using Face ID is approximately 1 in a million.
- Facebook’s DeepFace can determine whether two depicted faces correspond to the same individual, with an accuracy rate of about 97%.
- By the conclusion of 2023, an estimated 97% of United States airports are anticipated to integrate FRT.
- The initial instance of an arrest assisted by facial recognition technology occurred at Washington Dulles International Airport in August 2018.
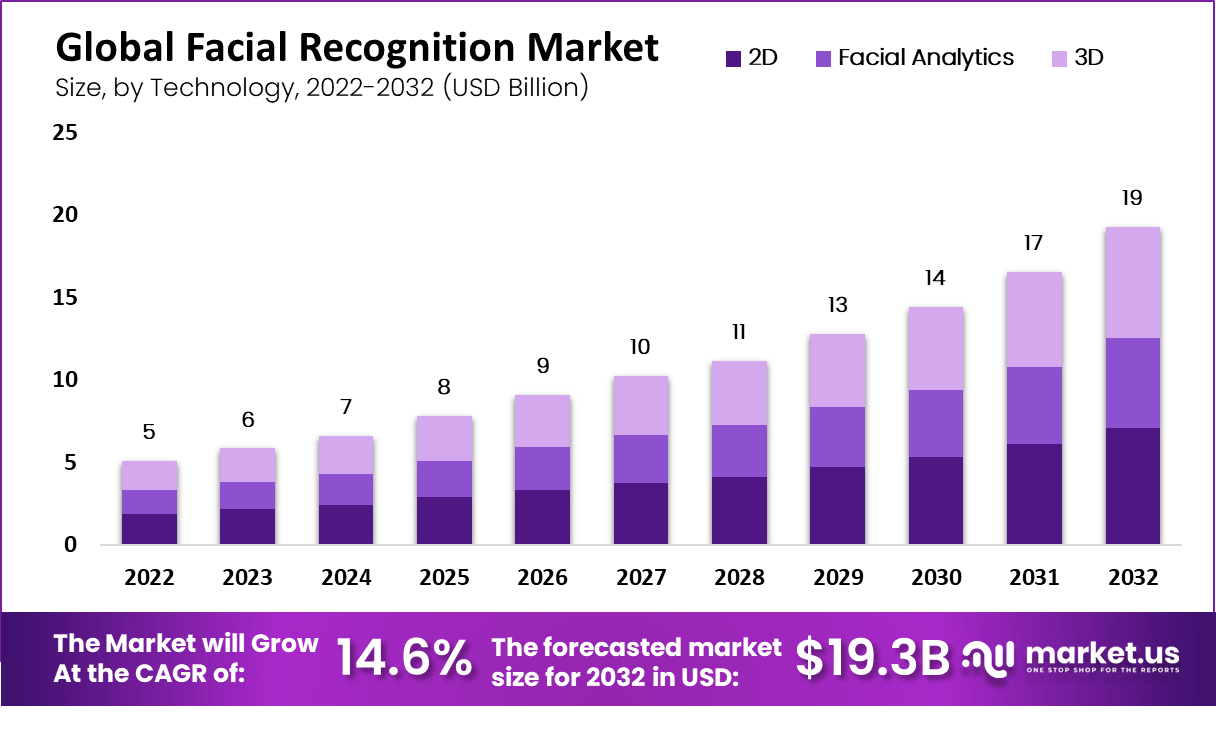
Global Facial Recognition Market Statistics
- The revenue generated from facial recognition technology exhibits a steady upward trajectory at a CAGR of 14% over the projected years. In 2022, it stood at 5 billion USD, marking the initiation of its growth.
- Subsequent years witnessed a consistent increase, with revenue reaching 6 billion USD in 2023 and further climbing to 7 billion USD in 2024.
- The trend continues as the technology’s prominence strengthens.
- Amassing 8 billion USD in 2025 and ascending to 9 billion USD in 2026.
- The following years display a sustained progression, with revenues of 10 billion USD in 2027.
- 11 billion USD in 2028, and 13 billion USD in 2029.
- As the technology matures, it achieves even greater financial success.
- Accumulating 14 billion USD in 2030 and escalating to 17 billion USD in 2031.
- The growth trajectory remains robust, culminating in projected revenues of 19 billion USD in 2032. This evolving financial landscape underscores facial recognition technology’s increasing integration and significance across various sectors and industries.
(Source: Market.us)

Facial Recognition Statistics by Key Players
- The market for facial recognition technology is characterized by a distribution of market shares among several key players. Among them, Ayonix Corporation leads with a share of 15%.
- Closely followed by IBM Corporation and Aware, Inc., with 11% and 10%, respectively.
- Other significant contributors include FacePhi and Gemalto NV, each holding a 10% and 9% market share, respectively.
- Additionally, Cognitec Systems GmbH, 3M Company, and Fujitsu command a collective share of 26%, divided amongst them with 9%, 9%, and 8%, respectively.
- The remaining portion accounts for 19% of the market.
- It is attributed to other key players in the facial recognition technology sector.
(Source: Market.us)

Country-Wise Facial Recognition Statistics
China
- China ranks 5 out of 40 on the list, which is hardly unexpected given its reputation as a significant facial recognition technology provider. The government and law enforcement agencies extensively employ this technology, sometimes resorting to intrusive video surveillance methods.
- An illustrative case involves Suzhou, which used technology to publicly humiliate seven individuals for venturing outside in their pajamas.
- The city subsequently shared its images on its WeChat account by employing Facial Recognition Technology (FRT) to identify these individuals. Another instance highlights a Chinese park’s utilization of FRT to deter the pilfering of toilet paper.
Russia
- Ranked at number 9 out of 40, Russia’s prominent position on the list is hardly unexpected.
- Facial recognition technology features prominently across all the categories discussed, signifying that Russia.
- Like other nations, is increasingly adopting facial recognition technology across diverse domains.
United Arab Emirates (UAE)
- Ranked at number 10 out of 40, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is taking a page from other top-ranking countries by implementing facial recognition technology extensively.
- This deployment is aimed at expediting processes and reducing fraudulent activities.
- The technology’s applications are diverse, from accessing government services to recording school attendance, making its integration pervasive throughout the UAE.
Japan
- Japan has a score of 12 out of 40. Facial recognition technology (FRT) is employed across all the categories examined in Japan. A noteworthy area of focus is the utilization of FRT in conjunction with citizens’ social media profiles to locate individuals involved in criminal activities. This practice raises substantial concerns.
- The National Public Safety Commission (NPC), responsible for maintaining facial images of approximately 10 million Japanese citizens, has granted the police access to this repository. Consequently, law enforcement can apply this database in conjunction with FRT for their operations.
India
- Ranked 12 out of 40, India showcases the implementation of approximately 16 distinct Facial Recognition Technology (FRT) systems across Central and State governments.
- Moreover, an additional 17 systems are currently in the process of being developed.
Australia
- Australia occupies the 13th spot out of 40 countries.
- Australian law enforcement was found to be employing the contentious facial recognition technology provided by Clearview
- A company that garnered attention for building its database from social media images. Following this revelation, Victoria police opted to distance themselves from this technology.
United States
- The United States holds the 18th position out of 40 countries. While the adoption of this technology is expanding within the U.S.
- There is currently no indication of Facial Recognition Technology (FRT) being implemented in buses.
(Source: Comparitech – Datawrapper)

Breakdown of Industries Using Facial Recognition Statistics
Facial Recognition in Business Statistics
- Public attitudes toward facial recognition technology vary across different United States scenarios. For instance, approximately 30% of American adults find it acceptable for companies to utilize facial recognition for monitoring employee attendance.
- A separate study underscores that a mere 32% of consumers feel at ease with private companies employing facial recognition.
- In the context of advertising, contrasting opinions emerge. About 54% of adults in the U.S. do not support using facial recognition technology to assess consumer reactions to advertisement displays.
- Conversely, 30% of respondents regard this trend as acceptable.
- Regarding security enhancements in apartment complexes, perspectives are divided. Around 30% of U.S. adults support the integration of facial recognition by apartment owners to bolster security measures, while 34% express reservations.
- In the hospitality sector, optimism prevails. 74% of hotel operators believe biometrics will become a mainstream method for identifying hotel staff by 2025.
- Likewise, customers’ opinions are notable: 62% agree that adopting facial recognition for identifying hotel guests would enhance their overall experience.
- Furthermore, 41% assert a greater likelihood of selecting hotels that offer automated facial recognition services.
- The potential impact of facial recognition technology is evident in the retail domain. Its implementation in stores can potentially reduce violent incidents by 91%.
- Additionally, nearly half of the individuals (49%) believe equipping stores with facial recognition technology can effectively combat shoplifting cases.
- Shifting focus to Spain, CaixaBank’s study reveals a high level of receptiveness. In this country, 70% of users are open to using facial recognition instead of PINs for withdrawing money from ATMs.
(Source: Smith, 2020, Capers, 2020, Smith, 2020, Oracle Hospitality, FaceFirst, 2019, Statista, CaixaBank, 2019)
Facial Recognition in Crime and Law Enforcement Statistics
- As of July 2021, the Government Accountability Office at the federal level disclosed that 42 federal agencies.
- Law enforcement personnel have incorporated facial recognition technology to varying extents.
- 59% of Americans deem it acceptable for law enforcement to utilize Facial Recognition Technology (FRT) to evaluate security threats in public areas.
- Trust in law enforcement’s handling of FRT differs among racial groups, with 64% of White adult Americans, 47% of Black individuals, and 55% of Hispanic respondents agreeing.
- Interpol’s facial recognition system holds facial images from more than 179 nations, establishing a distinctive global criminal database.
- Since its launch in late 2016, Interpol’s facial recognition system has identified around 1.5K individuals of interest, criminals, terrorists, missing persons, or fugitives.
- In 2021, Maine pioneered enforcing stringent state-wide boundaries, permitting FRT solely for serious crime investigations.
- Over half of the American populace (54%) believes FRT can mitigate human bias in inquiries. While 47% perceive it as a means to reduce racial injustice and discrimination.
- Most Americans (83%) advocate for governmental collaboration with law enforcement to enhance FRT’s usage rather than imposing a ban.
- A substantial 74% of U.S. adults support law enforcement’s use of FRT in locating missing senior citizens affected by Alzheimer’s, dementia, or other cognitive impairments.
- When considering its potential effects, 46% of adults in the United States believe that law enforcement’s widespread adoption of facial recognition technology would benefit society.
- Conversely, 27% believe that this adoption would have negative implications.
- An additional 27% remain uncertain whether such utilization would be advantageous or disadvantageous for police to employ facial recognition technology extensively.
(Source: Government Accountability Office, Pew Research Center)

Facial Recognition in Healthcare Statistics
- In June 2021, the Geisinger hospital network in northcentral Pennsylvania introduced facial recognition technology (FRT) across three facilities as part of its positive patient identification system. This FRT system uses facial biometrics to scan a patient’s facial features, storing and connecting the data to their electronic health record.
- This setup permits patients to securely confirm their identity by performing a one-time facial scan, expediting the appointment check-in process. The implementation of this system commenced in June, and it has already registered the facial profiles of more than 4,000 patients within the hospitals’ medical records.
- After conducting a survey involving more than 4,000 adults in the United States, researchers discovered that a notable segment of participants deemed using facial image data in healthcare inappropriate across eight situations (15-25 percent).
- When combined with those who expressed uncertainty about the acceptability of these applications. Approximately 30-50% of respondents signaled varying levels of apprehension regarding the implementation of facial recognition technologies in healthcare contexts.
(Source: Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, Katsanis, S. H., et al. (2021), A survey of U.S. public perspectives on technology and imaging data practices in health and research contexts. PLOS One.)
Facial Recognition in Banking and Finance Statistics
- According to Aite-Novarica Group, approximately 15% to 20% of the 11,000 financial establishments in the United States employ a combination of selfie photo imaging and document verification to validate the usage of mobile or online banking and online application procedures.
- Prominent U.S. banks such as JP Morgan, Chase, City National Bank of Florida, and Wells Fargo have either experimented with or explored using artificial intelligence systems that incorporate facial recognition technology.
- Within the Latin American region, 42 percent of participants wanted future banking applications to incorporate the facial recognition feature.
- In 2017, Apple introduced Face ID as a novel login feature boasting security levels 20 times stronger than fingerprint identification. As users grew accustomed to this technology, financial institutions recognized its potential and began adopting it to offer quicker and safer services.
(Source: Aite-Novarica Group, Reuters, Statista, Cyberlink)
Facial Recognition at Airports Statistics
- Regarding airport security, 54.3% of Americans support using facial recognition for safety screenings.
- Similarly, 54.8% concur that facial recognition should not face limitations if it enhances public safety.
- By 2023, facial recognition technology will be implemented in 97% of airports.
- The Customs and Border Control agency retains facial exit scans for up to 14 days post-identification.
- Since its adoption, the agency has applied facial recognition to over 2 million passengers across more than 15,000 flights.
- Their target is to extend this practice to passengers on 16,300 flights per week by the conclusion of 2021.
- Currently, facial recognition technology is operational in 18 airports across the United States. Most airlines, including Delta, United, American, and JetBlue, adopted it, except for Southwest.
- The inaugural arrest facilitated by facial recognition occurred at Washington Dulles International Airport in August 2018, three days after the technology’s implementation.
- In 2018, facial recognition technology thwarted the entry of 26 suspected imposters into the United States within three months.
- It is projected that by 2021, facial recognition will be applied to all international passengers, including American citizens, at the top 20 U.S. airports.
- At Los Angeles’ LAX airport, American Airlines is piloting the practice of verifying passengers’ identities by scanning their faces, eliminating the need for traditional boarding pass scans.
- Notably, one out of every three Americans disagrees with the government’s utilization of facial recognition at airports to enhance security and streamline boarding procedures.
(Source: Center for Data Innovation, Reservations.com, USA Today, Defense One, Reservations.com, USA Today)
Facial Recognition Accuracy Statistics
- As of April 2020, the most accurate face identification algorithm exhibits an error rate of merely 0.08%, a significant improvement from the top algorithm in 2014, which displayed an error rate of 4.1%.
- Algorithms employed for verification, which compare individuals to well-defined reference images such as passport photos or mugshots, can achieve accuracy rates as impressive as 99.97% on established evaluations like NIST’s Facial Recognition Vendor Test (FRVT).
- In practical applications, actual accuracy rates tend to be significantly less impressive. For instance, the FRVT discovered that a prominent algorithm’s error rate increased from 0.1% when comparing against high-quality mugshots to 9.3% when comparing against images of individuals taken “in the wild,” where factors like the subject’s gaze not being directly at the camera or potential obstructions like objects or shadows could impact the results.
- NIST’s Face in Video Evaluation (FIVE) 2017 assessed that the most proficient algorithm demonstrated a % accuracy rate of 94.4%.
More Insights
- Conversely, when identifying individuals moving through a sports venue—a notably more complex scenario—prominent algorithms yielded accuracies ranging from 36% to 87%, contingent on camera placement.
- The FIVE results also highlight that, while one top algorithm achieved 87% accuracy within the sporting venue context, the median algorithm only managed 40% accuracy when working with imagery from the same camera.
- For a specific group of algorithms evaluated in the FRVT, when matching photos obtained from uncontrolled environments, the average failure rate to identify was 4.7%, without imposition of any confidence threshold.
- However, when a threshold demanding the algorithm only to provide results if it had a confidence level of 99% or higher was introduced, the failure rate increased significantly to 35%.
- This implies that the algorithm correctly identified the correct individual in approximately 30% of instances but did so with a confidence level below 99%.
(Source: National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST))
Facial Recognition Prominent Examples of Inaccuracy Statistics
- In 2018, the ACLU gained attention for uncovering that Amazon’s facial recognition technology mistakenly associated 28 members of Congress with individuals who had been arrested.
- In their examination, the ACLU uploaded images of Congress members and queried a database containing 25,000 mug shots of apprehended individuals, aiming to observe if the system would yield any matches.
- Amazon generated 28 matches among the tested members, accounting for roughly 5% of those examined. The ACLU contended that these findings underscored the insufficient accuracy of facial recognition for widespread use, highlighting the potential dangers of erroneous matches.
- The ACLU investigated employing an 80% confidence threshold, Amazon’s default setting. This threshold stands notably lower than Amazon’s recommended threshold of 95% for law enforcement applications.
- In 2019, the Washington County Sheriff’s Office in Oregon employed Amazon’s facial recognition product. Conveyed that they do not establish or employ confidence thresholds when utilizing the system. This instance underscores the significance of guaranteeing that operators handle facial recognition for critical purposes. Which possess adequate training and supervision to ensure the correct configuration of these systems.
(Source: ACLU, Washington County Sheriff’s Office, Oregon)
Public Views of Facial Recognition Technology Statistics
- A recent survey in the U.K. aimed to gauge public sentiment concerning using Automated Facial Recognition (AFR) technology by various entities and in different settings, such as police, government, private sector, airports, public transport, schools, supermarkets, and workplace human resources departments. The survey revealed that 46% of respondents believed that the public should have the option to consent to or opt out of AFR use.
- Moreover, 55% agreed that the government should impose limitations on the police’s utilization of facial recognition technology.
- It was noted that support for AFR use varied among different contexts: 70% of participants supported its use by the police, while support was lower for airports (50%), supermarkets (7%), schools (6%), and workplaces (4%). This survey underscored disparities in attitudes toward AFR usage among users and for diverse applications.
- A separate survey among London residents indicated that the specific use case influenced support for live AFR usage by the police. For serious crimes, support ranged from 81% to 83%, contingent on the nature of the threat, whereas support was 55% for minor crimes and dropped below 50% for nuisance behavior.
- Moving to Australia, a public opinion survey found that 50% of respondents considered the deployment of AFR in public spaces as an intrusion of privacy. Nonetheless, similar to the U.K., there was discernible support for specific technology uses, particularly in policing scenarios.
- A China Beijing News Think Tank survey revealed that over 80% of Chinese participants opposed AFR use in Beijing commercial zones.
- Furthermore, 96% of respondents expressed concerns about securing personal information and data to AFR technology.
(Source: London Policing Ethics Panel’s Final Report On Live Facial Recognition- May 2019, Ada Lovelace Institute Survey, Australian Attitudes to Facial Recognition: A National Survey- Monash University, South China Morning Post)
Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- Apple acquires Xnor.ai: In early 2023, Apple acquired Xnor.ai, a company specializing in edge-based AI and facial recognition technology, for $200 million. This acquisition aims to enhance Apple’s facial recognition capabilities on devices like iPhones and iPads.
- Microsoft acquires Nuance Communications: In 2023, Microsoft completed its acquisition of Nuance Communications for $19.7 billion. While primarily focused on healthcare AI, the acquisition also includes advanced facial recognition technology for security and authentication purposes.
New Product Launches:
- Amazon Rekognition Update: In mid-2023, Amazon Web Services (AWS) updated its Rekognition service with improved facial analysis features, offering better accuracy in identifying emotions, demographics, and facial landmarks.
- Google Face Match API: Google launched its Face Match API in late 2023, designed for secure authentication in smart home devices and Android smartphones, providing developers with tools to integrate advanced facial recognition into their apps.
Funding:
- SenseTime raises $620 million: In 2023, Chinese AI company SenseTime raised $620 million in a Series D funding round to expand its facial recognition technology and AI research capabilities.
- Clearview AI secures $100 million: Clearview AI, a controversial facial recognition firm, secured $100 million in funding in 2024 to enhance its technology and expand its customer base, despite ongoing legal challenges.
Technological Advancements:
- Edge-Based Facial Recognition: There is a growing trend toward edge-based facial recognition technology, which processes data locally on devices rather than in the cloud. This approach improves privacy and reduces latency, making it ideal for applications in smartphones and security cameras.
- AI-Powered Accuracy Improvements: Advances in deep learning and AI algorithms have significantly improved the accuracy and reliability of facial recognition systems, reducing error rates and enhancing performance in diverse environments.
Market Dynamics:
- Increased Adoption in Security: The adoption of facial recognition technology in security and surveillance has increased, with global spending on facial recognition systems projected to grow at a CAGR of 16% from 2023 to 2028.
- Consumer Electronics Integration: Facial recognition is becoming a standard feature in consumer electronics, including smartphones, laptops, and smart home devices, driven by demand for secure and convenient authentication methods.
Regulatory and Strategic Developments:
- EU’s AI Regulation: The European Union is developing comprehensive AI regulations that include guidelines for the use of facial recognition technology, emphasizing ethical considerations and privacy protection.
- US State-Level Bans: Several US states, including California and Massachusetts, have implemented bans or restrictions on the use of facial recognition by law enforcement and government agencies, citing privacy and civil rights concerns.
Research and Development:
- Bias Mitigation Efforts: Researchers are focusing on mitigating biases in facial recognition systems, aiming to improve accuracy across different demographic groups and ensure fair and equitable use of the technology.
- Healthcare Applications: R&D efforts are exploring the use of facial recognition in healthcare, such as monitoring patient conditions, detecting genetic disorders, and improving telemedicine interactions.
Conclusion
Facial Recognition Statistics – Facial recognition technology has become a significant and evolving aspect of modern society, with its applications spanning various sectors and raising diverse opinions among the public.
The technology’s revenue growth reflects its increasing integration across industries. While its potential for enhancing security, convenience, and efficiency is evident, there are substantial concerns regarding privacy, accuracy, and ethical considerations.
Public attitudes vary widely, as highlighted by surveys from different countries. Image quality, environmental conditions, and confidence thresholds influence the technology’s accuracy and performance.
While facial recognition has demonstrated promise in controlled environments, its effectiveness diminishes in real-world scenarios.
FAQs
Facial recognition technology is an advanced system that employs algorithms and artificial intelligence. To analyze and identify unique facial features for authentication, security, and identification purposes.
The accuracy of facial recognition technology varies based on factors such as image quality, lighting conditions, and the algorithm used. Accuracy can be high in ideal conditions, but real-world scenarios often result in lower accuracy rates, especially in challenging environments.
Facial recognition technology has diverse applications, including security and access control, law enforcement, banking, retail, healthcare, and more.
Concerns include privacy issues, the potential misuse of data, and accuracy disparities among different demographic groups. Algorithm biases, and the possibility of mass surveillance infringing on civil liberties.
Public sentiment varies widely. Surveys show that attitudes depend on the context and use case. While some individuals support its use for security and convenience, others are concerned about privacy and potential abuse.


