Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Editor’s Choice
- Factoring Market Overview
- Factoring Market Share – By Region Statistics
- Factoring Volume Statistics – By Region Statistics
- Factoring Turnover – By Region Statistics
- Factoring Across Various Sectors Statistics
- Factoring Debt Statistics
- Factoring Funds Statistics
- Factoring Companies Statistics
- Factor-based Products Currently Making Up AUM Worldwide
- Key Preferences and Trends
- Challenges and Concerns
- Financial Factoring Regulations
- Recent Developments
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Factoring Statistics: Factoring is a financial transaction where businesses sell their accounts receivable to a third party, known as a factor, at a discount, allowing for immediate cash flow.
There are two primary types: recourse and non-recourse factoring, which determine liability for unpaid invoices.
The process involves application, approval, and funding, providing businesses with benefits such as improved cash flow, credit risk management, and outsourced collections without incurring debt. However, factors charge fees based on invoice amounts and payment timelines, which can vary.
With the growth of alternative financing and advancements in technology, factoring is becoming increasingly popular among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) seeking quick access to capital while maintaining operational flexibility.

Editor’s Choice
- The global factoring market revenue is projected to reach USD 7,019.8 billion by 2033.
- Overall, the total factoring volume in North America reached EUR 92,800 million in 2023.
- Overall, the total factoring volume for the Asia Pacific region increased from EUR 555,536 million in 2016 to EUR 942,078 million in 2023
- Overall, the total factoring volume across Europe grew from EUR 1,844,721 million in 2020 to EUR 2,555,266 million in 2023, reflecting a total growth of 2.30%.
- In Poland, as of 2023, the total number of entities engaged in factoring operations amounted to 46. This total includes a predominant number of participants from the non-financial sector, comprising enterprises and natural persons, which accounted for 39 entities.
- In the United Kingdom, the outcome of factoring or invoice discounting applications for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) as of 2019 showed that a significant majority of respondents experienced positive results. Specifically, 76% of the SMEs reported that all their applications were successful, indicating a high level of accessibility to these financial services within the sector.
- In 2017, incumbents in India faced a variety of challenges when working with fintech companies, as reflected in the opinions of respondents. The most prominent challenge cited was the difference in business models, affecting 47% of respondents, which highlights the fundamental disparities in how traditional financial institutions and fintech startups operate.
Factoring Market Overview
Global Factoring Market Size Statistics
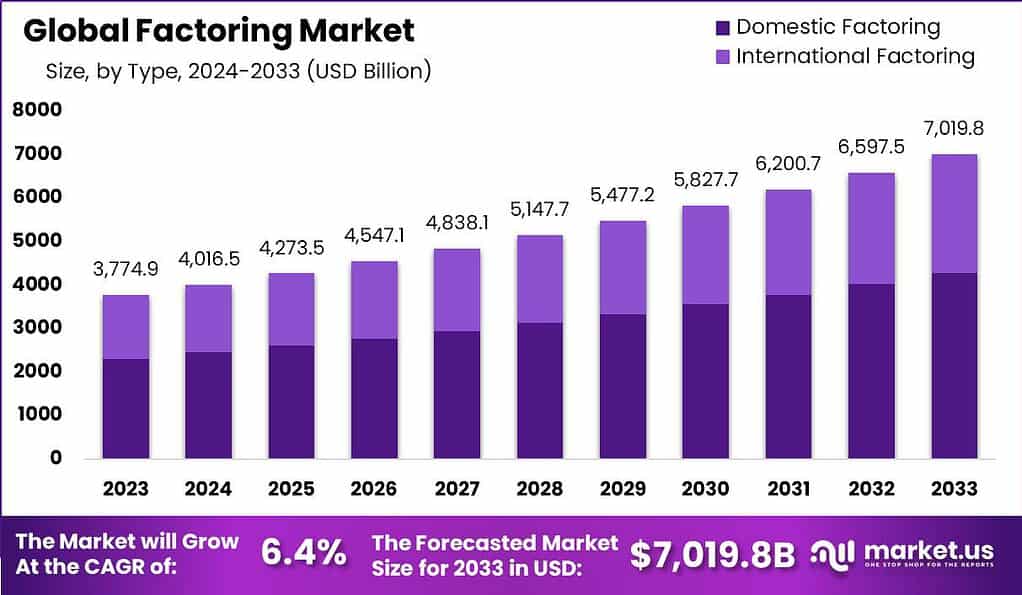
- The global factoring market is projected to exhibit a consistent growth trajectory from 2023 to 2033 at a CAGR of 6.4%.
- In 2023, the revenue stands at USD 3,774.9 billion, which is expected to rise to USD 4,016.5 billion by 2024.
- A continued upward trend is forecasted, with revenues reaching USD 4,273.5 billion in 2025, USD 4,547.1 billion in 2026, and USD 4,838.1 billion by 2027.
- The market’s expansion is set to sustain momentum, culminating in revenues of USD 5,147.7 billion in 2028, USD 5,477.2 billion in 2029, and USD 5,827.7 billion by 2030.
- The growth pattern persists, with projected revenues of USD 6,200.7 billion in 2031, USD 6,597.5 billion in 2032, and finally reaching USD 7,019.8 billion by 2033.
- This consistent increase highlights the robust nature of the global factoring market over the coming decade.
- The Global Reverse Factoring Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1,631.9 Billion By 2033, from USD 590.5 Billion in 2023
(Source: market.us)

Global Factoring Market Size – By Type Statistics
2023-2026
- The global factoring market is segmented into domestic and international components, exhibiting substantial growth from 2023 to 2026.
- The total market revenue is projected to increase from USD 3,774.9 billion in 2023, with domestic factoring at USD 2,302.69 billion and international factoring at USD 1,472.21 billion.
- By 2024, the market is anticipated to grow to USD 4,016.5 billion, with domestic factoring rising to USD 2,450.07 billion and international factoring to USD 1,566.44 billion.
- The trend continues, with total revenue reaching USD 4,273.5 billion in 2025, where domestic and international factoring account for USD 2,606.84 billion and USD 1,666.67 billion, respectively.
- The market is expected to expand further to USD 4,547.1 billion in 2026, with domestic factoring at USD 2,773.73 billion and international factoring at USD 1,773.37 billion.
2027-2033
- By 2027, the total market is projected to grow to USD 4,838.1 billion, split between USD 2,951.24 billion in domestic and USD 1,886.86 billion in international factoring.
- Continued growth is evident in 2028, with total revenue at USD 5,147.7 billion (domestic: USD 3,140.10 billion, international: USD 2,007.60 billion), increasing to USD 5,477.2 billion in 2029 (domestic: USD 3,341.09 billion, international: USD 2,136.11 billion).
- The upward trajectory is projected to carry the market to USD 5,827.7 billion in 2030, USD 6,200.7 billion in 2031, and USD 6,597.5 billion in 2032, culminating at USD 7,019.8 billion in 2033, with respective splits between domestic and international factoring demonstrating proportionate increases alongside the total market growth.
(Source: market.us)

- The factoring market share by region from 2019 to 2020 experienced varied rates of change across different areas, measured in euro billions.
- In Europe, the market decreased from EUR 1,976.2 billion in 2019 to EUR 1,844.7 billion in 2020, reflecting a decline of 6.70%.
- North America saw a more pronounced decrease of 23.20%, with market size reducing from EUR 86.7 billion to EUR 66.6 billion.
- South America experienced the most significant drop of 36.70%, going from EUR 132 billion to EUR 83.6 billion.
- In contrast, some regions witnessed growth or smaller declines. Africa saw a slight increase of 2.80%, with the market growing from EUR 24.6 billion in 2019 to EUR 25.2 billion in 2020.
- The Asia-Pacific region also experienced growth, albeit modest, with an increase of 1.40% from EUR 687.6 billion to EUR 697.1 billion.
- The Middle East, however, experienced a decrease of 4.20%, with the market shrinking from EUR 9.9 billion to EUR 9.5 billion.
- Overall, the total factoring market declined by 6.50% from EUR 2,917.11 billion in 2019 to EUR 2,726.73 billion in 2020.
(Source: FCI Report)

Factoring Volume Statistics – By Region Statistics
North America
- The total factoring volume in North America, measured in millions of EUR, has seen varied trends over the last seven years, spanning from 2016 to 2023.
- In Canada, the factoring volume showed fluctuations, beginning at EUR 5,609 million in 2016, slightly decreasing to EUR 5,392 million in 2017, and then significantly dropping to EUR 2,280 million in 2018.
- The volume then moderately recovered to EUR 2,985 million in 2019, followed by a dip to EUR 2,448 million in 2020 and a subsequent rise to EUR 2,700 million in 2021, stabilizing at EUR 3,100 million in both 2022 and 2023, with 0% growth in the last reported year.
- In contrast, the United States exhibited a different pattern. Starting with EUR 89,463 million in 2016, the volume saw a slight decrease to EUR 87,000 million in 2017 and a minor increase to EUR 87,821 million in 2018. A drop occurred to EUR 83,757 million in 2019, followed by a more significant fall to EUR 64,150 million in 2020.
- However, a sharp recovery was noted in 2021, with the volume reaching EUR 94,300 million, surging to EUR 100,800 million in 2022, and then descending again to EUR 89,700 million in 2023, marking an 11% decline.
- Overall, the total factoring volume for North America began at EUR 95,072 million in 2016, decreased over the years to EUR 66,598 million in 2020, but rebounded to EUR 97,000 million in 2021, peaking at EUR 103,900 million in 2022, and then slightly decreased to EUR 92,800 million in 2023, reflecting an overall decline of 10.70% over the period.
(Source: FCI Report)

Asia Pacific
- The factoring volume in the Asia Pacific region, expressed in millions of EUR, has demonstrated diverse trends across various countries over the last seven years, spanning from 2016 to 2023.
- Australia’s factoring volume has remained stable at EUR 47,658 million from 2017 onwards, showing no variation and maintaining a steady figure of EUR 54,330 million from 2018 through 2023.
- China experienced substantial growth, starting at EUR 301,635 million in 2016 and escalating dramatically to EUR 634,574 million by 2023, marking a growth rate of 10%.
- Hong Kong, however, faced a decline, with the volume decreasing from EUR 42,676 million in 2016 to EUR 35,920 million in 2023, a significant reduction of 20.20%.
- India showed remarkable growth, starting from a modest EUR 3,881 million in 2016 and soaring to EUR 17,378 million by 2023, reflecting a growth rate of 10.20%.
- Japan’s factoring volume also grew, rising from EUR 49,466 million in 2016 to EUR 60,622 million in 2023, which translates to a 5.80% increase.
- South Korea’s volume, however, remained unchanged at EUR 25,604 million from 2020 through 2023 after initial fluctuations.
- Overall, the total factoring volume for the Asia Pacific region increased from EUR 555,536 million in 2016 to EUR 942,078 million in 2023, indicating a cumulative growth of 6.90% over the period.
- This reflects varying economic dynamics within the region, with some countries experiencing robust growth while others faced stagnation or decline.
(Source: FCI Report)

Europe
- The total factoring volume in Europe, expressed in millions of EUR, has shown varied growth across different countries from 2020 to 2023.
- Belgium’s factoring volume exhibited significant growth, rising from EUR 81,716 million in 2020 to EUR 135,734 million in 2023, marking a growth rate of 9.30%.
- France also saw an increase, with volumes rising from EUR 323,567 million in 2020 to EUR 426,600 million in 2023, a more modest growth of 1.20%.
- Germany’s factoring market expanded from EUR 275,000 million in 2020 to EUR 384,444 million in 2023, reflecting a growth rate of 3.10%. Italy showed a slight growth, with the volume increasing from EUR 234,842 million in 2020 to EUR 298,678 million in 2023, which translates to a 0.90% increase.
- The Netherlands experienced a 3% growth, with volumes growing from EUR 113,758 million in 2020 to EUR 168,528 million in 2023.
- Conversely, Russia observed a decline in its factoring volume, decreasing from EUR 42,302 million in 2020 to EUR 78,299 million in 2023, a reduction of 5.20%. Spain’s factoring volume grew by 5%, from EUR 182,264 million in 2020 to EUR 270,393 million in 2023.
- The United Kingdom also experienced growth, with the factoring volume increasing from EUR 272,677 million in 2020 to EUR 363,182 million in 2023, marking a growth rate of 2.70%.
- Overall, the total factoring volume across Europe grew from EUR 1,844,721 million in 2020 to EUR 2,555,266 million in 2023, reflecting a total growth of 2.30%. This growth highlights the varying economic conditions and market dynamics within different European countries.
(Source: FCI Report)

Factoring Turnover – By Region Statistics
Africa
- The factoring turnover in Africa in 2023, expressed in millions of EUR, varies significantly across different countries.
- In Egypt, the total factoring turnover reached EUR 1,287.0 million, comprised of EUR 1,102.0 million from domestic transactions and EUR 185.0 million from international dealings.
- Mauritius reported a smaller factoring market with a total turnover of EUR 325.0 million, split between EUR 250.0 million domestically and EUR 75.0 million internationally.
- Morocco displayed a more substantial turnover at EUR 2,350.0 million, with EUR 2,200.0 million coming from domestic factoring and EUR 150.0 million from international activities.
- South Africa dominated the regional factoring market with a significant turnover of EUR 42,627.68 million, overwhelmingly from domestic sources at EUR 42,490.19 million and a minor contribution from international factoring at EUR 137.48 million.
- Tunisia, on the other hand, had a total factoring turnover of EUR 392.0 million, with EUR 375.0 million from domestic operations and EUR 17.0 million internationally.
- This distribution reflects diverse market dynamics and the varying emphasis on domestic versus international factoring across the African continent.
(Source: FCI Report)

Asia Pacific
- The factoring turnover in the Asia Pacific region in 2023, expressed in millions of EUR, showcases significant variation across countries in both domestic and international sectors.
- In Australia, the total factoring turnover is EUR 54,330.00, with the domestic sector accounting for EUR 54,319.00 and a minimal international contribution of EUR 11.00.
- China stands out with a massive total turnover of EUR 634,573.50, driven by EUR 519,950.51 in domestic factoring and EUR 114,622.99 from international sources.
- Hong Kong reported a total of EUR 35,920.00, with domestic factoring at EUR 10,000.00 and a substantial international portion of EUR 25,920.00.
- India’s total factoring turnover reached EUR 17,378.41, with the majority coming from domestic activities at EUR 16,378.41 and a smaller international input of EUR 1,000.00.
- Japan displayed a total turnover of EUR 60,622.00, heavily dominated by domestic factoring at EUR 59,000.00, complemented by EUR 1,622.00 internationally.
- South Korea’s total factoring turnover amounted to EUR 25,604.00, with domestic factoring contributing EUR 16,387.00 and international EUR 9,217.00.
- Singapore shows a balanced contribution with a total turnover of EUR 60,000.00, split between EUR 25,000.00 domestically and EUR 35,000.00 internationally.
- Taiwan has a total turnover of EUR 43,000.00, with domestic factoring at EUR 11,000.00 and a significant international contribution of EUR 32,000.00.
- This data reflects a dynamic factoring market in the Asia Pacific region with varying degrees of domestic and international engagement across different countries.
(Source: FCI Report)

Europe
- The factoring turnover across various European countries in 2023, expressed in millions of EUR, highlights a diverse landscape in terms of domestic and international contributions for the year.
- Austria reported a total factoring turnover of EUR 36,463.00, with EUR 15,966.77 from domestic operations and EUR 20,496.23 internationally. Denmark saw a total of EUR 19,494.00, nearly evenly split between domestic at EUR 10,392.00 and international at EUR 9,102.00.
- France’s factoring market was substantial, with a total turnover of EUR 426,600.00, derived from EUR 275,300.00 domestically and EUR 151,300.00 internationally.
- Germany also had a notable factoring volume totalling EUR 384,443.81, with EUR 275,865.37 from domestic and EUR 108,578.44 from international sources. Italy, with a total of EUR 298,678.15, had EUR 232,219.20 domestically and EUR 66,485.95 internationally.
- Poland’s factoring market stood out, particularly with a significant domestic contribution of EUR 87,047.61 against an international total of EUR 16,441.58, amounting to a total turnover of EUR 103,489.19.
- Portugal reported a total turnover of EUR 44,193.48, majorly domestic at EUR 38,495.19, with a smaller international contribution of EUR 5,698.29. Spain saw a turnover of EUR 270,393.00, consisting of EUR 233,005.00 domestically and EUR 37,388.00 internationally.
- The United Kingdom reported a total factoring turnover of EUR 363,181.64, with a robust domestic component of EUR 340,087.45 and an international part of EUR 23,094.18.
- This breakdown reflects the dynamic and varied nature of the factoring market across Europe, with each country displaying unique proportions of domestic and international factoring activities.
(Source: FCI Report)

North America
- The factoring turnover in North America, presented in millions of EUR, reflects significant domestic activity with a more modest international engagement for the year.
- In Canada, the total factoring turnover amounted to EUR 3,100 million, with EUR 1,850 million from domestic operations and EUR 1,250 million from international transactions.
- The United States showed a much larger scale of factoring activity, totalling EUR 89,700 million, overwhelmingly dominated by domestic factoring, which contributed EUR 85,700 million, while international factoring accounted for EUR 4,000 million.
- Combining both countries, the total factoring turnover for North America reached EUR 92,800 million. This total was primarily driven by domestic activities, amounting to EUR 87,550 million, and complemented by international activities contributing EUR 5,250 million.
- This highlights the significant reliance on domestic factoring operations within the North American market, with international factoring playing a lesser, albeit important, role in the region’s overall factoring economy.
(Source: FCI Report)

Factoring Across Various Sectors Statistics
- The total factoring value in the Netherlands from the first half of 2018 to the first half of 2023, segmented by key sectors and expressed in million euros, illustrates a significant trend of growth across various industries.
- In the first half of 2018, the wholesale trade sector reported a factoring value of 24,250 million euros, which steadily increased, reaching 45,796 million euros by the first half of 2023.
- The industry sector also saw a rise from 12,786 million euros in the first half of 2018 to 19,198 million euros in the first half of 2023.
- The transportation sector experienced growth from 4,004 million euros in H1 2018 to a peak of 6,092 million euros in H2 2022, slightly decreasing to 5,806 million euros by H1 2023.
- Business services factoring value began at 2,572 million euros in H1 2018, nearly doubling to 4,637 million euros by H1 2023.
- The “other sectors” category started at 6,191 million euros in H1 2018 and saw significant growth, reaching 11,211 million euros by H1 2023.
- These figures demonstrate a robust and expanding factoring market in the Netherlands, with substantial growth in almost all sectors, particularly notable in wholesale trade and business services over the observed period.
(Source: Statista)

Factoring Debt Statistics
Relevance of Debt Financing for SMEs
- The relevance of debt financing for SMEs in the Netherlands has shown a fluctuating trend from 2014 to 2020, as indicated by the share of respondents who consider it significant.
- In 2014, a substantial 80% of respondents recognized the importance of debt financing.
- This perception slightly increased over the next two years, reaching 81% in 2015 and peaking at 83% in 2016.
- However, a gradual decline was observed after that, with the percentage dropping to 82% in 2017, then further to 77% in 2018, and stabilizing somewhat at 78% in 2019.
- By 2020, the proportion of respondents acknowledging the importance of debt financing for SMEs decreased to 74%, reflecting a notable decline over the latter half of the decade.
- This trend suggests shifting sentiments or changing conditions that might be influencing SMEs’ reliance on or access to debt financing within the country.
(Source: Statista)

Debts Purchased by Factoring Entities Statistics
- The value of debts purchased by factoring companies in Poland has seen substantial growth from 2020 to 2023, as measured in million zloty.
- In 2020, the total debts purchased amounted to 308,975 million zloty. This figure increased significantly to 468,263 million zloty in 2022 and further rose to 499,995 million zloty in 2023.
- Breaking it down by type, national factoring forms the bulk of the activity. In 2020, national factoring accounted for 259,804 million zloty, which grew to 413,871 million zloty in 2022 and 447,652 million zloty in 2023.
- Within national factoring, recourse transactions, where the factor has recourse to the seller for debts that cannot be collected, increased from 67,762 million zloty in 2020 to 98,408 million zloty in 2023 after peaking at 102,241 million zloty in 2022.
- Non-recourse factoring, where the factor assumes the risk of bad debts, also showed growth from 125,070 million zloty in 2020 to 237,862 million zloty in 2023, with 2022 recording 215,027 million zloty.
- International factoring, though smaller in volume compared to national factoring, increased from 49,171 million zloty in 2020 to 52,343 million zloty in 2023, despite a slight decrease from 54,365 million zloty in 2022.
- These figures illustrate a robust expanding trend in both national and international factoring markets in Poland over the observed period.
(Source: Statista)

Overdue Debt and Provisions for Factoring Transactions Statistics
- The overdue debt and provisions for factoring transactions in Russia from July 1, 2019, to July 1, 2021, showed notable fluctuations in billion Russian rubles.
- Initially, on July 1, 2019, the non-performing loans (NPL) were 90+ days overdue and stood at 14.7 billion rubles, with restructuring volume at a mere 0.4 billion rubles. This figure remained stable through October 1, 2019, with a slight increase in restructuring volume to 0.5 billion rubles.
- By January 1, 2020, the NPL had slightly increased to 14.8 billion rubles, and the restructuring volume had more than doubled to 1.2 billion rubles.
- Over the next quarter, the NPL rose marginally to 14.9 billion rubles by April 1, 2020, with restructuring volume reducing to 0.8 billion rubles.
- However, by July 1, 2020, a significant shift occurred as the NPL reached 15 billion rubles, and restructuring volume dramatically increased to 7.2 billion rubles, indicating heightened financial stress and efforts to manage debt.
- The trend continued with the NPL slightly increasing to 15.6 billion rubles by October 1, 2020, while restructuring volume grew further to 7.3 billion rubles.
- The start of 2021 saw a slight decline in both NPL, settling at 15.5 billion rubles, and restructuring volume reducing to 5.4 billion rubles by January 1.
- However, by April 1, 2021, while the NPL remained at 15.5 billion rubles, restructuring volume peaked at 14.9 billion rubles.
- Finally, by July 1, 2021, there was a noticeable reduction in NPL to 12.8 billion rubles, alongside a decrease in restructuring volume to 4.5 billion rubles, suggesting some stabilization or successful restructuring efforts in the factoring transaction landscape in Russia during this period.
(Source: Statista)

Factoring Funds Statistics
Sources of Financing the Factoring Activity Statistics
- The sources of financing for factoring activity in Poland from 2020 to 2023, measured in million zloty, have shown varied trends across different categories.
- In 2020, the total financing amounted to 42,543 million zloty, which increased significantly to 61,041 million zloty in 2022 and slightly further to 61,257 million zloty in 2023.
- Credits formed a substantial part of the financing, starting at 16,162 million zloty in 2020, rising to 29,236 million zloty in 2022, and slightly decreasing to 28,661 million zloty in 2023.
- Loans showed a decrease over the observed period, starting at 11,354 million zloty in 2020, dipping to 9,557 million zloty in 2022, and further decreasing to 9,440 million zloty in 2023.
- Corporate bonds exhibited a steady increase, beginning at 3,361 million zloty in 2020, growing to 4,478 million zloty in 2022, and expanding to 6,193 million zloty in 2023.
- Own funds or equity, another critical source, started at 9,885 million zloty in 2020, peaked at 15,557 million zloty in 2022, and then decreased to 14,308 million zloty in 2023.
- This data reflects the evolving landscape of financing sources for factoring activities in Poland, indicating an increased reliance on credits and corporate bonds over the years.
(Source: Statista)

Factoring Funds in Use Statistics
- The average factoring funds in use in the Netherlands from the first half of 2018 to the second half of 2022, categorized by revenue size, reveal notable trends and shifts over the period.
- Starting in the first half of 2018, companies with less than 10 million euros in revenue used an average of 510 million euros in factoring, which saw various fluctuations and ultimately increased to 403 million euros by the second half of 2022.
- For companies with revenues between 10 and 50 million euros, the average factoring usage began at 1,234 million euros in H1 2018 and experienced fluctuations before slightly increasing to 1,555 million euros by H2 2022.
- The category for companies with revenues between 50 and 100 million euros started at 798 million euros in factoring funds in use in H1 2018 and showed a general upward trend, reaching 1,391 million euros by H2 2022.
- The most significant increases were observed in companies with more than 100 million euros in revenue; starting with 2,454 million euros in H1 2018, the figure rose substantially to 4,688 million euros by H2 2022.
- This data indicates a growing reliance on factoring solutions, particularly among larger companies, reflecting broader economic trends, shifts in financing needs, and possibly the accessibility and attractiveness of factoring as a financing option in the Dutch market over these years.
(Source: Statista)

Factoring Companies Statistics
Entities Operating Factoring Statistics
- In Poland, as of 2023, the total number of entities engaged in factoring operations amounted to 46.
- This total includes a predominant number of participants from the non-financial sector, comprising enterprises and natural persons, which accounted for 39 entities.
- The remaining seven entities operating in the factoring domain were banks.
- This distribution underscores a significant involvement of non-financial entities in the Polish factoring market, indicating a diverse range of players facilitating credit and financing solutions outside traditional banking institutions.
(Source: Statista)

Portfolio of Factoring Companies Statistics
- The portfolio of factoring companies in Russia has shown significant growth from January 1, 2019, to January 1, 2024, measured in billion Russian rubles.
- Starting at 610.69 billion rubles at the beginning of 2019, there was a notable increase to 808.11 billion rubles by January 2020.
- The growth continued more aggressively through the following years, reaching 1,105.76 billion rubles by January 2021 and further expanding to 1,513.45 billion rubles by January 2022.
- However, there was a slight dip to 1,434.31 billion rubles by January 2023 before an impressive surge to 2,256.65 billion rubles by January 2024.
- This trajectory highlights a robust expansion in the scale of factoring operations within Russia, reflecting the growing acceptance and utilization of factoring services amidst fluctuating economic conditions.
- This upward trend, despite the temporary setback in 2023, indicates a strong and resilient factoring industry poised for continued growth.
(Source: Statista)

Share of Factoring Companies – By Share of Sector’s Total Assets Statistics
- In Belgium, the market share of the leading factoring companies in 2015 and 2016 demonstrated notable trends in the distribution of the sector’s total assets.
- BNP Paribas Fortis Factor remained a dominant player, although its share decreased slightly from 38.1% in 2015 to 37% in 2016.
- KBC Commercial Finance also saw a reduction in its market share, dropping from 29.7% in 2015 to 25.7% in 2016.
- ING Commercial Finance, however, experienced a marginal increase in its share, rising from 10.3% in 2015 to 10.9% in 2016.
- Belfius Commercial Finance’s share decreased from 11.2% in 2015 to 10.6% in 2016, reflecting a slight reduction in its market presence.
- Volkswagen Finance Belgium’s participation was noted at 7.4% in 2016, without comparable data from 2015.
- Factoring Service Center witnessed a decrease from 7.6% in 2015 to 5.7% in 2016.
- The category labelled as ‘Others’, representing smaller factoring firms, remained relatively stable, with a minor decrease from 3.1% in 2015 to 3% in 2016.
- This overview indicates shifts in market control among leading factoring firms, reflecting competitive dynamics and possibly varying client preferences or economic conditions influencing the sector.
(Source: Statista)

Profit and Loss of Non-Banking Factoring Companies Statistics
- The net profit and loss of non-banking factoring companies in Poland from 2018 to 2023 have demonstrated significant fluctuations and an overall upward trend, measured in thousands of zloty.
- Starting in 2018, these companies experienced a substantial loss amounting to 511,851 thousand zloty. However, the scenario shifted positively in the following years.
- In 2019, they recorded a net profit of 146,282 thousand zloty, which slightly decreased to 110,217 thousand zloty in 2020.
- By 2021, a notable increase in profitability was observed, with a net profit of 247,550 thousand zloty, which slightly decreased to 246,493 thousand zloty in 2022.
- The year 2023 marked a significant rise in profitability, with the companies achieving a net profit of 641,206 thousand zloty.
- This progression from a substantial loss in 2018 to a robust profit in 2023 highlights a remarkable recovery and growth trajectory for non-banking factoring companies in Poland over this period.
(Source: Statista)

Factor-based Products Currently Making Up AUM Worldwide
- The composition of assets under management (AUM) with factor-based products among professional investors worldwide has seen varied changes from 2020 to 2023.
- In 2020, 12% of investors had less than 5% of their AUM in factor-based products, a figure that remained steady into 2021, then dropped to 7% in 2022 and slightly increased to 9% in 2023.
- For those with 6-10% of their AUM in factor-based products, there was a decrease from 31% in 2020 to 24% by 2023, following a peak of 34% in 2021.
- The 11-20% range saw an increase from 40% in 2020 to 47% in 2022 before levelling back to 40% in 2023, indicating a fluctuating but significant interest in this investment level.
- Investors with more than 20% of their AUM in factor-based products were 11% in 2020, decreasing to 10% in 2021 and peaking at 17% in 2022 before settling at 12% in 2023.
- Notably, the proportion of investors uncertain about their percentage of AUM in factor-based products rose sharply from 2% in 2021 to 17% in 2023, highlighting increasing uncertainty or variability in reporting or decision-making processes concerning factor-based investment allocations over these years.
(Source: Statista)

Key Preferences and Trends
Factors Affecting Project Management Software Choice
- In the United States, the priorities affecting the purchase decision of project management software shifted notably between 2015 and 2019.
- In 2015, functionality was the most significant factor, influencing 40% of the decision-making, but this decreased to 36% by 2019.
- Ease of use, which was the second most critical factor in 2015 at 24%, saw a significant decline in its influence, dropping to just 10% in 2019.
- Price became increasingly important, rising from 9% in 2015 to 22% in 2019, making it a critical factor in the purchase decision by the end of the period.
- Customer support also saw an increase in importance, moving from 9% to 14%. Similarly, implementation and training considerations grew slightly in relevance, from 8% to 10%.
- Company reputation remained a relatively minor factor, with a slight decrease from 5% to 4%. Software popularity saw the most significant decline in importance, halving from 5% to just 2%.
- These shifts indicate a changing landscape in project management software acquisition, with a growing emphasis on cost and support over ease of use and popularity.
(Source: Statista)

Invoice Factoring Platform Users Statistics
- The user base of FinTech invoice factoring platforms in the United Kingdom showed steady growth from 2014 to 2020.
- Starting in 2014, the platform had approximately 1.88 million users.
- This number modestly increased year over year, reaching 1.95 million in 2015 and continuing to rise to 2.02 million by 2016.
- The growth continued at a gradual pace, with the user count reaching 2.09 million in 2017.
- By 2018, the number of users slightly increased to 2.13 million, and it saw a minimal rise to 2.15 million in 2019.
- The growth trajectory persisted into 2020 when the user potential reached approximately 2.17 million.
- This consistent increase over the years highlights the growing acceptance and reliance on FinTech solutions for invoice factoring in the UK market.
(Source: Statista)

Trends in Invoice Factoring Sales Statistics
- From the first quarter of 2016 to the first quarter of 2018, the quarterly sales volumes in factoring and invoice finance in the United Kingdom exhibited varied trends across different types of factoring.
- In the first quarter of 2016, domestic invoice discounting sales stood at 56,339 million GBP, which increased over the next few quarters, reaching a high of 62,114 million GBP in the fourth quarter of 2016.
- After a slight fluctuation, this figure somewhat stabilized, rounding off at 58,116 million GBP by the first quarter of 2018.
- Export invoice discounting started at 4,610 million GBP in the first quarter of 2016, gradually increasing each quarter to peak at 7,218 million GBP in the second quarter of 2017 before slightly retracting to 5,791 million GBP by the first quarter of 2018.
- Domestic factoring began at 4,480 million GBP and saw a gentle increase in most quarters, peaking at 5,052 million GBP in the fourth quarter of 2017 and then slightly decreasing to 4,713 million GBP in the first quarter of 2018.
- Export and import factoring was the least in volume, starting at 428 million GBP in the first quarter of 2016 and experiencing modest increases over the period, reaching 483 million GBP by the first quarter of 2018.
- Overall, these figures demonstrate a generally positive trajectory in the factoring and invoice finance sector, with all types seeing growth or stable performance over the observed period.
(Source: Statista)

Invoice Factoring Platforms Benchmarked Transactions Statistics
- The transaction value of the FinTech invoice factoring platforms sector in the United Kingdom from 2014 to 2020 showed a clear trend of growth in its market share, though it remained a small fraction of the total factoring market.
- Initially, in 2014, FinTech platforms held a mere 0.06% of the transaction value, dwarfed by the traditional factoring methods, which dominated at 99.90%.
- However, by 2015, the share of invoice factoring platforms doubled to 0.13%, indicating a burgeoning interest in FinTech solutions.
- The subsequent years saw more significant growth: the share jumped to 0.31% in 2016 and more than doubled again to 0.70% by 2017.
- Interestingly, despite traditional methods holding a steady grip on the market, peaking again at 99.90% in 2018, the FinTech platforms maintained their share of 0.70% through 2020.
- By the end of this period, the traditional factoring methods slightly reduced their share to 99.30%, the same level as in 2019 and 2020, showing some level of stabilization in the adoption of FinTech platforms in the factoring industry.
- This data underscores the gradual yet persistent penetration of FinTech into a domain traditionally dominated by conventional financial services.
(Source: Statista)

Factoring or Invoice Discounting Application Outcomes for SME Statistics
- In the United Kingdom, the outcome of factoring or invoice discounting applications for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) as of 2019 showed that a significant majority of respondents experienced positive results.
- Specifically, 76% of the SMEs reported that all their applications were successful, indicating a high level of accessibility to these financial services within the sector.
- In contrast, 15% of the SMEs noted that only some of their applications were approved, suggesting partial success in securing this type of financial support.
- A small fraction, 5%, reported that none of their applications were successful, highlighting challenges faced by a minority in accessing such financial mechanisms.
- Additionally, 3% of the SMEs had decisions pending on their applications at the time of the survey, indicating ongoing processes.
- This distribution underscores the varying degrees of success and challenges SMEs encounter when engaging with factoring or invoice discounting services in the UK.
(Source: Statista)

Challenges and Concerns
- In 2017, incumbents in India faced a variety of challenges when working with fintech companies, as reflected in the opinions of respondents.
- The most prominent challenge cited was the difference in business models, affecting 47% of respondents, which highlights the fundamental disparities in how traditional financial institutions and fintech startups operate.
- Regulatory uncertainty was also a significant concern, with 42% of respondents identifying it as a hurdle, pointing to the evolving regulatory landscape that often accompanies the rapid innovation in fintech.
- Operational challenges were equally significant, with 37% of respondents each citing differences in operational processes and IT security concerns, indicating that integrating new technologies and maintaining data security are critical issues.
- Differences in management and culture were noted by 32% of respondents, underscoring the cultural and procedural adjustments needed when traditional and modern financial practices meet.
- Required financial investments were a concern for 21% of the respondents, suggesting that the cost of technology adoption and integration can be a barrier.
- Other notable challenges included IT compatibility, differences in knowledge/skills, and other unspecified issues, each cited by 16% of respondents.
- These findings illustrate the multifaceted challenges that incumbents face when partnering with or adapting to fintech innovations, requiring adjustments in strategy, operations, and mindset.
(Source: Statista)

Financial Factoring Regulations
- The regulatory landscape for financial factoring is evolving globally with significant variations by country, influenced by efforts to harmonize practices while also addressing local market needs.
- The UNIDROIT Model Law on Factoring, adopted by many jurisdictions, aims to provide a unified legal framework to support the receivables finance industry, which is crucial for providing liquidity in various markets.
- In the United States, states like New York and Utah have implemented stringent regulations such as the NYCRR 600 / SB5470 and SB183, respectively, which mandate detailed disclosures and registration requirements for factoring companies to enhance transparency and protect stakeholders.
- Furthermore, the International Finance Corporation (IFC) has released guidelines recommending cohesive regulatory frameworks to support non-banking financial institutions in the factoring sector. These guidelines suggest best practices for policymakers and central banks to foster a supportive environment for factoring activities, which is essential for inclusive economic growth.
- The BCR Publishing World Factoring Yearbook 2023 illustrates that such regulations are vital for maintaining orderly market conditions and safeguarding the interests of all parties involved in factoring transactions across 38 countries.
- Each country’s approach to regulation reflects its unique financial landscape and the maturity of its factoring market. Thus, companies and stakeholders must stay informed of both global trends and local requirements to navigate this complex regulatory environment effectively.
(Source: UNIDROIT, Сapflow Funding, IFC, FCI)
Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- BNP Paribas acquires FinTech firm: In 2023, BNP Paribas, a leading European banking group, acquired a FinTech company specializing in digital factoring solutions for $150 million. This acquisition aims to enhance BNP Paribas’ capabilities in offering faster and more efficient factoring services for small and medium-sized enterprises.
- eCapital acquires CNH Industrial Capital’s factoring portfolio: In early 2024, eCapital, a leading factoring company in North America, completed the acquisition of CNH Industrial Capital’s factoring portfolio valued at $200 million. This move is expected to expand eCapital’s reach in the industrial sector.
New Product Launches:
- Tungsten Network launches digital factoring platform: In late 2023, Tungsten Network launched a new cloud-based factoring platform aimed at providing quick and easy access to cash for small businesses. This platform integrates AI to automate the factoring process, reducing approval time by 30%.
- HSBC introduces ESG-linked factoring: In early 2024, HSBC launched an ESG-linked factoring solution that offers businesses financial incentives for meeting sustainability goals. This innovative product is aimed at promoting environmentally responsible practices within the factoring industry.
Funding:
- MarketFinance secures $280 million in funding: In mid-2023, MarketFinance, a UK-based factoring and invoice finance company, raised $280 million in funding to expand its operations and improve its digital factoring services. This funding round was led by venture capital firms aiming to disrupt traditional financial services.
- BlueVine raises $60 million for SMB factoring solutions: In 2024, BlueVine, a financial technology company focused on providing working capital to small and medium-sized businesses, secured $60 million to enhance its digital factoring solutions.
Technological Advancements:
- AI-powered risk assessment in factoring: AI is increasingly being integrated into factoring platforms for real-time credit risk analysis. By 2025, it is projected that 40% of factoring transactions will leverage AI to improve risk assessment and reduce defaults.
- Blockchain technology in factoring: Blockchain is being adopted to enhance transparency and security in factoring transactions. By 2026, 20% of global factoring solutions are expected to utilize blockchain technology to streamline payment processes and reduce fraud.
Conclusion
Factoring Statistics – Factoring offers businesses a valuable financial alternative by providing immediate cash flow through the sale of accounts receivable to a third party at a discount.
This method enhances operational management by freeing up tied capital, reducing overhead associated with collections, and mitigating credit risk, which is especially beneficial for SMEs.
Factoring agreements are scalable and flexible, adapting to changing business needs, and often include additional services like credit management.
However, while factoring can relieve financial and administrative burdens, allowing companies to focus more on growth and customer service, it is generally more costly than traditional financing.
Businesses must also consider potential impacts on customer relationships due to the factor’s collection practices.
Factoring is a strategic tool that, when used judiciously, can significantly support business operations and expansion.
FAQs
Factoring is a financial transaction where a business sells its accounts receivable (invoices) to a third party, called a factor, at a discount in exchange for immediate cash. This helps businesses improve their cash flow without waiting for customers to pay their invoices.
Unlike a loan, factoring does not create debt or require collateral in the traditional sense. Instead, the creditworthiness is based on the financial strength of the invoice debtors, not the company selling the invoices.
The key benefits include immediate access to cash, reduction in administration related to accounts receivable, risk reduction related to customer non-payment, and the ability to manage and stabilize cash flow more effectively.
The primary disadvantages include potentially high costs compared to other types of financing, the possibility of damaging customer relationships due to aggressive collection tactics by factors, and dependence on the financial health of customers.
Factoring is particularly beneficial for businesses with long invoice payment cycles, such as those in manufacturing, wholesale, textiles, and staffing agencies. It is also useful for fast-growing companies that need immediate funding to capitalize on new opportunities.


