Table of Contents
Introduction
Industrial robotics services encompass a range of activities that support the operational efficiency of robots in various industries. These services include system integration, programming, maintenance, and repair, all tailored to ensure that industrial robots perform optimally. By catering to different sectors such as automotive, electronics, and heavy machinery, these services help businesses streamline production processes and reduce downtime.
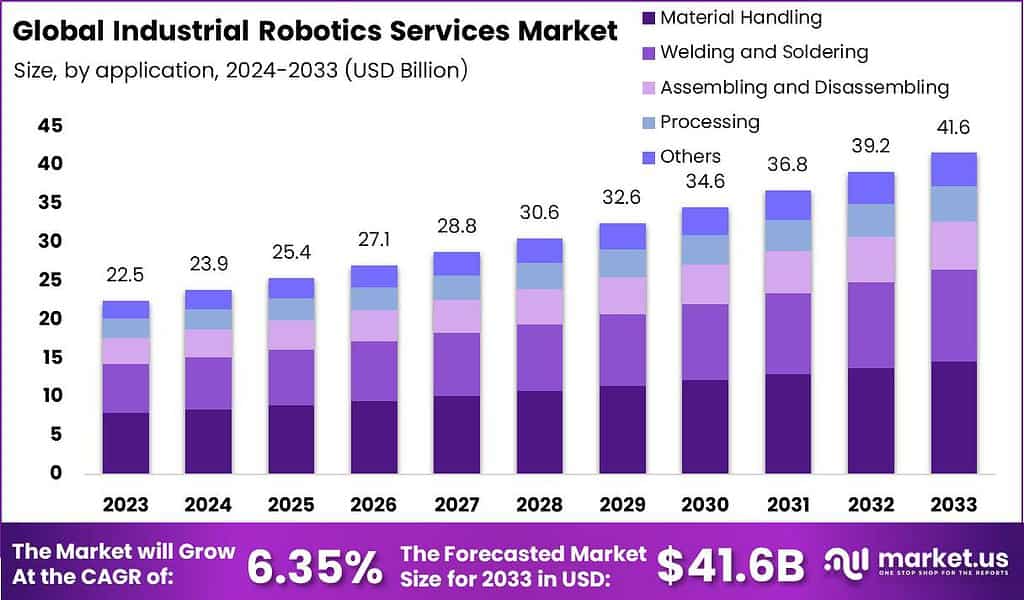
As per the latest insights from Market.us, The Global Industrial Robotics Services Market is on track for significant expansion. By 2033, it’s projected to reach a market size of USD 41.6 Billion, up from USD 22.5 Billion in 2023. This growth represents an annual increase of 6.35% over the ten-year forecast period. In 2023, the Asia-Pacific region led this market, accounting for 35.4% of the global share, translating to revenues of USD 7.9 Billion. This dominance highlights the region’s pivotal role in the industrial robotics services sector.
The Industrial Robotics Services Market is experiencing robust growth as industries increasingly adopt automation to enhance productivity and reduce labor costs. This market is crucial for the deployment, operation, and maintenance of robotic systems across manufacturing facilities worldwide.
The market is driven by the rising demand for automation in manufacturing processes and the ongoing need for operational efficiency. Technological advancements in robotics and the integration of AI and machine learning technologies are also significant growth stimulators. Additionally, the push towards improving workplace safety and the ability to perform complex tasks with precision are accelerating the adoption of industrial robotics services.
There is a high demand for these services in industries that require precision and efficiency, such as automotive, electronics, and food processing. The demand is particularly strong in regions that are hubs for manufacturing and technological innovation, like Asia-Pacific and North America. New developments in robotics, such as collaborative robots (cobots) and mobile robots, open up numerous market opportunities. These innovations allow robotics services to expand into new sectors, including healthcare and logistics, providing more tailored solutions and expanding their market reach.
The expansion of the market is supported by the increasing investment in R&D by key players aiming to diversify their service offerings and improve their competitive edge. Globalization of trade and the expansion of manufacturing capabilities in emerging economies also contribute to the broadening scope of the market, making industrial robotics services integral to modern industrial strategies.
Key Takeaways
- The Industrial Robotics Services Market is poised for significant growth, projected to reach a value of USD 41.6 billion by 2033, up from USD 22.5 billion in 2023. This growth represents a steady CAGR of 6.35% from 2024 to 2033.
- A standout in this market is the Material Handling segment, which accounted for 31.8% of the market share in 2023. The demand for this segment is on the rise, primarily due to industries increasingly adopting automated systems to boost efficiency in manufacturing and logistics.
- The Automotive sector is another major contributor, capturing over 37% of the market in 2023. Automation via robotics has become crucial in this sector, enhancing both the precision and efficiency of automotive production processes.
- On a regional basis, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region dominates the market, holding 35.4% of the total share with revenues of USD 7.9 billion in 2023. The region’s robust manufacturing capabilities and escalating automation investments significantly contribute to this leading position.
Industrial Robotics Services Statistics
- In 2023, North America observed a sharp 30% decline in industrial robot orders. Only 31,159 robots were ordered, a significant drop compared to 44,196 in 2022 and 39,708 in 2021. This downturn reflects a broader hesitation in investments, possibly influenced by economic conditions.
- Despite the decline, a strong interest in robotics persists. An impressive 88% of companies indicate plans to integrate more robotics into their operations. This demonstrates a continuing commitment to automation as a long-term investment for increasing efficiency and productivity.
- Worldwide, approximately 3 million industrial robots are currently operational. Annually, around 400,000 new robots are introduced to the market, supporting various industries in enhancing their operational capacities.
- The automotive sector remains the largest user of industrial robots, absorbing 33% of the global supply. However, other sectors are catching up. The electronics industry, for instance, is projected to see an annual growth of 17% in robot adoption. Meanwhile, the food and beverage industry anticipates a 29% rise in robot usage by 2025.
- The global industrial robotics market is valued at $43.8 billion. For North America, the sector’s revenue is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.67% through 2026, signaling a robust recovery phase and potentially high returns on robotics investments.
- In the U.S., there is a robot density of 228 units per 10,000 employees, which underscores the significant role automation plays in the American industrial landscape. Furthermore, the U.S. is home to about 132,500 robotics engineers, highlighting the skilled workforce driving this technological advancement.
- Honda Motor stands out as the world’s largest robotics company, with revenues reaching $142.4 billion and nearly 220,000 employees globally, illustrating the scale and impact of robotics within major industrial players.
Biggest Robotics Companies in the World
| Company | Revenue (In Billions Usd) | Market Cap (In Billions Usd) |
|---|---|---|
| Honda Motor | 142 | 42 |
| Siemens AG | 97 | 75 |
| Sony | 79 | 78 |
| Denso Corp | 47 | 227 |
| Midea Group | 39 | 52 |
Demographic Factors Affects
Demographic factors significantly influence the industrial robotics services market. One key demographic aspect is the aging workforce in industrial sectors, especially in developed regions like Europe and North America. As the workforce ages, there is a rising demand for automation to counteract the decreasing labor pool, particularly in manufacturing and production industries. This trend is driving the adoption of robotics to maintain production rates and reduce the physical strain on older workers.
Another demographic factor is the urbanization rate, which impacts where companies decide to establish new factories and subsequently affects the deployment of industrial robots. As urban centers grow, they offer better infrastructure and connectivity, making them attractive for new industrial setups that incorporate advanced robotic solutions. Additionally, educational attainment and technical skills levels across different regions also influence the adoption of industrial robotics. Areas with higher levels of technical education and training programs are quicker to adopt and integrate advanced robotic technologies, as they have a workforce capable of managing and maintaining these systems.
Gender dynamics also play a role. Historically, industries like manufacturing have been male-dominated. With increasing gender diversity and inclusion, there’s a push to design and implement robotic solutions that can accommodate a more diverse workforce, potentially altering demand dynamics in the robotics services sector.
Economic Environments Affects
Economically, the industrial robotics services market is affected by several factors, such as investment in technology and the overall health of the global economy. During periods of economic growth, companies are more likely to invest in robotics to enhance productivity and efficiency. For instance, the rise in Industry 4.0 investments, characterized by increased automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies, has significantly propelled the growth of robotics services.
Global trade dynamics also influence the market. Trade policies that encourage open markets and lower tariffs on robotic components can decrease costs and boost market growth. Conversely, restrictive trade policies can increase costs and slow down market expansion. Currency fluctuations and economic stability in key markets like China, the U.S., and Germany also play crucial roles, as these countries are major players in both the production and adoption of industrial robotics.
Furthermore, the cost of labor is a critical economic factor. In regions where labor costs are high, there’s a stronger incentive for companies to invest in robotics to reduce operational costs. Conversely, in regions with lower labor costs, the adoption of robotics might be slower. The overall economic environment, including factors such as interest rates and corporate profits, also dictates how much companies are willing to invest in new technologies like industrial robotics.
Emerging Trends
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Industrial robots are being designed to consume less energy, which not only reduces operating costs but also supports sustainability targets within manufacturing. Innovations such as robots that convert kinetic energy back into electricity are becoming more commonplace, reflecting a broader push toward greener production technologies.
- Rise of Reshoring: The trend of reshoring manufacturing operations is gaining traction, driven by the need for proximity to consumer markets and the rising costs of overseas labor. Robotics plays a crucial role in this shift by enabling high-precision manufacturing such as microchip production and battery assembly close to market locations, making operations more cost-effective and sustainable.
- Ease of Use: Robotics technology has become more accessible with the development of no-code and low-code platforms that simplify robot programming. This democratization is making robotics more appealing to a broader range of industries and skill levels, encouraging wider adoption.
- Integration of AI and Automation: Artificial intelligence is becoming integral to robotics, enhancing the capabilities of robots to handle variability and unpredictability in production environments. This integration supports functions like predictive maintenance and quality control, and is facilitated by advancements in cloud computing and big data analytics.
- Robotics as a Service (RaaS): The RaaS model is expanding, offering businesses the ability to adopt robotics solutions on a subscription basis. This approach lowers the barrier to entry for using advanced robotics by minimizing upfront capital investments and providing scalability to meet changing business needs.
Top Use Cases
- Manufacturing and Assembly: Robots are increasingly used in manufacturing to perform complex assembly tasks with high precision and repeatability, reducing human error and increasing production efficiency.
- Warehouse Automation: Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are revolutionizing warehouse operations by automating tasks such as picking, packing, and sorting. This automation improves operational efficiency and reduces costs associated with manual labor.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, robotics is enhancing the precision of surgeries and enabling remote operations, which improves patient outcomes and extends the reach of specialized medical care.
- Agriculture: Robots are used in agriculture for tasks such as planting, harvesting, and pest control. They help increase yield and reduce the reliance on human labor, which is particularly valuable in the context of global labor shortages.
- Service Industry: In the service sector, robots are employed for jobs ranging from customer service to cleaning and maintenance tasks. This helps businesses manage costs and improve service delivery in environments like hotels, airports, and public spaces.
Major Challenges
- High Initial Costs and Return on Investment: Many companies face significant challenges with the high initial costs associated with purchasing and implementing robotic systems. There is also a concern about the actual return on investment these technologies may provide, which can be a deterrent to their adoption.
- Integration and Compatibility Issues: Integrating new robotic technologies with existing systems can be problematic. Many companies struggle with the compatibility of new robots with their current infrastructure, which can hinder wider adoption.
- Skilled Worker Shortage: The shortage of skilled workers capable of operating and maintaining sophisticated robotic systems remains a persistent issue. As robotics technology advances, the gap in required technical skills grows wider.
- Safety and Cybersecurity Concerns: As industries increasingly rely on robotics, concerns about the safety of these systems and their vulnerability to cyberattacks have become more pronounced. Ensuring the safety of workers and protecting systems against cyber threats are crucial for the broader acceptance of robotics in manufacturing.
- Economic and Market Fluctuations: Economic downturns and market uncertainties can drastically affect the investment in new technologies. With industrial orders for robots dropping significantly in some regions, it’s clear that economic factors play a critical role in the deployment of robotics.
Top Opportunities
- Labor Efficiency and Automation: Robotics offers a significant opportunity to fill labor shortages and improve productivity. Automation allows companies to maintain output with fewer workers, which is increasingly important in industries facing labor shortages.
- Advancements in AI and Machine Learning: The integration of AI with robotics is transforming manufacturing processes. AI enables robots to perform complex tasks with greater efficiency and precision, from material handling to predictive maintenance.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Robotics can play a key role in sustainable manufacturing practices. Companies are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices, and robots can contribute by reducing waste, optimizing energy use, and improving material recycling.
- Reshoring of Manufacturing: With rising labor costs abroad and the decreasing costs of automation, there is a growing trend of reshoring manufacturing operations. Robotics can make domestic production more feasible and economically viable, reducing dependency on overseas operations.
- Expansion into New Industries and Applications: Robotics is no longer limited to traditional manufacturing sectors. New applications in healthcare, agriculture, and services are expanding the market for robotics, offering new avenues for growth and innovation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Industrial Robotics Services market is positioned for robust growth, driven by the continual advancements in automation technologies and the increasing need for operational efficiency across industries. While challenges such as high initial costs and the requirement for skilled labor present hurdles, the numerous opportunities in emerging markets and evolving technological landscapes offer a promising horizon. As industries worldwide strive to enhance precision and productivity, the demand for industrial robotics services is expected to soar, underscoring a future where automation plays a pivotal role in shaping business operations.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



