Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Editor’s Choice
- Global EdTech Market Overview
- Global Smart Learning Market Overview
- Frequently Used Teaching Applications and Tools
- Global Interactive Whiteboard Market Statistics
- Use of Interactive Whiteboard Among Students Statistics
- Interactive Whiteboard/ Smart Board Statistics
- Collaborative Whiteboard Industry
- Funding Sources for Interactive Whiteboard Statistics
- Interactive Whiteboard Preferences Statistics
- Advantages and Benefits
- Concerns and Challenges
- Key Innovations and Developments in Interactive Whiteboard Technology Statistics
- Recent Developments
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Interactive Whiteboard Statistics: Interactive whiteboards (IWBs) are large touchscreen displays connected to computers and projectors designed to facilitate collaborative learning and presentations.
They allow users to interact directly with displayed content through touch or a stylus, supporting annotation, multimedia integration, and simultaneous interaction.
Widely used in educational settings, corporate training, and presentations. IWBs enhance engagement and flexibility while enabling easy access to digital resources.
However, considerations such as technical training, maintenance, and initial costs are essential for effective implementation. Overall, IWBs significantly improve communication and collaboration across various environments.

Editor’s Choice
- In the Netherlands in 2017, teachers frequently used a variety of teaching applications and tools. As evidenced by the distribution of their preferences. Interactive whiteboards led to a substantial 77% of teachers using them.
- The global interactive whiteboard market revenue reached USD 4.2 billion in 2023.
- By 2032, the market is forecasted to grow to $7.6 billion. With portable and fixed projections reaching $4.20 billion and $3.40 billion, respectively.
- The global interactive whiteboard market is segmented by technology. With resistive membrane technology holding the largest market share at 33%.
- In the 2017/18 academic year, the distribution of lower secondary level students per interactive whiteboard in selected European countries showed a diverse range. France exhibited the highest number of students per whiteboard, with a significant count of 176 students.
- According to students, the main benefits of interactive whiteboards (IWBs) encompass a range of educational enhancements. The most significant advantage was noted by 23.5% of students. It is access to the Internet, which provides a wealth of information and resources at their fingertips.
- According to teachers, the main challenges associated with using interactive whiteboards (IWBs) are predominantly technical. A significant 70.60% of teachers report facing technical problems. Which include issues such as system malfunctions, software glitches, and connectivity troubles.
Global EdTech Market Overview
Global EdTech Market Size
- The projected growth of the global EdTech market is robust. With revenue forecasts indicating a consistent upward trajectory from 2022 through 2032.
- In 2022, the market began with a revenue base of USD 220.5 million.
- By 2023, this figure is expected to rise to USD 251.1 million. Followed by an increase to USD 286.1 million in 2024.
- The growth momentum continues, with revenues expected to reach USD 325.8 million in 2025 and further expand to USD 371.1 million in 2026.
- The upward trend persists, with projections for 2027 showing a revenue of USD 422.7 million, and by 2028, revenues are anticipated to soar to USD 481.4 million.
- The market is expected to grow significantly in the subsequent years. With revenues projected at USD 548.4 million in 2029, USD 624.6 million in 2030, USD 711.4 million in 2031, and finally reach USD 810.3 million by 2032.
- This consistent increase underscores the burgeoning demand and expanding influence of educational technologies globally.
(Source: market.us)

Global EdTech Market Size – By Deployment Mode
- The global EdTech market size, categorized by deployment mode, exhibits significant growth over the forecast period from 2022 to 2032.
- In 2022, the total revenue for the EdTech market was estimated at USD 220.5 million. With on-premise solutions generating USD 156.1 million and cloud-based solutions contributing USD 64.4 million. This trend of growth is projected to continue, with total market revenues expected to rise steadily each year.
- Further, By 2023, the market size is anticipated to increase to USD 251.1 million, split between USD 177.8 million from on-premise and USD 73.3 million from cloud solutions.
- The progression remains upward, with the total market size reaching USD 286.1 million in 2024, USD 325.8 million in 2025, and USD 371.1 million in 2026. With respective contributions from on-premise and cloud deployments expanding accordingly.
- By 2027, the market is expected to grow to USD 422.7 million. Continuing to USD 481.4 million in 2028 and further to USD 548.4 million in 2029.
- The growth trajectory will be sustained into the next decade as the market is projected to increase to USD 624.6 million by 2030, USD 711.4 million by 2031, and finally reach USD 810.3 million by 2032.
- Throughout this period, the revenue from on-premise deployments will grow from USD 573.7 million in 2032. In contrast, cloud deployments will see an increase to USD 236.6 million, indicating a robust expansion within the EdTech sector.
(Source: market.us)

Global Smart Learning Market Overview
Global Smart Learning Market Size
- The global smart learning market has demonstrated robust growth from 2022 to 2032.
- Starting at USD 55.9 billion in 2022, the market revenue is projected to increase steadily each year.
- In 2023, the market size is anticipated to reach USD 66.2 billion. Followed by a further increase to USD 78.5 billion in 2024.
- This upward trajectory continues through the mid-2020s. With the market expanding to USD 93.0 billion in 2025 and then to USD 110.2 billion in 2026.
- The growth momentum is maintained into the latter part of the decade. The market is expected to grow to USD 130.6 billion by 2027, USD 154.8 billion by 2028, and an impressive USD 183.4 billion by 2029.
- Entering the 2030s, the smart learning market is forecasted to reach USD 217.3 billion in 2030. Escalating further to USD 257.6 billion in 2031 and achieving a remarkable size of USD 305.2 billion by 2032.
- This consistent expansion highlights the increasing adoption and investment in smart learning technologies globally.
(Source: market.us)

Global Smart Learning Market Share – By End-user
- In the global smart learning market, the distribution of market share by end-user segments reveals a significant skew towards the academic sector.
- As of the latest data, the academic segment holds a commanding 66% of the market share. Underscoring its predominant role in the adoption and utilization of smart learning solutions.
- Conversely, the corporate sector accounts for the remaining 34% of the market.
- This distribution highlights the heavier reliance and integration of smart learning technologies within educational institutions compared to corporate environments. Reflecting differing priorities and investment scales in these sectors.

Frequently Used Teaching Applications and Tools
- In the Netherlands in 2017, teachers frequently used a variety of teaching applications and tools. As evidenced by the distribution of their preferences.
- Interactive whiteboards led to a substantial 77% of teachers using them. Followed by method-specific learning materials at 71%, and paper workbooks and learning materials at 67%.
- Desktop computers or laptops were employed by 51% of respondents. While the Internet served as a source of information for 40%.
- Non-method-specific learning materials and practice software were utilized by 36% and 35%, respectively.
- Presentation software, such as PowerPoint, was used by 29% of teachers, and processing software like Word and Excel by 27%.
- About a quarter of respondents (24%) utilized explanatory videos from sources such as YouTube.
- Tablet computers were used by 21%, and communication software, including email, Skype, and chat, by 20%.
- Other tools mentioned include evaluation software (13%), programs combining instruction, practice, and feedback (10%), digital progress reports (10%), mobile phones (9%), electronic learning environments (9%), educational games (6%), cognitive support programs (4%), e-books (3%), digital measurement and weighing instruments (3%), social media (3%), and simulation software (1%).
(Source: Statista)

Global Interactive Whiteboard Market Statistics
Global Interactive Whiteboard Market Size Statistics
- The global interactive whiteboard market has been witnessing a steady growth in revenue at a CAGR of 7.1%.
- In 2022, the market revenue stood at USD 3.9 billion. The following year, it rose to USD 4.2 billion.
- By 2024, it is projected to reach USD 4.4 billion, demonstrating a gradual increase.
- This upward trend is expected to continue, with the market size growing to USD 4.8 billion in 2025 and USD 5.2 billion in 2026.
- By 2027, the revenue is anticipated to be USD 5.5 billion, and further growth is expected. With the market reaching USD 5.8 billion in 2028.
- The forecast for the subsequent years shows an accelerating growth pattern. With revenues projected at USD 6.2 billion in 2029, USD 6.6 billion in 2030, USD 7.0 billion in 2031, and finally, USD 7.6 billion by 2032.
- These figures illustrate a robust growth trajectory for the global interactive whiteboard market over the coming decade.
(Source: market.us)

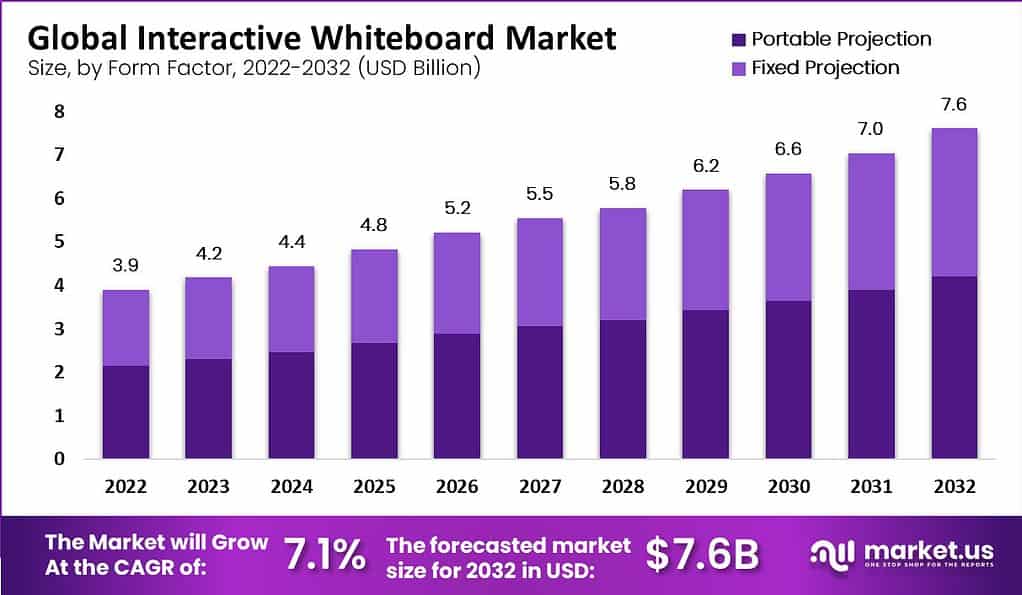
Global Interactive Whiteboard Market Size – By Form Factor Statistics
2022-2027
- The global interactive whiteboard market has been projected to experience consistent growth from 2022 to 2027.
- In 2022, the total market revenue was estimated at $3.9 billion. With portable projection whiteboards accounting for $2.16 billion and fixed projection whiteboards at $1.74 billion.
- This growth trend is anticipated to continue, reaching $4.2 billion in 2023. Divided between $2.32 billion for portable and $1.88 billion for fixed projection systems.
- By 2024, the market size is expected to increase to $4.4 billion. With portable projections rising to $2.43 billion and fixed projections to $1.97 billion.
- In subsequent years, the market is forecasted to expand further, hitting $4.8 billion in 2025. With portable and fixed projections capturing $2.65 billion and $2.15 billion, respectively.
- The growth is projected to accelerate, leading to a market size of $5.2 billion in 2026. With portable projections increasing to $2.88 billion and fixed projections to $2.32 billion.
- By 2027, the market is expected to reach $5.5 billion. With contributions from portable projections at $3.04 billion and fixed projections at $2.46 billion.
2028-2032
- The upward trend is likely to persist, with market revenues anticipated to reach $5.8 billion by 2028. Divided into $3.21 billion for portable and $2.59 billion for fixed projections.
- By 2029, the total market size is projected to grow to $6.2 billion. With portable projections accounting for $3.43 billion and fixed projections for $2.77 billion.
- The market is expected to further increase to $6.6 billion by 2030. With portable projections at $3.65 billion and fixed at $2.95 billion.
- By 2031, the market is projected to expand to $7.0 billion. With portable projections rising to $3.87 billion and fixed projections to $3.13 billion.
- Finally, by 2032, the market is forecasted to grow to $7.6 billion. With portable and fixed projections reaching $4.20 billion and $3.40 billion, respectively.
- This consistent growth reflects the increasing adoption and technological advancements in interactive whiteboards across various sectors.
(Source: market.us)

Global Interactive Whiteboard Market Share – By Technology Statistics
- The global interactive whiteboard market is segmented by technology. With resistive membrane technology holding the largest market share at 33%.
- Infrared technology accounts for 27% of the market, followed by capacitive technology with an 18% share.
- Electromagnetic pen technology represents 11% of the market, while the remaining 11% is attributed to other technologies.
- This distribution highlights the dominance of resistive membrane and infrared technologies within the interactive whiteboard sector. While other technologies occupy smaller yet significant portions of the market.
(Source: market.us)

Use of Interactive Whiteboard Among Students Statistics
Primary Level Students
- In the 2017/18 academic year, the number of primary-level students per interactive whiteboard varied significantly across selected European countries.
- According to data, the European Union in 2011/12 had an average of 111 students per interactive whiteboard. Further, by contrast, more recent figures show a lower average of 58 students per interactive whiteboard across the EU.
- Greece had about 101 students per whiteboard, making it one of the higher ratios observed. Lithuania and Italy followed with 96 and 92 students per whiteboard, respectively, while France had 90.
- Other countries reported lower ratios; Belgium had 70 students per whiteboard, Poland had 61, and Finland reported 58. Sweden and Austria both recorded an average of 55 students per interactive whiteboard.
- Further down the scale, Portugal had 47, Ireland 38, and both Hungary and Cyprus had 33 students per whiteboard. Spain reported 30 students per whiteboard, and the United Kingdom had an even lower figure at 27.
- Czechia had 24 students per interactive whiteboard, the Netherlands 22, Malta 19, and Slovakia had the lowest with only 12 students per whiteboard.
- These figures underscore the varying levels of access to interactive educational technology across Europe.
(Source: Statista)

Lower Secondary Level Students
- In the 2017/18 academic year, the distribution of lower secondary level students per interactive whiteboard in selected European countries showed a diverse range.
- France exhibited the highest number of students per whiteboard, with a significant count of 176 students.
- The European Union average was substantially lower, standing at 109 students per whiteboard.
- Following these, Lithuania and Austria had relatively high ratios as well, with 83 and 82 students per whiteboard, respectively.
- Czechia, Greece, and Italy showed more moderate figures. With Czechia at 65, Greece at 57, and Italy slightly lower at 53 students per interactive whiteboard.
- Slovakia and Denmark demonstrated even better accessibility to this technology, with only 35 and 23 students per whiteboard, respectively.
- These figures highlight the varying levels of technological integration into education systems across different European countries. Denmark leading in terms of lower student-to-whiteboard ratios, suggesting potentially more individualized use of technology in education.
(Source: Statista)

Upper Secondary Level Students
- In the academic year 2017/18, the number of upper-secondary level students per interactive whiteboard varied significantly across selected European countries.
- Bulgaria had the highest ratio, with a staggering 302 students per whiteboard. Indicating lower accessibility to this technology in educational settings.
- France and Croatia also had high numbers, with 237 and 226 students per whiteboard, respectively.
- The European Union average stood at 166 students per whiteboard. Italy, Lithuania, and Poland reported somewhat lower but still substantial numbers, with 156, 140, and 135 students per whiteboard, respectively. Czechia followed closely with 124 students per whiteboard.
- Finland, Slovakia, and Hungary exhibited much lower ratios, demonstrating better accessibility to interactive whiteboards in upper secondary education.
- Finland had 110 students per whiteboard, Slovakia had 83, and Hungary had the lowest number in the data set, with only 80 students per whiteboard.
- These figures highlight the disparity in the integration of interactive educational technologies across Europe. With significant variations in access to such resources among the countries.
(Source: Statista)

Interactive Whiteboard/ Smart Board Statistics
Smart Board Costs – By Screen Size
- The costs of smart boards vary based on their screen sizes, ranging from a low to a high price point.
- For screen sizes up to 55 inches, the cost ranges from USD 1,000 to USD 2,000.
- A 55-inch smart board has a price range between USD 2,000 and USD 4,000.
- As the screen size increases, so does the price; a 65-inch smart board costs between USD 3,000 and USD 5,000.
- For a 75-inch screen, the price is set between USD 4,000 and USD 6,000.
- Larger screens, such as the 86-inch model, are priced between USD 5,000 and USD 9,000. The largest in the data, the 96-inch screen, costs between USD 7,000 and USD 10,000.
- These price variations reflect the differing technological capabilities and sizes offered in the market.
(Source: Tutors)

Smart Board Installation Hardware Prices
- Smartboard installation hardware can significantly vary in price depending on the type of mounting component used.
- Wall mounts are priced between $150 and $850. They offer the advantage of taking up less room space, making them easier to clean and maintain. Additionally, because they are mounted on the wall. They are less likely to be damaged by bumps or knocks and can be adjusted to any desired height.
- However, wall mounts have their drawbacks; they are more difficult to install and offer limited viewing angles. Which can be a disadvantage in some room layouts.
- On the other hand, floor stands range from $250 to $1,500. These stands are appreciated for their ease of installation and greater portability. They can be easily moved and rotated, which allows for optimal viewing within a space.
- Despite these benefits, floor stands do take up more room, making them harder to clean and maintain. They are also more susceptible to damage from accidental bumps, which could be a consideration for high-traffic environments.
(Source: Tutors)
Smart Board Add-on Costs
- Smartboard add-on costs encompass a range of components that enhance functionality and user experience. HDMI cables, priced between $5 and $30, are essential for connecting the smart board to other devices, transmitting both audio and video signals.
- Stylus and annotating tools, which range from $25 to $200. Allow users to add notes and drawings directly on the smart board display. An eraser tool, costing between $5 and $15, is used to remove these notes from the board.
- Software solutions also play a critical role in leveraging the full potential of smart boards. Whiteboard software, which can be free or cost up to $600 per year. Enables users to create and share whiteboards on the screen.
- Presentation software, similarly, may be free or cost up to $150 per year and is utilized to create and display presentations on the screen.
- Interactive learning software is crucial for educational settings. Ranges from $2,000 per year and is designed to create engaging and interactive learning experiences for students. This software typically comes with limitations on the number of users.
- Additionally, shipping and sales tax are variable costs that can add up to $200, depending on the buyer’s location. These fees vary significantly and are an important consideration when budgeting for smart board installations and upgrades.
(Source: Tutors)
Smart Board Maintenance and Repair Costs
- Smartboard maintenance and repair entail a variety of costs that ensure the functionality and longevity of the equipment.
- For minor repairs, such as replacing lost or damaged pens or erasers. The average cost per year ranges from $50 to $100. These are common needs that may occur due to regular wear and tear or accidental damage.
- Major repairs, which can include replacing the projector bulb or fixing issues related to touch sensitivity, tend to be costlier, ranging from $200 to $300 or more. These repairs address more significant issues that can affect the usability of the smart board.
- Software maintenance is another crucial aspect. While some software updates and security patches are provided for free. Other upgrades might come at a cost, depending on the manufacturer, with prices up to $200. These updates are essential for keeping the software functional and secure.
- Additionally, an extended warranty can be purchased, typically costing between $100 and $500. This warranty extends the regular coverage for up to five years. Depending on the brand, model, and terms of the original warranty.
- Extended warranties provide additional peace of mind by covering potential future repairs and maintenance needs. Thereby safeguarding the investment in smart board technology.
(Source: Tutors)
Smart Board Costs – By Brand
- Smartboard costs and features vary significantly by brand, each presenting a distinct set of pros and cons.
- BenQ boards are priced between $3,000 and $5,000 and are known for their brighter displays and powerful cloud whiteboarding software, which is included for free.
- Google Jamboard, with a price range of $5,000 to $6,000, offers an easy-to-use. Cloud-based whiteboard experience with tools suitable for presentations and brainstorming.
- LG CreateBoard offers a wider price range from $2,300 to $8,000, featuring large. High-resolution boards that are very responsive and compatible with various software applications.
- The Microsoft Surface Hub is notably more expensive, ranging from $9,000 to $22,000, catering primarily to enterprises with higher budgets.
- Promethean boards cost between $2,000 and $10,000, and they are described as akin to a large iPad, which makes them user-friendly, especially for classroom settings.
- SMART boards, ranging from $2,000 to $6,000, are known for their ease of use across all ages, bright displays, and remote management features.
- Vibe smart boards are more affordable, priced between $2,500 and $3,500, and offer a simple user experience with robust built-in integrations such as Google Drive, Slack, and Zoom.
- Finally, ViewSonic offers boards priced from $1,500 to $6,000, known for their durability and suitability for both education and business environments, featuring built-in cameras and speakers.
- Each brand offers unique benefits tailored to specific needs, from high-tech features for collaborative projects to simpler, more affordable options for basic educational or business use.
(Source: Tutors)
Collaborative Whiteboard Industry
Competitor Analysis
- In the competitive landscape of the collaborative whiteboard industry, several key players are distinguished by their rankings on Capterra and G2, along with their respective total number of reviews.
- Miro stands out with high scores, achieving a 4.7 on Capterra and a 4.8 on G2, backed by a substantial 4,261 reviews.
- LucidSpark also performs strongly, matching Miro’s Capterra score of 4.7 and securing a 4.5 on G2, with 2,132 reviews.
- Mural and InVision both score 4.6 on Capterra, with G2 ratings of 4.5 and 4.4, respectively; Mural has 1,037 reviews, while InVision has 1,420.
- Creately, while slightly lower in its rankings, it still maintains competitive scores of 4.3 on Capterra and 4.4 on G2, though it has fewer reviews at 373.
- This data illustrates a robust sector where each company offers strong products, but it also highlights Miro and LucidSpark as particularly well-received options in the market.
(Source: Foundation Marketing)

Funding Sources for Interactive Whiteboard Statistics
- In London, the funding for interactive whiteboards is sourced from various channels, reflecting a diverse commitment to integrating technology in educational settings.
- The primary source of funding, accounting for 51% of the total, comes from the London Challenges initiative, highlighting significant local investment in educational technology.
- School funds also contribute a substantial portion, making up 29% of the funding, indicating schools’ direct investment in enhancing their technological resources.
- The Central Government provides 9% of the funding, showcasing a level of national support for educational technology integration.
- Joint sources and other miscellaneous funding supply 7% of the total, while Local Education Authorities (LEAs) contribute the least, at 4%.
- This funding landscape shows a strong local and school-level commitment, supplemented by government support, to advance interactive learning environments in London.
(Source: School of Educational Foundations and Policy Studies, Institute of Education, University of London)

Interactive Whiteboard Preferences Statistics
Frequency of Usage of Interactive Whiteboard Features and Statistics
- The usage frequency of various interactive whiteboard (IWB) features among respondents highlights distinct preferences and practical applications within educational or corporate settings.
- The mouse function emerges as the most frequently used feature, with 68% of respondents utilizing it, followed closely by the screen-shade feature at 58%.
- Annotating and spotlight features are equally used, each by 41% of respondents, indicating their importance in highlighting and detailing information during presentations or lessons.
- The gallery or library feature is used by 32% of respondents, allowing users to access preloaded or saved content readily. Highlighting is also a notable feature employed by 29% of respondents to emphasize key information.
- More specialized functions like recording and snapshot are used less frequently, at 15% and 11%, respectively, which may point to specific needs such as record-keeping or capturing particular moments or annotations.
- Usage drops further for features like IWB software and Zoom tools, used by only 10% and 7% of respondents, respectively.
- These tools, along with even less commonly used features such as the slayt tool (5%), screen keyboard (4%), network capabilities (2%), and OCR (1%), might be indicative of more niche requirements or possibly the availability and awareness of these functions among users.
- This data underscores a landscape where basic functions are heavily relied upon while more advanced or specific tools see limited but potentially important use.
(Source: Research Gate)

Teachers Using ICT Resources with Interactive Whiteboard Statistics
- In London, a significant percentage of teachers utilize various ICT resources alongside interactive whiteboards to enhance teaching and learning experiences.
- The most widely used ICT resource is the Internet, employed by 84% of teachers, followed closely by school-specific internet access at 76%.
- Speakers are also commonly used, with 68% of teachers incorporating them into their lessons. Electronic pens, which allow interactive engagement with whiteboard content, are used by 64% of teachers.
- Teacher laptops and printers are also integral, utilized by 46% and 42% of teachers, respectively, facilitating the integration of digital content and physical handouts. Visualizers, which project physical documents onto interactive whiteboards, are used less frequently, with only 14% adoption.
- Very niche technologies such as slates, standalone pupil laptops, and teacher tablets each see minimal use at 5%.
- Even less common are voting pods and networked pupil laptops, each used by only 4% of teachers, indicating a more selective application of these specific technologies within educational settings.
- This diverse usage of ICT resources reflects the varied approaches to digital integration in classrooms, emphasizing a broad spectrum of tools to support educational objectives.
(Source: School of Educational Foundations and Policy Studies, Institute of Education, University of London)

Frequency of Interactive Whiteboard Use by Teachers Statistics
- In London, the frequency with which teachers utilize interactive whiteboards varies, reflecting diverse integration levels within educational practices.
- A substantial 38% of teachers report using interactive whiteboards in every lesson, demonstrating a high level of dependency on this technology for daily teaching activities.
- Additionally, 29% of teachers use them in most lessons, indicating a significant but not exclusive use of whiteboards.
- A further 25% of teachers use them in some lessons, suggesting occasional integration into their teaching methods depending on the subject matter or lesson objectives.
- On the other end of the spectrum, a smaller segment of teachers—4%—hardly ever use interactive whiteboards, and another 4% never use them at all.
- This minimal usage could reflect either a lack of access to technology, a preference for traditional teaching methods, or specific educational settings where technology integration is less applicable.
- Overall, these statistics highlight a predominant adoption of interactive whiteboards among London teachers, although the extent of use varies considerably.
(Source: School of Educational Foundations and Policy Studies, Institute of Education, University of London)

Usage Frequency of Interactive Whiteboard Features by Teachers Statistics
- In London, teachers use various features in interactive whiteboards (IWBs) during most or every lesson, revealing a diverse application of this technology.
- The most frequently used feature is preloading pages, utilized by 44% of teachers, facilitating preparedness and smooth transitions in lessons.
- Close behind, both the drag or hide and color, shading, and highlighting features are used by 42% of teachers, enhancing the visual and interactive aspects of teaching.
- Downloading images or sounds is employed by 34% of teachers, enriching lesson content with multimedia elements.
- Additionally, 32% of teachers make use of the annotate and save feature, while 31% revisit and save their work, emphasizing the importance of interactive note-taking and lesson continuity.
- Downloading from the school network is done by 26% of teachers, and subject-specific software is used by 25%, indicating a tailored approach to integrating digital resources.
- Lesser-used features include search engines and movement or animation, each by 13% of teachers, subject websites by 11%, and national curriculum materials by 8%, showing a more selective application for specific educational needs.
(Source: School of Educational Foundations and Policy Studies, Institute of Education, University of London)

Teachers Undergoing Training for Interactive Whiteboard Statistics
- In London, the formal training that teachers receive for using interactive whiteboards (IWBs) covers a range of features, each aimed at enhancing the educational experience through technology.
- A significant proportion of teachers, 46%, have been trained in familiarization with IWB-dedicated software, which is crucial for the effective utilization of the technology. Slightly fewer, 42%, have received training in familiarization with the key tools of IWBs, which is essential for basic operation.
- Training in solving common technical difficulties is provided to 12% of teachers, ensuring that minor issues can be handled efficiently in the classroom setting. Moreover, 20% of teachers are trained in connecting computers to IWBs and operating projectors, a fundamental skill for integrating digital content into lessons.
- Other specific training includes using the IWB for subject-specific resources (9%), bookmarking resources from the Internet (10%), and importing multimedia into their texts (11%).
- Less common areas of training include downloading video clips (6%), supporting mixed learning styles (5%), and reinforcing learning (6%), each critical for creating diverse and engaging learning environments.
- Training also covers enhancing pupil motivation (9%), encouraging an interactive teaching style (14%), and recapping previous lessons (11%).
- Additionally, creating lesson sequences and diagrams is included (7%). Making a school-based resource bank (9%) aids in resource sharing and continuity.
(Source: School of Educational Foundations and Policy Studies, Institute of Education, University of London)

Advantages and Benefits
Perception of How Interactive Whiteboard Have Contributed to Departmental Activity Statistics
- In London, teachers’ perceptions of how interactive whiteboards (IWBs) have contributed to departmental activities reveal a generally positive outlook.
- A significant 46% of teachers feel that IWBs have slightly enhanced their departmental activities, indicating a moderate improvement in efficiency or effectiveness.
- An additional 32% of teachers report a more substantial enhancement, suggesting that IWBs have strongly benefited their educational practices.
- Together, these responses show that a substantial majority of teachers recognize the value added by IWBs to their teaching environments.
- Conversely, 18% of teachers perceive no difference in departmental activity due to the use of IWBs. This group may reflect a scenario where the impact of IWBs is neutral or where the potential benefits are not fully realized due to various factors such as insufficient training or integration challenges.
- Only a small fraction, 4% of teachers, believe that IWBs have detracted slightly from their departmental activities, indicating minimal negative impacts.
(Source: School of Educational Foundations and Policy Studies, Institute of Education, University of London)

Main Benefits of Interactive Whiteboard According to Student Statistics
- According to students, the main benefits of interactive whiteboards (IWBs) encompass a range of educational enhancements.
- The most significant advantage, noted by 23.5% of students, is access to the Internet, which provides a wealth of information and resources at their fingertips. Visual support follows closely, valued by 19.1% of students, highlighting the importance of visual aids in enhancing understanding and retention of information.
- Videos are another key benefit, appreciated by 12.2% of students, offering dynamic and engaging ways to present information. IWBs also boost motivation to learn for 11.8% of students, indicating that technology makes learning more appealing.
- Diversified teaching methods are recognized by 9.3% of students, suggesting that IWBs allow for a variety of teaching styles that cater to different learning preferences.
- Further, 9.1% of students feel that IWBs facilitate learning, making it easier and more interactive. Time-saving benefits are acknowledged by 7.2% of students, pointing to the efficiency of using IWBs in education.
- The organization of the teacher, assisted by IWBs, is noted by 5.8% of students, underscoring the role of technology in improving educational structure and delivery.
- However, communication improvements and interactivity are seen as less significant, cited by only 1.3% and 0.7% of students, respectively. These relatively low percentages may reflect underutilization or specific contexts where these features are less impactful.
- This data provides a comprehensive overview of how IWBs are perceived by students, demonstrating their valuable role in modern educational environments.
(Source: Research Gate)

Main Benefits of Interactive Whiteboard According to Teacher’s Statistics
- According to teachers, the benefits of interactive whiteboards (IWBs) vary in terms of importance, but all contribute significantly to the educational environment.
- Internet access is the most highlighted benefit, with its perceived value ranging from a minimum of 18.80% to a maximum of 29.20% of teachers emphasizing this point. Moreover, this suggests that IWBs are highly valued for their ability to provide immediate access to online resources, enhancing the scope and depth of learning materials available.
- Student motivation is another significant benefit noted by teachers, with 11.60% citing it as a maximum benefit and 9.50% at the minimum. This indicates that IWBs are effective in engaging students more actively in the learning process.
- Effective teaching is also recognized, though to a lesser degree, with values closely packed between 6.10% and 6.30%, showing a consistent acknowledgment of IWBs in improving teaching efficiency.
- Teacher organization is valued by between 4% and 5.90% of respondents. Suggesting that IWBs help in structuring lessons more effectively. The impact on student outcomes is observed with a lesser emphasis, cited by 3.90% at its maximum and 2.80% at its minimum. This may reflect variations in how IWBs are used across different settings or subjects.
- Lastly, communication improvements facilitated by IWBs are noted by a small fraction of teachers, ranging from 0.60% to 1.30%. This might indicate that while useful, IWBs are not primarily seen as communication tools but more as educational enhancers.
- Overall, these insights provide a snapshot of how IWBs are valued by teachers, underlining their role in modernizing and enriching the teaching and learning environment.
(Source: Research Gate)

Concerns and Challenges
Main Challenges of Interactive Whiteboard According to Teachers Statistics
- According to teachers, the main challenges associated with using interactive whiteboards (IWBs) are predominantly technical.
- A significant 70.60% of teachers report facing technical problems, which include issues such as system malfunctions, software glitches, and connectivity troubles. These technical difficulties represent the largest hurdle to effective IWB usage, potentially impacting lesson flow and reducing the technology’s overall efficacy.
- Additionally, 17.30% of teachers find using IWBs to be time-consuming, which may relate to the preparation required to integrate these tools effectively into lessons or the learning curve associated with mastering new technologies.
- A smaller percentage of teachers, 9.60%, cite the small screen size of IWBs as a challenge, indicating that the dimensions of the board can sometimes be insufficient for student visibility or interactive work.
- Classroom management issues are noted by only 1.40% of teachers, suggesting that while IWBs can influence classroom dynamics, they do not commonly complicate overall management. Lastly, inadequate training is a challenge for 1.10% of teachers, pointing to a need for better professional development to ensure educators can fully leverage IWB capabilities.
- Overall, while IWBs offer substantial educational benefits, these challenges highlight the need for ongoing technical support, training, and potentially upgrading equipment to optimize their use in educational settings.
(Source: Research Gate)

Main Challenges of Interactive Whiteboard According to Students’ Statistics
- According to students, the main challenges associated with using interactive whiteboards (IWBs) encompass several areas, each affecting their learning experience differently.
- Technical problems are the most commonly reported issue, cited by 33.50% of students, highlighting difficulties such as malfunctioning hardware or software issues that can disrupt the educational flow.
- The small screen size is another significant challenge, noted by 25.40% of students, which can limit visibility and interaction for those further from the board.
- Further, a considerable 19% of students perceive their teachers’ inability to effectively use IWBs as a challenge, suggesting that not all educators are equally proficient with this technology, potentially affecting the quality of instruction.
- Additionally, 18.30% of students report a loss of motivation, which may stem from lessons that fail to engage or capitalize on the interactive capabilities of IWBs fully.
- Lastly, a small percentage of students (3.80%) feel there is no interactivity involved with the IWBs, which contradicts the core benefit of these tools and points towards a possible underutilization in some educational settings.
- Further, these insights underscore the importance of adequate training, proper technical support, and thoughtful integration of IWBs to maximize their potential benefits for student engagement and learning.
(Source: Research Gate)

Key Innovations and Developments in Interactive Whiteboard Technology Statistics
- Moreover, recent advancements in interactive whiteboard (IWB) technology have been driven by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), enhancing collaboration and learning experiences across various settings.
- Companies like IMAGO Technologies are at the forefront of developing AI-powered virtual whiteboards that offer features such as real-time translation, smart data analysis, and personalized learning environments.
- These whiteboards enhance interactive experiences by allowing for dynamic participation from remote locations, ensuring that all participants, regardless of their physical presence, can engage equally.
- Samsung has also introduced new displays with enhanced connectivity and usability tailored for educational settings. It aims to transform classrooms by supporting interactive learning and making it easier for educators to integrate technology with traditional teaching methods.
- Such innovations are not only improving the efficiency of collaborative tasks but are also setting new standards for technology integration in the education and business sectors.
(Sources: IMAGO Smart Boards, Electronic Office Systems, Samsung News)
Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- Boeing Acquires Nanotech Innovations: In 2024, Boeing acquired Nanotech Innovations for $50 million to enhance its research and development capabilities in aerospace materials, particularly focusing on lightweight nanomaterials for aircraft.
- Airbus Partners with Advanced Nanotech: Airbus announced a partnership with Advanced Nanotech in early 2024, investing $30 million to co-develop nanotechnology solutions aimed at improving the fuel efficiency and structural integrity of its aircraft.
New Product Launches:
- Nanoscale Coatings by Lockheed Martin: Lockheed Martin launched a new line of nanoscale coatings in March 2024, designed to improve the durability and corrosion resistance of aircraft components. Initial tests show a 20% increase in lifespan compared to traditional coatings.
- 3D Printed Nanomaterials: In January 2024, a startup unveiled a new 3D printing technology utilizing nanomaterials, allowing for the production of aerospace components with a 25% weight reduction while maintaining strength and safety standards.
Funding:
- Funding Round for NanoTech Labs: NanoTech Labs raised $15 million in Series B funding in February 2024 to expand its research on nanomaterials for aerospace applications. Focusing on environmental sustainability.
- Investment in Aerospace Nanotech Startups: In late 2023, several venture capital firms invested a total of $40 million in various startups specializing in nanotechnology applications within the aerospace sector, signaling growing interest and confidence.
Technological Advancements:
- Use of Nanosensors: Recent developments in nanosensors have improved the monitoring of aircraft health, enhancing safety measures. Reports indicate a 30% improvement in the detection of structural issues using these advanced sensors.
- Nanotechnology in Fuel Cells: Research indicates that integrating nanotechnology into fuel cell designs can increase efficiency by 15%. Promising significant advancements in aerospace propulsion systems by 2025.
Conclusion
Interactive Whiteboard Statistics – Interactive whiteboards (IWBs) significantly enhance educational environments by providing dynamic, multimedia-rich tools that improve teaching and learning.
Moreover, for teachers, IWBs foster a more interactive classroom, making lessons more engaging with integrated internet resources, videos, and interactive software, alongside organizational benefits like accessible lesson materials.
Students experience increased motivation and understanding through diverse, visual, and interactive content that suits various learning styles.
However, challenges such as technical issues, teacher proficiency, limited screen size, and insufficient interactivity can hinder effectiveness.
Further, the successful utilization of IWBs depends on proper implementation, consistent technical support, and comprehensive teacher training.
Addressing these issues is crucial to ensure IWBs effectively enhance education and adapt to the evolving digital landscape in schools.
FAQs
An interactive whiteboard is a large display that connects to a computer and projector. Users can interact with the display’s surface, controlling the computer using a pen, finger, or other device. IWBs are commonly used in classrooms for teaching and presentations.
IWBs enhance teaching by allowing educators to integrate multimedia resources, such as videos, images, and internet resources, into their lessons. They support varied learning styles through visual, auditory, and kinesthetic elements. For students, IWBs make learning more engaging and interactive, helping to increase motivation and understanding of complex subjects.
Common features of IWBs include touch recognition, pen and gesture input, the ability to save and print notes, multimedia integration, and connectivity with various devices. Advanced IWBs also offer features like multi-user interaction and access to cloud-based resources.
Key challenges include technical issues such as software glitches and hardware malfunctions. A need for ongoing teacher training to effectively use the technology and physical limitations like inadequate screen size. Additionally, ensuring all students benefit equally from IWB features can require significant classroom management and planning.
While IWBs are versatile and beneficial, their suitability can vary based on the specific educational context, such as the age of students, subject matter, and classroom setup. Proper assessment of these factors is necessary to determine the appropriateness and potential impact of IWBs in a given setting.


