Table of Contents
Introduction
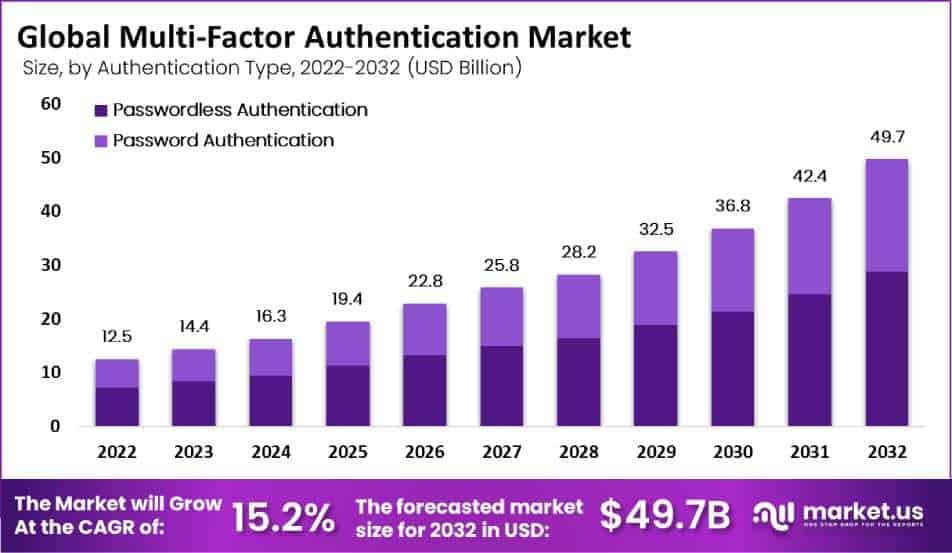
The Global Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Market was valued at USD 14.4 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 49.7 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 15.2%. The growth can be attributed to the increased demand for advanced security measures amid growing cyber threats and the adoption of digital and cloud-based solutions in various industries.
The rise in cyberattacks, fraud, data identity thefts, and data breaches across organizations drives the demand for MFA solutions. Strict regulations aimed at protecting sensitive data also contribute to the market’s growth. The need for advanced data security solutions is significant due to the increasing adoption of digital technologies in both developing and developed economies. This trend, along with investments in enterprise mobility and cloud technologies, is expected to increase the adoption of MFA solutions worldwide. The emergence of authentication-as-a-service solutions, offering advanced security to organizations, presents promising growth opportunities for the market.
However, high implementation and maintenance costs, complexity in deployment, and potential resistance due to the inconvenience of certain authentication methods pose challenges to the market’s growth. Despite this, the industry is witnessing advancements in technology, such as the development of cloud-based MFA solutions and the increasing popularity of interconnected devices within the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, which are expected to offer lucrative growth opportunities.
Recent developments in the MFA market include a series of mergers and acquisitions, demonstrating the sector’s dynamic growth and increasing consolidation. Some notable examples include LOCH.io acquiring Avirtek, Lumifi acquiring Castra Managed Services, MC2 Titanium acquiring Singtel’s stake in Trustwave, Okta acquiring Uno, and Tesserent acquiring Beyond Binary for A$7 million. These activities highlight the value placed on advanced cybersecurity services and signal a robust and evolving MFA market.
Key Takeaways
- The global Multi-Factor Authentication Market is projected to reach a value of USD 49.7 billion by 2032, up from USD 14.4 billion in 2023
- This market is growing at a CAGR of 15.2% during the forecast period.
- The passwordless authentication segment holds the largest market share, accounting for 58% of the market revenue.
- Five-factor authentication is the dominant model type, capturing 31% of the market share.
- Hardware components lead the market, with a commanding share of 34%.
- Large enterprises dominate the market, holding a significant share of 64%.
- The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sectors are the major contributors to end-user applications, representing 25% of the market share.
- North America accounts for the largest revenue share, capturing 38% of the market.
- Leading market players such as OneSpan, RSA Security LLC, NEC Corporation, and Symantec Corporation are implementing strategic initiatives to strengthen their positions in the market.
Multi-Factor Authentication Statistics
- 87% of technology companies use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
- 95% of MFA users choose software like mobile apps for extra security.
- Big companies (over 10,000 employees) have an 87% MFA adoption rate.
- Medium-sized businesses (26-100 employees) adopt MFA at a 34% rate.
- Small businesses (up to 25 employees) have a lower adoption rate of 27%.
- Every second, Microsoft faces over 1,000 password attacks, but nearly all hacked accounts lack MFA.
- Globally, 57% of companies use MFA, up 12% from the year before.
- LastPass Authenticator is the most popular MFA tool, chosen by 39% of users.
- Duo Security (31%) and Google Authenticator (24%) are also popular choices.
- Only 4% use hardware MFA devices, and biometrics are used by just 1%.
- Despite having MFA, 28% of users are still attacked.
- The education sector has a 64% MFA adoption, lower than other sectors.
- Major players in MFA hold 45-50% of the market.
- The insurance sector, with a 77% MFA adoption rate, follows the technology industry.
- The government sector has the lowest MFA adoption at 48%.
- Large organizations (over 10,000 employees) see an 87% MFA adoption rate.
- 67% of people trust platforms more when they use MFA.
- Common passwords like “123456” still pose a risk.
- 62% of people write down their passwords, which is unsafe.
- The pandemic has pushed for more digital solutions, increasing the reliance on MFA.
- Threats like SIM-jacking and AiTM attacks make it crucial to update MFA methods.
- The construction sector shows strong MFA adoption at 74%.
- The adoption of 2FA increased by 51% from 2017 to 2021.
- 54% of SMBs don’t use MFA, and only 28% require it.
- Push notifications are the most common MFA method.
- Admins use MFA more than non-admin users.
- Adding a mobile phone for Google account verification can block most automated and phishing attacks.
- 83% of breaches in 2023 were by external actors, with 74% involving human error.
- Financial motives drive 95% of breaches, with an average cost of $4.35 million each.
- Breaches due to credential theft cost about $4.50 million and take months to resolve.
- Critical infrastructure breaches are even more expensive, averaging $4.82 million.
- 79% of critical organizations haven’t adopted zero-trust architectures yet.
- Password misuse remains common, with over half admitting to unsafe practices.
- MFA blocks 99.9% of automated attacks, highlighting its effectiveness.
- 69% prefer smartphone-based MFA over other methods.
- 40% of cyber insurance claims relate to credential compromise.
- Only 25% of small businesses use MFA.
- 67% of organizations report better cyber risk management with MFA.
- In North America, 56.7% of businesses use MFA for identity management.
- 22% find MFA too difficult or time-consuming.
- By 2023, many enterprises are expected to adopt passwordless methods for over half of their use cases.
- MFA usage increased from 53% to 62% between 2018 and 2019.
- 87% of IT decision-makers believe MFA improves cybersecurity.
- 84% of US consumers use MFA on at least one online account.
Use Cases
- Banking and Financial Transactions: A common MFA use case is logging into bank accounts. Users typically enter a password and then receive a verification code on their phone, adding an extra layer of security beyond the password.
- Government Website Access: Accessing government websites often requires MFA, starting with a username and password, followed by phone or email verification, and sometimes a secret question, enhancing security and ensuring that access is granted only to authorized users.
- Proprietary Software Access: For software that contains sensitive data, MFA ensures that access is limited to authorized users. This can include entering a password and using a physical token or biometric data as additional verification steps.
- Remote Access to Company Resources: MFA is crucial for employees accessing company networks remotely, requiring them to provide a password and a one-time code sent to their mobile device. This setup helps prevent unauthorized access to company resources.
- HR Software Login: HR managers accessing intranet software to manage sensitive employee information are protected by MFA, preventing hackers from gaining access even if they have the manager’s username and password.
- Cloud-based Services Access: For services like Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace, MFA helps counter brute force attacks by requiring additional authentication beyond the password, such as a code from a smartphone app.
- Healthcare Remote Access: In healthcare, where patient data security is paramount, MFA can include biometric verification like fingerprint scans, offering a secure and quick method to access patient records and medical systems remotely.
- Accessing CRM Software: Marketing managers using CRM platforms like Salesforce are safeguarded by MFA, which could include app-based authentication, protecting customer data even if a device is compromised by a keylogger.
- Software Development: For platforms like GitHub, MFA using security keys can protect code repositories from unauthorized access, ensuring that sensitive development work remains secure.
Recent Developments
Mergers and Acquisitions
- In December 2020, Cisco announced its plan to acquire IMImobile, with a purchase agreement of approximately $730 million. This move aims to integrate IMImobile’s communication solutions with Cisco’s own services.
- VMware introduced new Workspace ONE innovations in August 2019, showcasing its commitment to enhancing workplace technology and security.
New Product Launches
- IBM launched Watson Works in June 2020. This suite of products utilizes AI to assist companies in navigating the challenges of returning to the workplace amidst the pandemic.
- BlackBerry launched BlackBerry Spark Suites in May 2020, enhancing its enterprise mobility management and security solutions.
Partnerships and Collaborations
- Citrix and Microsoft joined forces in July 2020 to create new flexible workplace solutions. As part of this partnership, Microsoft Azure became the preferred cloud platform for Citrix, aiming to facilitate remote work and enhance productivity.
Key Players Analysis
Oracle Corporation
Oracle Corporation has enhanced its cloud infrastructure security by incorporating multi-factor authentication (MFA) into its native Identity and Access Management (IAM) system. This allows Oracle Cloud Infrastructure users to add a temporary one-time password (TOTP) device to their accounts for an additional layer of security. The process involves signing into the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure account, visiting the user profile page, enabling MFA, and installing a TOTP app like Oracle Mobile Authenticator on a mobile device. Users then use the app to generate a code for authentication, providing a secure way to protect assets in the cloud.
Microsoft Corporation
Microsoft Corporation, a global leader in technology and software services, is making significant strides in the Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) market, particularly within the broader context of cybersecurity and identity management. The necessity of MFA has been underscored by the dramatic increase in cyber threats, including ransomware attacks, which have surged in recent years.
Microsoft’s foray into the MFA market is characterized by its comprehensive suite of identity and access management solutions, offered under the Microsoft Entra product line. Microsoft Entra includes various MFA methods such as texts, biometrics, and one-time passcodes, catering to the diverse needs of organizations seeking to bolster their cybersecurity defenses. This is part of Microsoft’s broader strategy to provide more secure and resilient systems for its customers, ensuring protection against credential theft and unauthorized access.
The company’s efforts to enhance security measures and promote the use of MFA are aligned with global trends towards improving cybersecurity. With the increasing adoption of digital technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT), the demand for advanced security solutions like MFA is expected to continue growing. Microsoft, with its strong market presence and comprehensive security solutions, is well-positioned to address these emerging challenges and opportunities within the MFA market.
OneSpan
OneSpan, previously known as VASCO Data Security International, is a public company focused on providing comprehensive digital solutions aimed at enhancing identity security and business productivity. The company has specialized in a range of software products including electronic signature, cloud-based multifactor authentication, identity verification, and mobile app shielding, among others. These offerings are primarily targeted towards sectors such as retail and commercial banking, wealth management, insurance, healthcare, and more. Established in 1991 and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois, OneSpan operates globally with a presence in North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific regions.
The company’s product portfolio encompasses a broad array of security solutions, including regulatory and PSD2 compliance, fraud prevention, mobile app security, transaction signing, digital onboarding, and omnichannel security solutions. OneSpan’s commitment to security is further underscored by its recent endeavors, including acquisitions aimed at enhancing digital agreement security through blockchain technology and participating in initiatives like the Open Identity Exchange (OIX) to promote trust in digital transactions.
In the financial year of 2022, OneSpan reported a revenue of $219 million, marking a modest growth from the previous year. Despite facing challenges in net income, the company continues to invest in its product lineup and strategic acquisitions to bolster its market position. OneSpan’s competitive landscape includes firms such as RSA Technology, Callsign, Know Your Customer, and Axuall, indicating a dynamic market environment with significant opportunities for growth and innovation.
RSA Security LLC
RSA Security LLC, a significant player in the multi-factor authentication (MFA) market, has experienced both evolution and controversy over the years. Originally founded to focus on encryption and encryption standards, RSA has developed a suite of products that address cybersecurity needs, including multi-factor authentication through its RSA SecurID tokens. These tokens, which have been fundamental in the MFA space, generate authentication codes at fixed intervals, adding a layer of security beyond traditional passwords.
However, RSA’s journey has not been without challenges. In 2011, the company faced a severe security breach that compromised the SecurID tokens, leading to concerns about the effectiveness of these devices. Despite this, RSA SecurID maintained a dominant position in the two-factor authentication market, holding over 70% market share as of 2003. RSA was later acquired by Dell EMC in 2016, and in 2020, it became an independent company under Symphony Technology Group, marking a new chapter in its history.
NEC Corporation
NEC Corporation emerges as a formidable leader in the Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) market, renowned for its pioneering advancements in biometric authentication technologies. With an illustrious history of research and development in biometric technologies dating back to the 1970s, NEC has achieved global recognition for its contributions to enhancing digital security through biometric authentication. The company’s offerings encompass a wide array of technologies, including fingerprint recognition, palmprint recognition, face recognition, iris recognition, voice recognition, and its unique ear acoustic authentication technology. These innovations underscore NEC’s commitment to creating a secure and trustworthy digital world, catering to a diverse range of applications from crime prevention to secure payment solutions.
The global MFA market, characterized by its rapid growth and technological diversification, presents a fertile landscape for companies like NEC. As multi-factor authentication becomes increasingly crucial across various sectors, NEC’s biometric solutions are well-positioned to address the rising demand for advanced security measures. This demand is driven by the escalating risks associated with digital transactions and the need for more robust protection against unauthorized access. The BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) sector, in particular, has emerged as a significant adopter of MFA technologies, spurred by the necessity to safeguard sensitive financial data against cyber threats.
Conclusion
The global Multi-Factor Authentication market is poised for significant growth, driven by the increasing need for robust security solutions across various sectors. Despite facing challenges related to cost and complexity, advancements in technology and strategic initiatives by key market players are expected to create ample opportunities for the market’s expansion.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



