Table of Contents
Market Overview
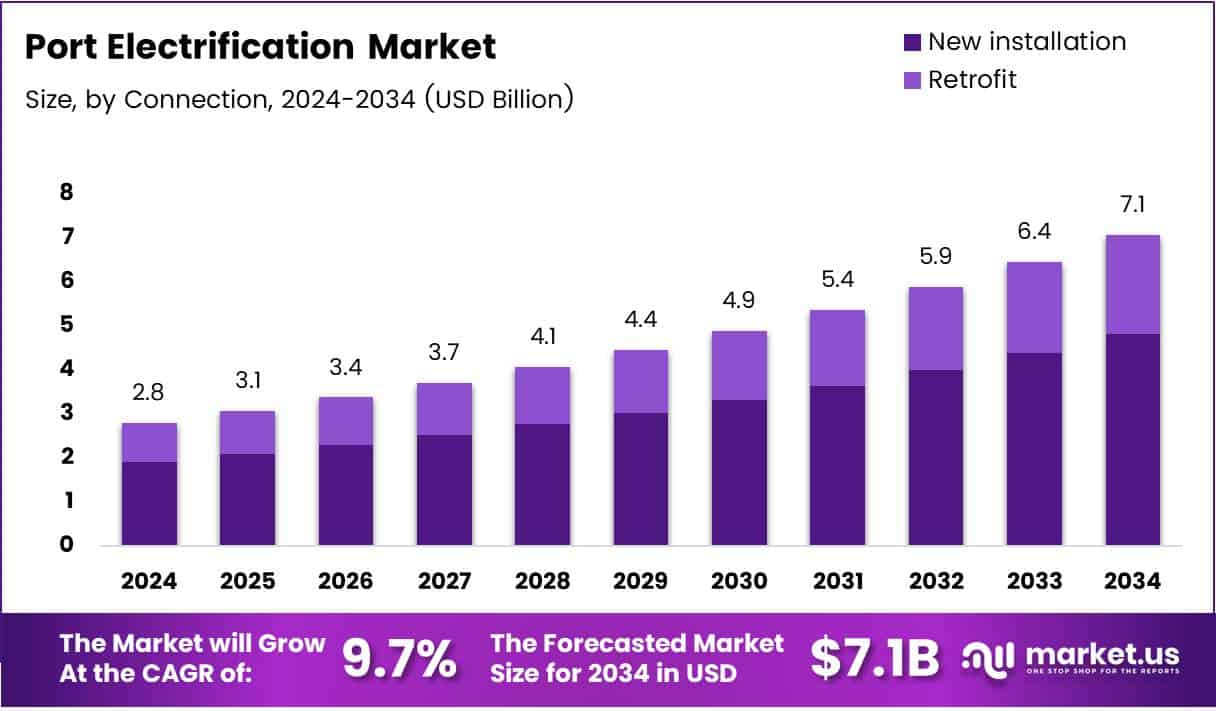
The Global Port Electrification Market size is expected to be worth around USD 7.1 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.8 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.7% during the forecast period.
The Port Electrification Market is gaining strong momentum as global ports shift towards greener, low-emission operations. This transition is not just environmentally necessary but economically strategic, with government support accelerating adoption. A key driver is regulatory pressure and funding initiatives aimed at reducing the carbon footprint of maritime activities. For instance, the EPA’s Clean Ports program has injected nearly $3 billion into infrastructure upgrades, enabling 55 ports to electrify systems and deploy cleaner technologies. Such large-scale investment is creating fertile ground for equipment manufacturers, software providers, and utility companies to enter the market.
Opportunities are particularly strong in regions offering financial aid and incentives. The Port of Everett, for example, received a $4.3 million grant from WSDOT to advance shore power capabilities an initiative that lowers vessel emissions while docked. In Europe, countries like Estonia are taking the lead, with a €25 million grant to modernize and green port vessels. This cross-regional push signals a broader trend: port authorities worldwide are preparing for a carbon-neutral future. As regulations tighten and sustainability goals become mandatory, the demand for electrification solutions from hybrid cranes to onshore power supply is projected to grow consistently. This makes the market ripe for partnerships, innovation, and long-term growth.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Port Electrification Market is expected to reach USD 7.1 Billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 9.7% from 2025 to 2034.
- New installation led the Connection segment in 2024 with a 68.5% market share, fueled by demand for sustainable port infrastructure.
- Shoreside installations dominated in 2024, accounting for 75.2% of the market due to their role in emissions reduction and efficiency.
- Transformers held the largest share in the Component segment in 2024 at 33.6%, underscoring their importance in energy transfer systems.
- Electric cargo handling equipment represented 64.2% of the Port Equipment segment in 2024, reflecting the drive toward decarbonized operations.
- Europe led the global market with a 35.6% share in 2024, valued at USD 1.0 Billion, driven by strict environmental regulations and green initiatives.
Key Drivers
- Environmental Regulations and Decarbonization Goals: Regulatory bodies and port authorities are mandating the reduction of carbon emissions. Stringent environmental norms like the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) emission reduction targets are compelling ports to adopt electric technologies.
- Technological Advancements: Improvements in battery technology, renewable energy integration, and energy management systems are making electrification more feasible and cost-effective. Innovations in charging infrastructure and energy storage solutions are also accelerating adoption.
- Operational Cost Reduction: Electrification helps in lowering fuel consumption and maintenance costs. Electric equipment tends to have fewer moving parts, which reduces the frequency and cost of repairs.
- Government Incentives: Financial support in the form of subsidies, tax incentives, and low-interest loans is motivating ports to shift to electric systems. These incentives are playing a pivotal role in driving demand.
- Sustainable Development Goals: As sustainability becomes a core part of corporate and governmental strategies, port authorities are aligning operations with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals. Electrification is seen as a critical part of these initiatives.
Market Challenges
- High Initial Investment: Upgrading port infrastructure to support electrification demands significant capital investment. This is a deterrent for smaller ports with limited budgets.
- Grid Dependency and Power Supply Issues: Ports require stable and high-capacity electricity supply. In regions with weak grids, reliability becomes a concern.
- Lack of Standardization: The absence of universal standards for electric equipment and charging infrastructure can complicate integration and increase costs.
- Training and Skill Gaps: Transitioning from conventional to electric systems requires workforce training, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
Market Segmentation
Connection Analysis
New installations lead with 68.5% share in 2024, as ports prefer building modern, energy-efficient systems from scratch. They’re easier to upgrade and cheaper to maintain than retrofits, which still matter but grow slower due to higher costs and complexity.
Installation Type Analysis
Shoreside systems dominate with 75.2% share, offering clean power to docked ships and helping ports meet emission rules. They’re easier to manage than shipside setups, making them the top choice for global port upgrades.
Component Analysis
Transformers hold the largest share at 33.6%, key to safe power distribution in ports. They support stable voltage and high loads, making them essential. Other components matter too but play supporting roles.
Port Equipment Type Analysis
Electric cargo handling equipment leads with 64.2%, replacing diesel machines to cut emissions and noise. It’s cost-effective and reliable. Other electric equipment is growing but used less due to higher costs or limited scope.
Regional Analysis
Europe
Europe leads the global port electrification market with a 35.6% share valued at USD 1.0 Billion, thanks to strict environmental rules and strong government backing. The region’s push for carbon neutrality and green port projects has increased demand for electrification. Western European countries are rapidly installing shore-to-ship power systems, reinforcing their dominant position in the global market.
North America
In North America, the port electrification market is growing due to rising environmental awareness and clean energy investments. U.S. ports are upgrading infrastructure to meet tougher air quality standards and emission regulations. Supportive policies are encouraging the adoption of electric systems, especially for cleaner and more sustainable port operations.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific is becoming a key growth area for port electrification. High levels of industrial activity and maritime trade are pushing countries like China, Japan, and South Korea to modernize ports with green technologies. Government-led initiatives and infrastructure investments are accelerating the shift toward cleaner and more efficient port operations in the region.
Middle East and Africa
The Middle East and Africa are slowly adopting port electrification, driven by national goals focused on sustainability and diversifying the economy. Though still in the early stages, investment in smart port infrastructure and growing international cooperation are creating opportunities for growth as environmental priorities become more important.
Latin America
Latin America is moving toward port electrification to boost operational efficiency and cut emissions. Efforts to upgrade outdated port systems and align with global climate goals are encouraging adoption of electric technologies. As regional governments begin to implement greener policies, the market is expected to grow steadily in the coming years.
Competitive Landscape
- Launching innovative electric port equipment
- Collaborating with governments and port authorities
- Developing scalable and modular electrification solutions
Emerging Trends
Integration of Renewable Energy: Ports are increasingly adopting solar and wind energy to power their electric infrastructure.
Smart Ports: Digital technologies like IoT, AI, and digital twins are being used to manage electric equipment efficiently.
Energy Storage Systems: These systems are crucial for ensuring stable power supply and managing energy loads effectively.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations between governments and private firms are accelerating electrification projects, especially in developing regions.
Recent Developments
In November 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency allocated $3 billion under the Inflation Reduction Act to modernize and electrify port infrastructure nationwide. As part of this initiative, California secured $49.7 million to implement advanced port improvement measures, advancing clean energy adoption in one of the busiest shipping hubs.
In December 2024, the European Investment Bank stepped in to accelerate Europe’s green port transition. It signed an €80 million loan agreement with the Port Authority of Bilbao, aimed at expanding and electrifying the port facilities to meet climate goals and improve operational efficiency.
In May 2025, ABB expanded its clean energy portfolio by signing a deal to acquire BrightLoop. This strategic move aims to strengthen ABB’s capabilities in electric power solutions and decarbonized technologies, further aligning its business with the growing demand for electrified infrastructure in global ports.
Conclusion
The port electrification market is poised for sustained growth, driven by regulatory pressure, environmental awareness, and the economic benefits of cleaner technologies. While challenges such as high initial investment and power infrastructure constraints remain, the long-term advantages of reduced emissions, cost savings, and operational efficiency are prompting global ports to invest in electrification. With ongoing innovation and support from both public and private sectors, the market is expected to play a crucial role in transforming the maritime logistics landscape into a greener, more efficient system.


