Table of Contents
Introduction
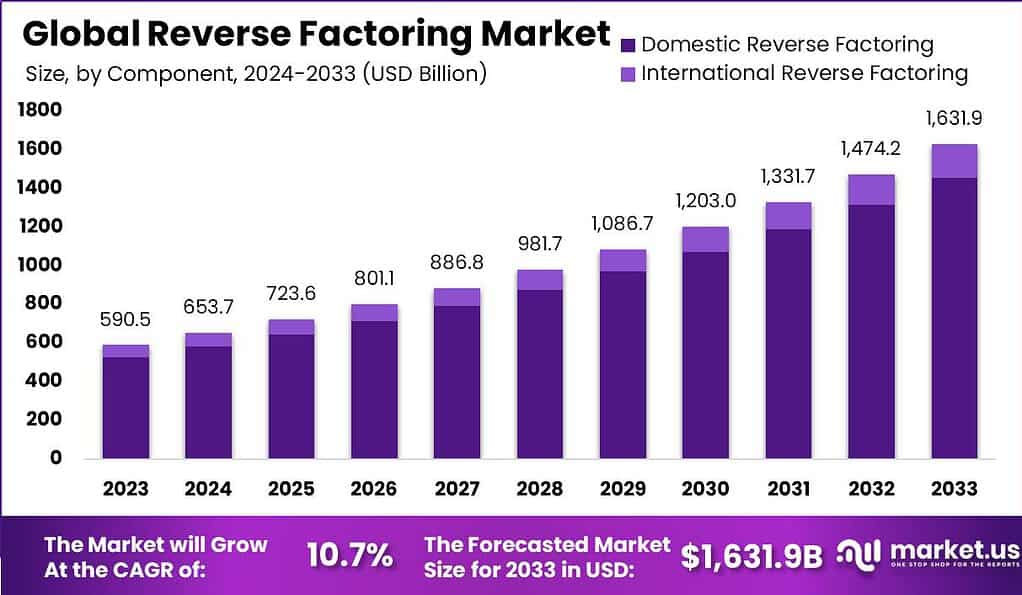
According to market.us, The global reverse factoring market is projected to reach approximately USD 1,631.9 billion by 2033, up from USD 590.5 billion in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.7% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
Reverse factoring, also known as supply chain financing, is a financial arrangement where a company uses a financial intermediary, typically a bank, to pay its suppliers at an accelerated rate in exchange for more favorable payment terms. The company’s suppliers benefit by receiving payments sooner, albeit often at a discounted rate, which improves their cash flow and reduces the financial strain. On the other side, the company gets to extend its payment terms, improving its own cash flow management without negatively impacting the supplier relationships.
The market for reverse factoring is on the rise, driven by the growing need for efficient working capital management among businesses. As global supply chains become more complex and integrated, companies are seeking solutions that can streamline payment processes and mitigate financial risks. This market growth is further fueled by technological advancements that facilitate smoother transactions and more robust financial arrangements. Financial institutions and fintech companies are capitalizing on this demand by offering tailored reverse factoring services that cater to diverse industries, thus broadening the reach and appeal of this financial solution.
However, the market faces challenges, primarily concerning the regulatory environment. Different countries have varied regulations regarding financial transactions, which can complicate the adoption of reverse factoring internationally. There is also a need for widespread understanding and trust in this financial mechanism, as misconceptions about its cost and benefits can hinder its acceptance.
Despite these challenges, there are significant opportunities in the reverse factoring market. It offers a win-win solution for both buyers and suppliers, with buyers able to negotiate better terms with suppliers, and suppliers benefiting from more predictable cash flows. This arrangement also reduces the risk of supply chain disruptions, which is increasingly important in today’s volatile market environment. As more businesses recognize the benefits of reverse factoring, its adoption is expected to rise, further stimulating market growth.
Key Takeaways
- The reverse factoring market is projected to experience substantial growth, with an anticipated valuation reaching approximately USD 1,631.9 billion by 2033, up from USD 590.5 billion in 2023. This indicates a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 10.7% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
- In the domestic reverse factoring segment, the market held a dominant share of 89.3% in 2023.
- The banks segment led the market significantly, capturing a 75.1% share in 2023.
- Among industry verticals, the manufacturing sector was a major contributor, accounting for 29.2% of the total market share in 2023.
- Europe emerged as the leading region in the reverse factoring market, holding a 47.5% market share, which translates to revenues of approximately USD 280.4 billion in 2023.
Reverse Factoring Statistics
- The Reverse Factoring Market is projected to reach a valuation of approximately USD 1,631.9 Billion by 2033, up from USD 590.5 Billion in 2023. This represents a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.7% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033
- The Global Reverse Factoring Market is projected to experience significant growth from 2023 to 2033.
- In 2023, the market size is estimated at $590.5 billion. By 2024, it is expected to increase to $653.7 billion, followed by a rise to $723.6 billion in 2025. The market is projected to reach $801.1 billion by 2026, and further expand to $886.8 billion by 2027.
- Continuing its growth trajectory, the market is forecasted to grow to $981.7 billion by 2028. By 2029, it is expected to reach $1,086.7 billion.
- The market size is projected to be $1,203.0 billion in 2030, and is anticipated to grow to $1,331.7 billion by 2031. In 2032, the market is expected to reach $1,474.2 billion, and by 2033, it is forecasted to grow to $1,631.9 billion. Overall, the market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.7% from 2023 to 2033.
- Reverse factoring, which currently handles approximately 3% of global trade finance, possesses the capability to manage up to 25% of this sector.
- In 2023, the total turnover for the factoring and commercial finance industry in Europe was reported at €2.044 trillion. Members of the European Union Factoring (EUF) constituted 94.7% of this turnover, with the top five countries collectively accounting for nearly 71.3% of the market.
- Notably, the turnover from the factoring industry represented 12% of Europe’s GDP in the same year.
- In reverse factoring, a finance provider may pay up to 100% of an outstanding invoice to the supplier of goods or services that have been delivered to a buyer, streamlining financial transactions and enhancing liquidity for suppliers.
Total Factoring Volume in Europe in 2023
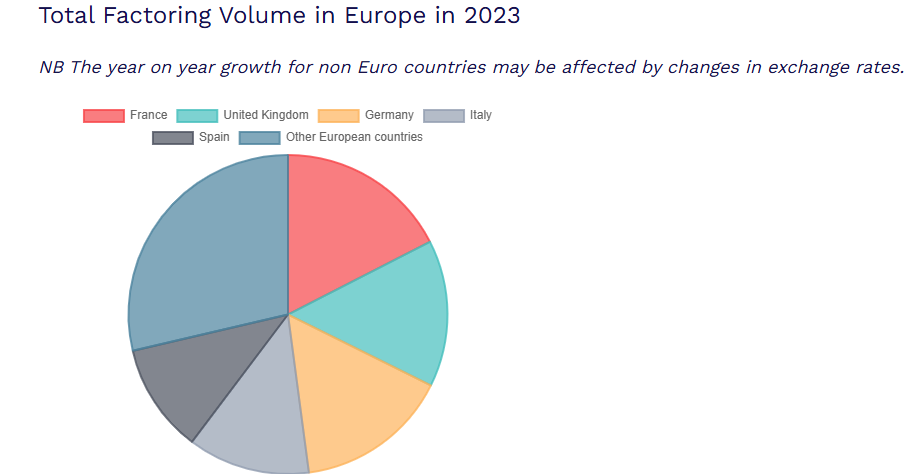
Source: EU National Associations and FCI statistics.
Emerging Trends
- Integration with Supply Chain Finance: Reverse factoring is increasingly being integrated with broader supply chain finance solutions. This integration optimizes the flow of funds within the supply chain, enhancing working capital management and reducing risks associated with financial operations.
- Technological Advancements: The adoption of new technologies such as artificial intelligence and digital platforms is reshaping reverse factoring. These technologies streamline the process, making it more efficient and accessible to a wider range of businesses.
- Rising Popularity of Non-Banking Financial Institutions (NBFIs): There’s a growing shift towards using non-bank financial services for reverse factoring, driven by the need for more flexible and tailored financial solutions.
- Economic and Geopolitical Influences: The broader economic environment, including interest rate fluctuations and geopolitical tensions, significantly impacts the reverse factoring market. These factors influence the liquidity and financing conditions, thereby affecting the adoption and execution of reverse factoring strategies .
- Regulatory and Compliance Developments: New commercial finance disclosure regulations are affecting the industry, requiring more transparent and consumer-style disclosures. This is changing how companies approach and manage reverse factoring, ensuring greater compliance and accountability in financial transactions.
Top Use Cases
- Automotive and Manufacturing: Companies in these sectors frequently utilize reverse factoring to manage payments to large networks of suppliers. This arrangement ensures that suppliers receive their payments promptly, which is crucial for maintaining uninterrupted production lines and meeting delivery timelines.
- International Trade: Reverse factoring is particularly beneficial for companies engaged in international trade. It allows them to manage open trade accounts more efficiently, helping overcome challenges related to foreign customs, documentation, and extended payment cycles. This use case is vital for enhancing liquidity and facilitating smoother trade operations across borders.
- Electronics and High-Tech Industries: In industries where the product lifecycle is short and the demand for rapid innovation is high, reverse factoring helps companies quickly pay suppliers for components and raw materials. This accelerates production processes and enables companies to bring new products to market more swiftly.
- Retail and Consumer Goods: Reverse factoring helps retail companies manage seasonal inventory demands by providing the necessary working capital to stock up in advance. It ensures suppliers are paid on time, which is essential for securing inventory during peak shopping seasons and for promotional events.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, reverse factoring facilitates the timely purchase of medical supplies and equipment, ensuring that healthcare providers can maintain service levels without cash flow interruptions. It also supports expansions and improvements in healthcare services by freeing up capital that can be invested in facility upgrades and new technologies.
Major Challenges in Reverse Factoring
- Trust Issues Between Supplier and Buyer: Reverse factoring necessitates a high level of trust, as both parties must adhere to the agreed terms. If the buyer fails to fulfill payment obligations, the supplier faces financial risks, which can strain or sever business relationships.
- Complexity in Agreement Terms: The drafting of reverse factoring agreements requires meticulous attention to detail to avoid ambiguity regarding payment schedules, interest rates, and terms. This complexity can deter some companies from adopting reverse factoring.
- VAT Compliance: Navigating VAT regulations can be challenging, especially when transactions involve multiple jurisdictions. Companies must implement precise systems to manage VAT correctly to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
- Technological Integration: To facilitate efficient reverse factoring, businesses must integrate their financial and invoicing systems with those of the financial institutions. This technological integration is crucial for real-time data sharing and automation but can be resource-intensive and complex to manage.
- Economic and Regulatory Changes: Reverse factoring can be susceptible to economic fluctuations and changes in financial regulations, which may affect the terms and viability of financing arrangements. Companies need to stay updated and adaptable to these changes to maintain the efficacy of their reverse factoring setups.
Market Opportunities in Reverse Factoring
- Enhanced Working Capital Management: By providing businesses with immediate access to cash, reverse factoring helps improve their working capital management, enabling them to fund operations or expand business activities more effectively.
- Financial Flexibility for Suppliers: Suppliers benefit from quicker payment processes, which can significantly improve their cash flow and financial stability. This advantage is particularly important for smaller suppliers who may have less financial buffer.
- Strengthened Supplier Relationships: By offering reverse factoring, buyers can solidify their relationships with suppliers. This financial tool demonstrates the buyer’s commitment to the supplier’s financial health, potentially leading to more favorable terms and cooperation.
- Technological Advancements: The integration of advanced technologies like blockchain in reverse factoring processes promises greater transparency, security, and efficiency. These innovations can reduce costs and streamline operations, making reverse factoring more attractive and accessible.
- Global Market Expansion: As more businesses recognize the benefits of reverse factoring, its adoption is expected to grow, particularly in emerging markets. This expansion provides significant opportunities for financial institutions and technology providers to develop new products and services tailored to diverse market needs.
Recent Development
- HSBC Holdings plc: HSBC has launched a new digital platform for reverse factoring aimed at streamlining the supply chain finance process for its corporate clients. This platform leverages blockchain technology to ensure transparency and security in transactions, making it easier for suppliers to get early payments on their invoices (July 2024).
- JPMorgan Chase & Co.: JPMorgan has announced a significant investment in expanding its branch network, including enhancements in its reverse factoring services. The bank is focusing on providing better access to financing for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) through improved digital tools and localized support (February 2024).
- BNP Paribas and Deutsche Bank AG: BNP Paribas completed the transfer of Global Prime Finance and Electronic Equities from Deutsche Bank. This move strengthens BNP Paribas’ position in the European market and enhances its ability to offer comprehensive reverse factoring solutions to its clients (February 2024).
- Standard Chartered PLC: Standard Chartered has rolled out a new reverse factoring program targeting sustainable supply chains. The initiative is designed to support suppliers who adhere to environmental and social governance (ESG) standards, providing them with access to more favorable financing terms (April 2024).
- DBS Bank Limited: DBS Bank has introduced a mobile app feature that enables real-time monitoring and management of reverse factoring agreements. This innovation aims to simplify the financing process for suppliers and enhance the overall efficiency of supply chain operations (March 2024).
- CaixaBank S.A.: CaixaBank has entered into a partnership with Traxpay GmbH to enhance its reverse factoring offerings. The collaboration will integrate Traxpay’s platform with CaixaBank’s services, allowing for more flexible and scalable financing solutions for its corporate clients (January 2024).
- Banco Santander S.A.: Banco Santander has expanded its reverse factoring services to include more diverse sectors such as healthcare and technology. This expansion is part of the bank’s strategy to support the growth of key industries in the post-pandemic economy (May 2024).
- UniCredit S.p.A.: UniCredit has launched a new initiative focused on digitizing its reverse factoring processes. This includes the use of AI to predict and mitigate risks in the supply chain, ensuring smoother transactions for all parties involved (June 2024).
- PrimeRevenue Inc.: PrimeRevenue has updated its reverse factoring platform to include advanced analytics features. These features help suppliers and buyers gain deeper insights into their cash flow and optimize their working capital management (March 2024).
Conclusion
In conclusion, the reverse factoring market is set to play a crucial role in modern financial ecosystems, offering a robust solution to enhance cash flow and fortify supplier relationships. By providing quick liquidity to suppliers, particularly SMEs, reverse factoring mitigates the financial strain caused by long payment terms.
Despite the complexities in setup and management, as well as the dependency on financial stability, the benefits are substantial. With increased awareness and understanding, these challenges can be navigated effectively. Buyers gain from improved negotiation terms, while suppliers enjoy predictable cash flows, collectively reducing supply chain risks. As the business community continues to recognize these advantages, the adoption of reverse factoring is poised to grow, fueling further market expansion and innovation in financial solutions.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



