Table of Contents
Introduction
Smart City Statistics: A smart city is an urban area that uses technology, data, and innovative solutions. To enhance the quality of life for its residents, optimize resource management, and improve overall urban operations.
The concept of a smart city revolves around integrating various digital technologies and data-driven strategies. To address urban challenges and create more sustainable, efficient, and livable environments.
Ultimately, a smart city aims to improve its inhabitants’ overall quality of life by providing efficient services. Like reducing pollution, enhancing public spaces, and promoting social inclusion.

Editor’s Choice
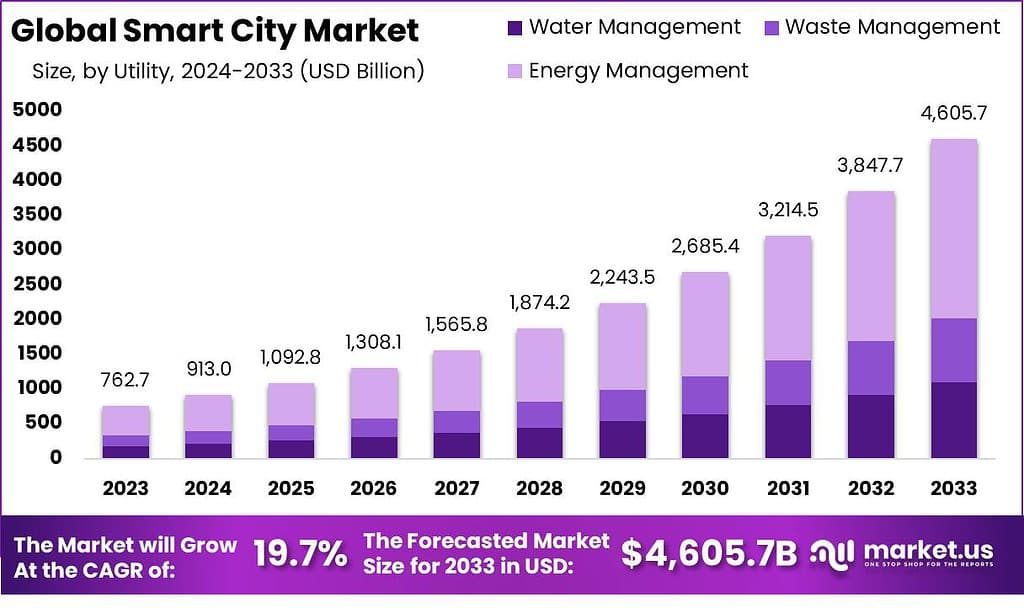
- The Global Smart City Market size is expected to be worth around USD 4,605.7 billion by 2033 from USD 762.7 billion in 2023.
- Growing at a CAGR of 19.7% during the forecast period from 2022 to 2032.
- Smart cities are expected to generate a substantial economic benefit of approximately $20 trillion by 2026.
- Cities embracing Smart City solutions could enhance their energy efficiency by 30% over two decades.
- Within OECD nations, the adoption of digital government services tripled from 2006 to 2016. With 36% of citizens chose online submissions in 2016.
- In the European Union, integrating digital services has led to an 85% reduction in city operating costs.
- According to Yonsei University’s Smart City Development Index, roughly one-third of cities provide Smart City services through apps or websites for transportation.
- 23% for culture and tourism, and 8% for city administration.
- Based on IMD’s Smart City Index, the top-ranked Smart Cities include Singapore, Helsinki, and Zurich.
- Leading Smart City governments globally encompass Singapore, Seoul, London, Barcelona, and Helsinki.
Smart City Statistics – By Market Revenue
- For the next decade, the revenue generated by Smart Cities is expected to exhibit substantial growth.
- In 2020, Smart City revenue stood at $43.72 billion, which surged to $58.98 billion in 2021, reflecting a notable uptick.
- The upward trajectory continued in 2022, reaching $74.24 billion; by 2023, it is projected to climb to $89.49 billion.
- The trend of remarkable expansion persists, with anticipated revenues of $104.8 billion in 2024 and $120 billion in 2025.
- As we progress to 2026, Smart City revenue is forecasted to reach an impressive $135.3 billion.
- Demonstrating the increasing significance of smart urban developments.
- Looking further ahead, the trajectory remains positive, with projected revenues of $150.5 billion.
- In 2027 and $165.8 billion in 2028, underscoring Smart Cities’ continued global economic vitality.
(Source: Statista)

Population and Urbanization
Smart City Statistics by Population Growth in Urban Areas
- Currently, 55% of the global population resides in urban regions, which is anticipated to rise to 68% by 2050.
- This shift from rural to urban living, known as urbanization, is coupled with overall population growth. Will result in an additional 2.5 billion people dwelling in urban areas by 2050.
- Approximately 90% of this growth is expected in Asia and Africa.
- Presently, the most urbanized region is North America (82% urban population in 2018).
- Latin America and the Caribbean (81%), Europe (74%), and Oceania (68%).
- In contrast, Asia’s urbanization rate is approximately 50%.
- Africa remains largely rural, with 43% of its population residing in urban areas.
(Source: United Nations)
Smart City Statistics by Cities Ranking and Mega Cities
- In the realm of global urban centers, Tokyo-Yokohama, Japan, stands as the most populous, boasting a staggering 37.7 million inhabitants.
- Jakarta, Indonesia, has 33.8 million residents, and Delhi, India, has 32.2 million, following closely behind.
- Other major metropolises on this list include Guangzhou-Foshan, China, at 26.9 million. Mumbai, India, has 25 million inhabitants, and Manila, Philippines, has 24.9 million inhabitants.
- Shanghai, China, is home to 24.1 million people.
- While Sao Paulo, Brazil, and Seoul-Incheon, South Korea, each house over 23 million residents.
- Meanwhile, Mexico City, Mexico, and New York, United States.
- Round out this list of global giants with populations of 21.8 million and 21.5 million, respectively.
- These cities showcase urban life’s incredible diversity and density across the world’s bustling metropolitan hubs.
(Source: Statista)

Infrastructure and Connectivity
Smart City Statistics by Internet Access and Broadband Penetration
- In 2022, approximately 66% of the global population was connected to the internet.
- Urban areas worldwide had an internet usage rate of about 82%, while rural areas lagged at 46%.
- The lowest internet access was recorded in rural regions of Landlocked Developing Countries (LLDCs), where only 26% of the population had internet access.
- In contrast, small island developing countries boast a high internet adoption rate.
- With 82% of their residents connected to the web.
- A report from Kaleido Intelligence predicts a substantial surge of over 140% in the use of data by smart cities between 2023 and 2027.
- This growth will be driven by increasing cellular connections in Internet of Things (IoT) projects within smart cities. These connections’ expected compound annual growth rate is 17.9% from 2022 to 2027, reaching over 122 million.
- With particularly rapid expansion in the next two years.
- Most of these connections will be in smart lighting applications, with projections of more than 161 million interconnected lights utilizing cellular connections.
- Despite the deployment of Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN).
- A significant amount of data traffic is expected due to the large network endpoints.
- To manage this effectively, Edge Computing will be essential, potentially reducing data transfer by over 80% in some instances.
- One of the most lucrative sectors in terms of connectivity revenues will be intelligent traffic management, primarily driven by video usage.
- Revenue per airtime in this sector is forecasted to surpass US$900 million by 2027.
- A substantial increase from the US$292 million recorded in 2022.
(Source: Statista, Kaleido Intelligence)
Energy Infrastructure in Smart City Statistics
- Smart cities in the United States, Denmark, Canada, India, and Australia efficiently meet their energy needs using Renewable Energy Sources (RES), accounting for 40% to 100% of their energy supply. RES is acknowledged as the most eco-friendly energy generation method.
- As per the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) net-zero plan.
- RES is set to contribute 84% of global electricity production, 65% to household heating, and 38% to industrial heating by 2040.
- Globally, the share of electricity generated from RES is projected to reach 61% by 2030 and a substantial 88% by 2050.
- However, it appears unlikely that Russia will achieve an 80% share of electricity generation from RES by 2040.
- Projections from the Skolkovo Research Center suggest that by 2040.
- The consumption of all renewable energy sources, including hydropower, will grow by 76% to 115%.
- The global energy consumption share provided by RES (excluding nuclear energy) is expected to range from 19% to 25% by 2040. Simultaneously, the share of oil and coal in primary energy consumption is anticipated to decline worldwide gradually.
(Source: Skolkovo Research Center)
Water Supply and Sanitation
- Between 2000 and 2030, Africa and Asia are expected to witness a doubling of their urban populations.
- There were notable improvements in drinking water and sanitation access between 1998 and 2008.
- With 1052 million gaining access to better drinking water and 813 million to improved sanitation, these gains were partly offset by a concurrent urban population increase of 1089 million.
- On a global scale, approximately one in four urban residents, 789 million individuals, lack access to improved sanitation facilities.
- Furthermore, the number of city dwellers relying on shared sanitation rose to 497 million, compared to 249 million in 1990.
- Additionally, in the developing world, 27% of urban residents do not have access to piped water in their homes.
- In metropolitan distribution systems, leakage-loss rates exceeding 50% are not unusual.
- Between 250 and 500 million m3 of potable water is lost annually in many megacities.
- In each megacity, this quantity may supply more than 10 to 20 million people with drinking water.
(Source: United Nations)
Smart City Statistics by Investments in Smart City Infrastructure
- Opportunities for investing in nature-based solutions and land-sparing interventions, promoting environmentally friendly urban development.
- They could reach approximately 600 billion U.S. dollars globally by 2030.
- In 2021, investments in nature-based solutions amounted to just 28 billion U.S. dollars, but there is the potential for this figure to increase to 113 billion U.S. dollars by the year 2030.
- As of October 2022, the High-Speed Rail Line in California, USA, stood out as one of the most valuable infrastructure endeavors globally, whether in the planning stages or actively being constructed.
- A significant portion of the notable infrastructure projects currently in progress worldwide primarily consists of railway systems.
- These railway projects spanned across various regions, including Norway and Sweden, the United Kingdom, the United States, parts of Asia, South-East Asia, and Japan.
- Notably, India had the highest count of substantial infrastructure initiatives valued at more than 25 million U.S. dollars.
(Source: Statista)

Economic Indicators of Smart Cities
Smart City Statistics by GDP Growth in Smart Cities
- At the top of the list, the City of San Marino stands out with a GDP of $1.54 billion, representing an astonishing 90.872% of San Marino’s national GDP.
- Similarly, Luxembourg City-Trier boasts a robust GDP of $69.45 billion, contributing significantly to Luxembourg’s economy at 79.925% of its national GDP.
- Moving across the globe, we find Montevideo in Uruguay, where its GDP of $49.70 billion accounts for 77.314% of the national GDP.
- Further east, Seoul in South Korea has a substantial GDP of $926.79 billion, making up 51.355% of the country’s total GDP.
- Riga in Latvia, with a GDP of $20.00 billion, contributes 49.670% to the national GDP, while Taipei in Taiwan follows closely behind, with a GDP of $407.84 billion, constituting 48.482% of Taiwan’s national GDP.
- Bangkok in Thailand, Lima in Peru, and Manila in the Philippines all play pivotal roles in their respective nations’ economies, with their metropolitan GDPs accounting for 48.299%, 47.344%, and 46.750% of their national GDPs, respectively.
- As we move on to Europe, Lisbon in Portugal and Athens in Greece demonstrate their economic significance, contributing 43.666% and 42.061% of their national GDPs, respectively.
- Meanwhile, Tokyo, Japan’s capital, with a massive GDP of $2055.70 billion, represents 41.849% of Japan’s total GDP.
- Further north, Copenhagen in Denmark and Paris in France play pivotal roles in their nations’ economic landscapes, contributing 33.676% and 28.920% to their national GDPs.
- Lastly, Auckland in New Zealand, Helsinki in Finland, Kabul in Afghanistan, and Budapest in Hungary each have their unique economic significance, contributing 30.971%, 30.509%, 29.797%, and 29.573% to their respective national GDPs.
- London, the United Kingdom’s capital, rounds out the list, with a massive GDP of $978.40 billion, representing 28.981% of the UK’s total GDP.
(Source: Visual Capitalist)
Smart City Statistics by Employment Rates
- In 2019, several major cities in the United States exhibited varying population growth rates, reflecting their dynamic appeal to residents. San Francisco County/City, CA, led the pack with an unemployment rate of 2.2%, securing the top rank in this list.
- Following closely were Honolulu County/City, HI, and Seattle City, WA, with a rate of 2.4%, sharing the second position.
- Austin City, TX, and Nashville-Davidson (consolidated) City, TN, tied for the fourth spot with an unemployment rate of 2.5%.
- Meanwhile, Denver County/City, CO, exhibited an unemployment rate of 2.6%, landing it in the sixth position. At the same time, Boston City, MA, and San Jose City, CA, shared the seventh spot with an unemployment rate of 2.7%.
- Joining them in seventh place was Virginia Beach City, VA, with a rate of 2.7%.
- Lastly, Miami City, FL, rounded out the list with an unemployment rate of 2.8%, making it the tenth-ranked city in terms of unemployment in 2019.
More Insights
- The employability rates in various Indian cities paint an intriguing picture of the job market landscape. Mumbai leads the way with a robust employability rate of 74%, reflecting its economic powerhouse and job hub status.
- Lucknow closely follows with a commendable employability rate of 73.5%, showcasing its growing employment opportunities.
- New Delhi, the capital city, maintains a healthy employability rate of 68.89%, indicative of its diverse job market.
- Pune and Faridabad are not far behind, boasting employability rates of 68.02% and 67.02%, respectively, highlighting their significance as employment centers.
- Kolkata, known for its cultural heritage, registers an employability rate of 65.38%, while Bengaluru, often dubbed the “Silicon Valley of India,” stands at 64.02%.
- Further down the list, Bellary and Kurnool exhibit employability rates of 63.49% and 59.24%, indicating employment opportunities in these regions.
- Mangalore rounds out the data with an employability rate of 56.48%.
(Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics, Statista)

Notable Smart City Initiatives Statistics
Singapore
- Singapore launched its Smart Nation initiative in 2014, implementing various smart technologies in the public and private sectors.
- This includes the widespread adoption of contactless payments for the 7.5 million passengers using public transportation.
- Singapore introduced a digital health system to address challenges posed by an aging population, promoting video consultations and wearable IoT devices for patient monitoring.
- In 2021, Singapore announced plans for an eco-smart city in Tengah, the western region, which will be entirely vehicle-free.
- This forest city will comprise five residential districts with 42,000 houses, prioritizing safe zones for pedestrians and cyclists.
(Source: Earth.org)
Helsinki, Finland
- Helsinki is determined to achieve carbon neutrality by 2035 and has made significant progress.
- In 2017, they had already reduced emissions by 27% compared to 1990.
- They are also committed to cutting traffic emissions by 69% by 2035 by transitioning the entire city bus fleet to electric, expanding public transportation networks, and increasing electric car charging infrastructure.
- Given that heating contributes to over half of the city’s emissions, Helsinki focuses on energy-efficient renovations that could reduce building emissions by 80%. Additionally, they aim to incorporate more renewable energy sources into city buildings.
(Source: Earth.org)
Oslo, Norway
- Oslo, Norway, with a population of around 670,000, is making a remarkable push for electric vehicles, aiming to have all vehicles in the city go electric by 2025.
- They’ve introduced incentives like free parking, access to bus lanes, and reduced taxes and toll prices for zero-emission cars.
- Oslo is committed to becoming carbon neutral by 2050. It implements various smart initiatives, such as zero-emission construction sites and retrofitting existing buildings to establish circular waste management and green energy systems.
(Source: Earth.org)
New York City, United States
- New York is outfitting 10,000 city intersections with cameras and sensors to create a connected infrastructure with adaptive signals.
- They’ve also launched a Connected Vehicle Pilot Program to gather and analyze data from connected vehicles, which will help enhance real-time safety and traffic management through V2X initiatives.
(Source: Otonomo)
London, United Kingdom
- In 2020, London introduced the Smart Mobility Living Lab (SMLL), a cutting-edge urban testing ground. SMLL offers 5G connectivity for connected and self-driving cars.
- According to O2, the mobile operator behind SMLL, this initiative could:
- Cut traffic time by 10% for drivers.
- Save £880 million annually.
- Lower yearly CO2 emissions by 370,000 metric tons.
(Source: Otonomo)
Paris, France
- Paris has made significant strides in road safety and traffic management since 2010, resulting in a 40% reduction in traffic fatalities.
- Additionally, the city is set to invest 100 million euros in enhancing its transportation infrastructure for connected and autonomous vehicles.
- Furthermore, Paris is in the process of replacing its entire bus fleet with electric vehicles.
(Source: Otonomo)
Recent Developments
Acquisitions:
- Siemens’ Acquisition of Brightly Software: Siemens Smart Infrastructure acquired Brightly Software, a leading U.S.-based SaaS asset and maintenance management solutions provider, for an undisclosed amount in June 2022. This acquisition aims to strengthen Siemens’ position in the building and infrastructure software market, enhancing its capabilities in smart city solutions.
- IBM’s Acquisition of Neudesic: IBM acquired Neudesic, a prominent Microsoft Azure consultancy, in February 2022. This acquisition expands IBM’s portfolio of hybrid multi-cloud services and supports its strategy in hybrid cloud and AI.
New Product Launches:
- Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure for eMobility: In December 2021, Schneider Electric launched EcoStruxure for eMobility in buildings.
- This end-to-end EV charging solution aims to enhance energy management and support net-zero buildings by accommodating increased power demand from electric vehicles.
Funding:
- Australian Government’s Investment in Digital Economy: In December 2021, the Government of Australia announced an investment of USD 135.9 million to transform the economy into a digital economy by 2030.
- This initiative includes the creation of a regulatory framework for BFSI infrastructure to support evolving payment systems and crypto ecosystems.
Market Growth:
- Global Smart Cities Market Expansion: This growth is driven by urbanization, technological advancements, and supportive government policies aimed at enhancing connectivity and quality of life in urban areas.
Innovation in Smart Utilities:
- Advancements in Energy Management: The energy management segment, which accounted for over 55% of the smart utilities revenue in 2022, is seeing significant advancements.
- Technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT are being integrated into virtual power plants to enhance security and efficiency.
- The waste management segment is also expected to grow at a CAGR of 27.0%, driven by smart trash bin installations and mobile apps for monitoring bin fill levels.
Strategic Partnerships:
- Sierra Wireless and Orange Partnership: In January 2023, Sierra Wireless partnered with Orange to enhance connectivity services and bolster smart connectivity solutions.
- This collaboration aims to improve the deployment of IoT products across various applications, supporting the growth of smart city infrastructure.
Conclusion
Smart City Statistics – In an era defined by urbanization and technological advancement, the concept of smart cities has emerged as a transformative force in shaping the future of urban living.
They are characterized by their reliance on data and technology to optimize services, improve efficiency, and enhance the quality of life for residents. Smart city initiatives have a tangible impact on the lives of residents.
Access to healthcare, education, cultural amenities, and safety all play pivotal roles in shaping a city’s livability.
Also, investments in innovation hubs, startups, and technology sectors fuel economic expansion and job creation, positioning smart cities as hubs for talent and entrepreneurship.
FAQs
A smart city is an urban area that uses data and technology to improve its residents’ efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life. It involves the integration of digital solutions, IoT devices, and data analytics to enhance various aspects of urban living.
Smart cities employ real-time traffic monitoring, smart traffic lights, and public transportation apps to reduce congestion, improve traffic flow, and enhance mobility options, such as bike-sharing and electric vehicles.
Smart cities often focus on sustainability by promoting renewable energy adoption, reducing carbon emissions, implementing green building standards, and optimizing waste management processes to minimize environmental impact.
Smart cities implement robust data privacy and security measures. They anonymize data, employ encryption, and adhere to strict regulatory frameworks to protect residents’ privacy while using data for urban improvements.
Smart cities encounter challenges such as funding infrastructure upgrades, ensuring equitable access to technology, addressing data privacy concerns, and balancing sustainability goals with economic growth.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



