Table of Contents
Introduction
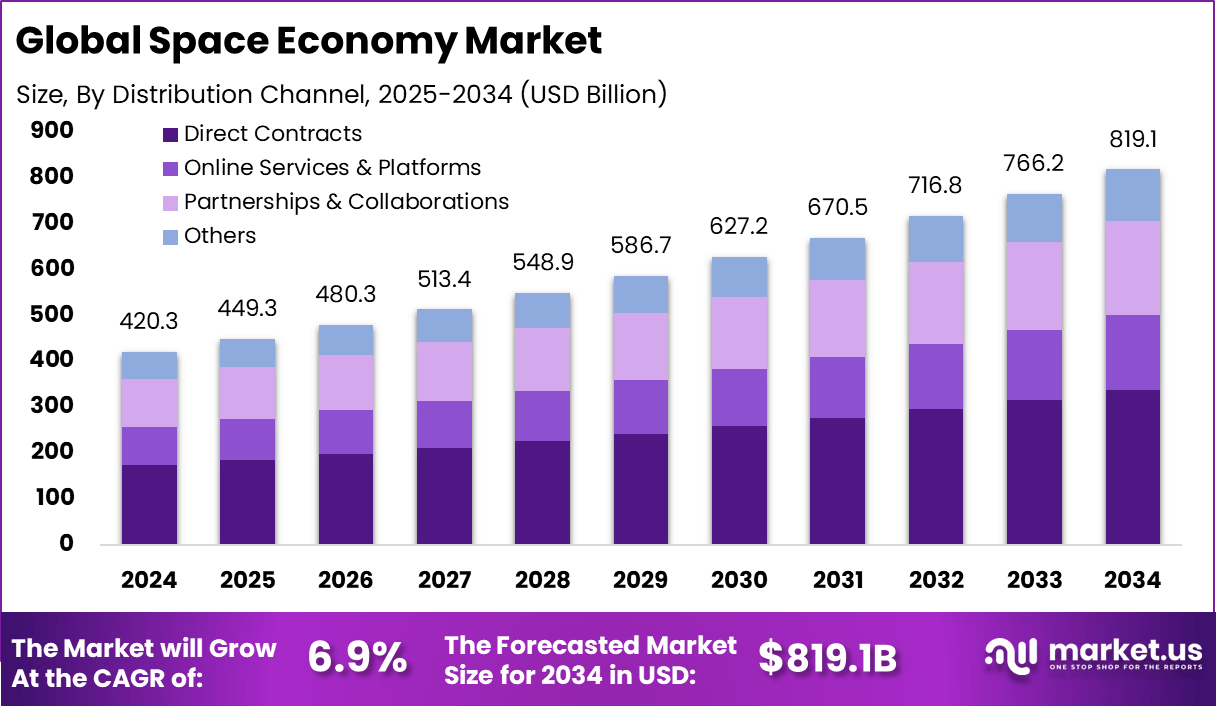
The Global Space Economy Market is on a trajectory of powerful expansion. In 2024, it generated USD 420.3 billion, with North America capturing over 35.5% of the market at USD 149.2 billion. Over 2025–2034, the market is forecast to grow from USD 449.3 billion to USD 819.1 billion, representing a CAGR of 6.9 %. This growth underscores accelerating investments in satellite deployment, space services, launch systems, and upstream technologies, as both public agencies and private players scale ambitions in low-Earth orbit (LEO), Earth observation, and space tourism.
How Growth is Impacting the Economy
The expansion of the space economy is generating widespread economic ripple effects. First, capital flows into aerospace, satellite manufacturing, launch services, and ground-segment infrastructure are boosting demand for specialty components, optics, sensors, propulsion, and materials — stimulating innovation and employment in high-tech supply chains.
Second, downstream services (e.g. satellite communications, Earth observation analytics, navigation, space-based IoT) are enabling new business models across agriculture, logistics, energy, environment and telecommunications — driving productivity and adding value across sectors. Third, nations investing heavily in space are enhancing sovereignty, national security, and technological leadership, attracting foreign investment and fostering exports of space services. Collectively, this supports high-value skilled jobs and strengthens the high-technology industrial base.
➤ Smarter strategy starts here! Get the sample – https://market.us/report/space-economy-market/free-sample/
Impact on Global Businesses
Rising Costs & Supply Chain Shifts
Entering or scaling in the space sector involves high capital expenditures, stringent regulatory compliance, and long lead times for components like propulsion systems, satellite buses, and launch vehicles. As demand surges, supply chains are under pressure: competition for specialty materials, sensors, and propulsion subsystems drives cost escalation and supplier consolidation. Firms may relocate production closer to aerospace clusters or vertically integrate.
Sector-Specific Impacts
- Telecommunications & Connectivity: Satellite internet providers are scaling networks, increasing competition with terrestrial providers.
- Earth Observation & Analytics: Growing use in agriculture, climate monitoring, disaster management, and insurance.
- Navigation & Positioning: Enhanced GNSS augmentation services, new constellations for precision applications.
- Space Tourism & Human Spaceflight: Firms developing suborbital / orbital experiences, life-support systems, and space habitats.
- Launch & Infrastructure: Companies investing in reusable rockets, small-sat launchers, space stations, and on-orbit servicing.
Strategies for Businesses
- Focus on modular & scalable architectures for satellites and launchers to reduce risk.
- Leverage partnerships and consortia (governments, research institutions, private firms) to share cost and technology.
- Invest in software, analytics, AI capabilities to enhance downstream service value.
- Develop in-house R&D and component sourcing to reduce reliance on external suppliers.
- Adopt lean iteration and rapid prototyping to shorten development cycles and manage capital allocation.
Key Takeaways
- The space economy is forecast to grow from ~USD 449.3 billion in 2025 to ~USD 819.1 billion by 2034 (CAGR ~6.9 %)
- North America is the dominant region with over 35.5 % share in 2024
- Growth stimulates high-tech investment, downstream services, and national competitiveness
- Businesses face high CapEx, tight supply chains, and regulatory barriers
- Strategies: modular design, partnerships, vertical integration, software value-add, lean prototyping
➤ Unlock growth secrets! Buy the full report – https://market.us/purchase-report/?report_id=161168
Analyst Viewpoint
Currently, the space economy is in transition from government-led programs toward more commercial, competitive markets. In the future, we expect broader democratization of space — with smaller entrants, commoditized launch services, and proliferation of analytics and data monetization models. As barriers to entry fall, the space economy will integrate intimately with terrestrial industries (agriculture, logistics, energy, communications). The long-term outlook remains strongly positive: space will become a vital frontier in the global digital infrastructure.
Use Cases & Growth Factors
| Use Case | Growth Factors / Drivers |
|---|---|
| Satellite broadband & connectivity | Rising demand for global internet, remote coverage |
| Earth observation & analytics services | Climate monitoring, precision agriculture, insurance |
| Navigation & positioning augmentation | High-precision demands in autonomous systems |
| Space tourism & human spaceflight | Consumer interest, reduced cost per seat |
| On-orbit servicing / debris removal | Satellite maintenance, sustainability, life extension |
| Growth Drivers | Falling launch costs, miniaturization, reusable rockets, AI analytics, private investment, regulatory support, constellations scaling |
Regional Analysis
North America leads with a mature aerospace and defense ecosystem, strong investment capital, and established agencies engaging private firms. Europe has strong capabilities in satellite systems, Earth observation, and policy support. Asia Pacific is rapidly expanding, led by China, India, Japan, and South Korea with national programs and commercial entrants. Latin America, Middle East, and Africa are emerging regions focusing on satellite connectivity and Earth observation to bridge infrastructure gaps. Regional dynamics reflect differences in regulation, capital access, and industrial base.
➤ More data, more decisions! see what’s next –
- AI Career Coach Market
- AI Mirror Market
- AI-Based Weather Modelling Market
- Neuromorphic Hardware Market
Business Opportunities
Numerous opportunities lie ahead: satellite manufacturing, propulsion & avionics subsystems, small-sat and cubesat platforms, launch services (especially small / reusable rockets), ground segment hardware & software, data analytics & AI services, remote sensing platforms, space tourism infrastructure, on-orbit servicing & in-space manufacturing, and regulatory / certification consulting. Consistent demand exists for scalable, modular systems and recurring service revenue models.
Key Segmentation
Key segments include component & subsystem (propulsion, avionics, sensors, structure), platform / satellite systems, launch services, data & services (analytics, connectivity, earth observation), and ground infrastructure/software. Also by verticals: telecommunications, defense, agriculture, environment, energy, navigation, tourism. Further segmentation by satellite size (small, medium, large) and orbit (LEO, MEO, GEO).
Key Player Analysis
The competitive landscape features a mix of established institutions and agile newcomers. Differentiators include vertical integration (from manufacturing to services), proprietary propulsion and reusable technologies, software & analytics platforms, partnerships with governments, and cost-efficient launch models. Some firms focus on mass production of small satellites; others emphasize on-orbit servicing and life extension. Success is tied to scalability, R&D agility, cost control, and end-to-end competence.
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- SpaceX
- Blue Origin
- NASA
- Lockheed Martin
- The Boeing Company
- ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation)
- Arianespace
- OneWeb
- Rocket Lab
- Planet Labs
- Relativity Space
- Virgin Galactic
- Eutelsat
- SES S.A.
- Maxar Technologies
- Others
Recent Developments
- A private company launched a large constellation of LEO broadband satellites to expand global coverage.
- Reusable rocket technology achieved multiple re-flights, reducing per-launch costs.
- A government initiative announced funding for spaceports and regulatory reforms in emerging markets.
- A startup successfully demonstrated on-orbit satellite servicing (refueling / repair).
- Earth observation analytics platforms introduced AI-driven climate and agricultural insights for global clients.
Conclusion
The global space economy is entering a new era of scale and commercial maturity. Entities that invest in modular tech, analytics, vertical integration, and strategic partnerships are best poised to capture value in this frontier ecosystem.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



