Table of Contents
Introduction
Space Tourism Statistics: Space tourism represents a groundbreaking endeavor within the aerospace and travel sectors, allowing ordinary individuals to enter outer space.
Moreover, this enterprise involves the commercial conveyance of paying passengers beyond Earth’s atmosphere, affording them a distinctive experience of floating in microgravity. Beholding breathtaking vistas of our planet, and participating in an unparalleled space journey.
Despite appearing as a recent notion, the origins of space tourism can be traced back to visionaries from the early 20th century. Like Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, and gained traction during the Space Race era.
In the early 2000s, initiatives like SpaceShipOne materialized the actualization of commercial space travel. Further, more recently, enterprises like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic have competed to democratize space tourism, heralding a notable transformation in the industry’s landscape.

Editor’s Choice
- The space tourism market has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years, at a CAGR of 36.6%, with its revenue soaring to new heights.
- By 2027, the space tourism market is expected to surpass USD 4,162.3 billion, and this upward trajectory will continue throughout the following years. Reaching a staggering USD 17,742.4 billion by 2032.
- In this dynamic industry, commercial entities dominate with a significant market share of 57%.
- SpaceX developed the Dragon spacecraft, the first commercial spacecraft to deliver cargo to the International Space Station (ISS) in 2012.
- On July 11, 2021, VSS Unity conducted its first fully crewed test flight. Carrying Sir Richard Branson and other Virgin Galactic employees to the edge of space. This marked a significant milestone for the company.
- The orbital space travel and tourism market is expected to generate approximately USD 555 million in revenue by 2030.
- Over 55% of American adults expect that in the next 50 years. It will become common for people to travel to space for tourism.
Space Tourism Market Size and Growth Statistics
Global Space Tourism Market Size Statistics
- The space tourism market has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years, at a CAGR of 36.6%, with its revenue soaring to new heights.
- In 2022, the market generated approximately USD 847.7 billion, marking a significant start to this nascent industry.
- This trend continued to escalate in 2023, with the market revenue surging to USD 1,158.0 billion, signifying a rapid expansion in consumer interest and investment.
- As we look ahead, the market is projected to experience exponential growth. With estimates reaching USD 1,526.9 billion in 2024, USD 2,232.6 billion in 2025, and USD 3,156.5 billion in 2026.
- By 2027, the space tourism market is expected to surpass USD 4,162.3 billion, and this upward trajectory will continue throughout the following years, reaching a staggering USD 17,742.4 billion by 2032.
- These impressive figures underscore the growing prominence and economic potential of space tourism as it evolves into a significant global travel and aerospace industry player.
(Source: Market.us)
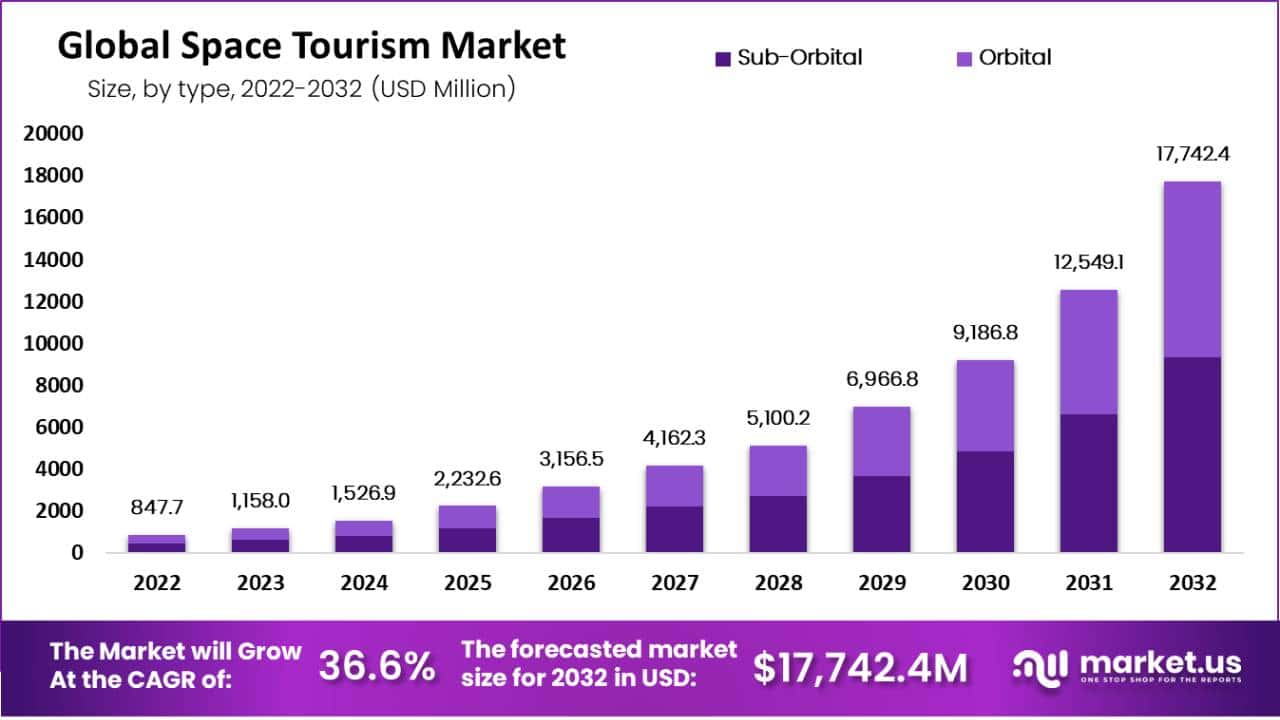
Space Tourism Market Size – By Type Statistics
- The global space tourism market has experienced remarkable growth in recent years. With revenue figures indicating its increasing popularity and economic significance.
- In 2022, the market generated a total revenue of USD 847.7 billion. With sub-orbital tourism contributed USD 446.7 billion and orbital tourism added USD 401 billion to the overall figure.
- However, this positive trend continued into 2023, as the total revenue soared to USD 1,158 billion, with sub-orbital tourism accounting for USD 610.2 billion and orbital tourism reaching USD 547.7 billion in revenue.
- The space tourism market is poised for substantial growth, with projected revenue figures showing continued expansion in sub-orbital and orbital segments.
- Further, By 2024, the total revenue is expected to reach USD 1,526.9 billion, with sub-orbital tourism generating USD 804.7 billion and orbital tourism contributing USD 722.2 billion.
- This growth trajectory persists, and by 2032, the market is forecasted to achieve a staggering total revenue of USD 17,742.4 billion.
- Sub-orbital tourism is anticipated to reach USD 9,350.2 billion. While orbital tourism is projected to account for USD 8,392.1 billion.
- These revenue figures highlight the growing appeal and economic potential of both sub-orbital and orbital space tourism segments.
- As the industry continues to evolve and mature, it is set to play a prominent role in the global travel and aerospace sectors, attracting both investors and enthusiasts alike.
(Source: Market.us)

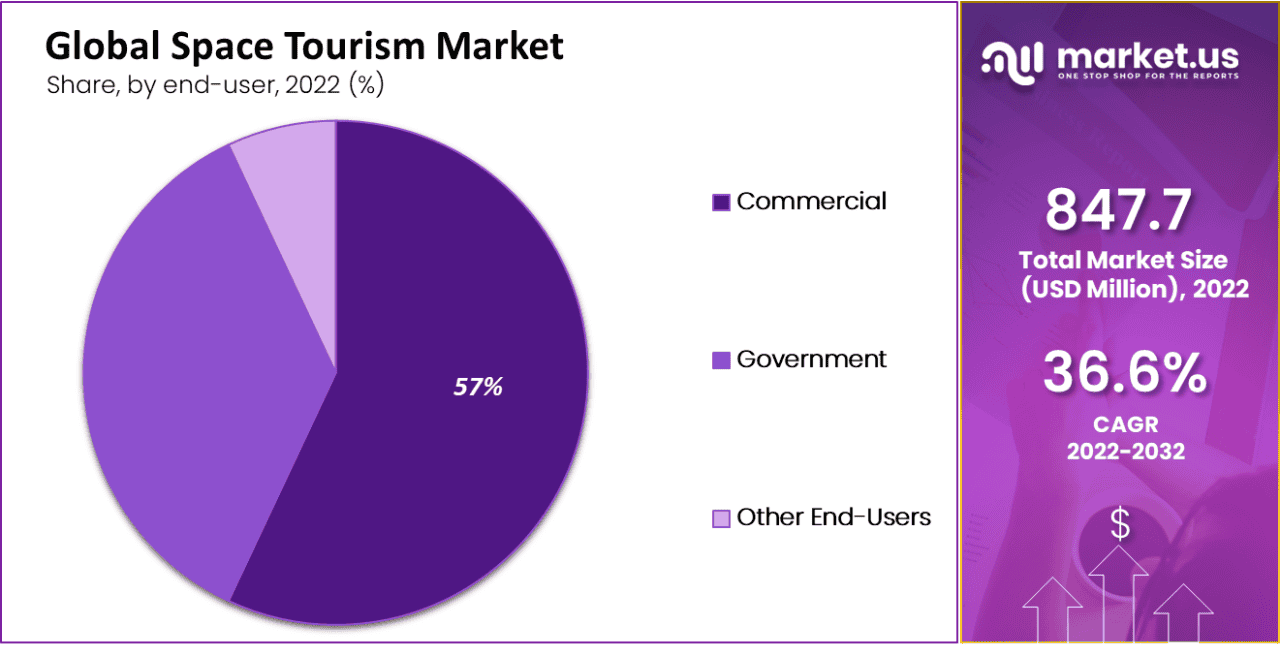
Space Tourism Market Size – By End-user Statistics
- The global space tourism market exhibits a diverse landscape regarding end-users and their respective market shares.
- In this dynamic industry, commercial entities dominate with a significant market share of 57%.
- These commercial players actively offer space tourism experiences to the public, catering to the growing demand for space travel adventures.
- In contrast, government participation in space tourism is also substantial, capturing a market share of 36%.
- Governments often play a vital role in space exploration and tourism initiatives. Contributing to developing infrastructure and regulatory frameworks that facilitate safe and responsible space tourism operations.
- Lastly, other end-users collectively account for 7% of the market share. This category may include a variety of participants, such as research institutions, educational organizations, or other specialized groups with interests in space tourism-related activities.
- This distribution of market shares among different end-users underscores the collaborative and multifaceted nature of the space tourism industry. With both commercial and governmental entities actively shaping its growth and development.
(Source: Market.us)
Space Tourism Industry Key Players Statistics
SpaceX
- SpaceX, or Space Exploration Technologies Corp., was founded by Elon Musk in March 2002.
- The company is headquartered in Hawthorne, California, USA.
- SpaceX became the first privately funded company to send a liquid-fueled rocket into orbit in 2008 with the Falcon 1.
- The company successfully launched the Falcon 9 rocket. Known for its reusability, reducing the cost of access to space.
- SpaceX developed the Dragon spacecraft, the first commercial spacecraft to deliver cargo to the International Space Station (ISS) in 2012.
- In 2020, SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft transported astronauts to the ISS as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, marking a private company’s first crewed orbital launch.
- SpaceX is developing the Starship spacecraft, designed for missions to Mars and beyond. It’s intended to be fully reusable and capable of carrying many passengers.
- SpaceX has received significant investments, estimated at over $100 billion.
- SpaceX has been increasing its launch frequency, conducting numerous commercial satellite launches and ISS resupply missions, and launching Starlink satellites for its ambitious satellite internet project.
- SpaceX’s Starlink project aims to create a global satellite internet constellation. As of 2021, it had launched thousands of satellites and initiated beta service in select areas.
(Source: SpaceXNow)
Blue Origin
- Blue Origin was founded by Jeff Bezos in 2000.
- The company is headquartered in Kent, Washington, USA.
- Blue Origin primarily focuses on the New Shepard suborbital rocket system, designed for space tourism and research missions. As of 2021, New Shepard had conducted multiple successful test flights, including crewed missions.
- Blue Origin unveiled plans for a lunar lander called “Blue Moon” in 2019. The lander is intended for missions to the Moon and is part of NASA’s Artemis program.
- Blue Origin is developing the New Glenn orbital launch vehicle, a large reusable rocket designed to carry payloads to orbit. It is expected to compete in the commercial launch market.
- Blue Origin has attracted several customers for New Shepard. Including research institutions and commercial entities interested in conducting experiments in microgravity.
- Jeff Bezos has invested a significant portion of his wealth into Blue Origin, and the company has secured contracts with NASA for various projects.
- Blue Origin has participated in space-related competitions. Such as the Google Lunar XPRIZE, which has offered substantial prizes for lunar lander development.
(Source: Blue Origin)
Virgin Galactic
- Virgin Galactic was founded by Sir Richard Branson in 2004.
- The company is headquartered in Las Cruces, New Mexico, USA, with operations at Spaceport America.
- Virgin Galactic’s flagship suborbital spaceplane is called SpaceShipTwo. It is designed to carry paying passengers on suborbital spaceflights.
- VSS Unity is the name of Virgin Galactic’s first SpaceShipTwo vehicle. It made several successful test flights before beginning its commercial operations.
- On July 11, 2021, VSS Unity conducted its first fully crewed test flight, carrying Sir Richard Branson and other Virgin Galactic employees to the edge of space. This marked a significant milestone for the company.
- Virgin Galactic operates its commercial spaceflight operations from Spaceport America in New Mexico, where SpaceShipTwo takes off and lands.
- Virgin Galactic had been selling tickets to the public for suborbital spaceflights, with prices starting at hundreds of thousands of dollars per ticket.
- Virgin Galactic intends to expand its operations and offer more frequent suborbital spaceflights to the public, potentially bringing down the cost of space tourism.
- In addition to passengers, SpaceShipTwo can carry research payloads for scientific experiments in microgravity.
- Virgin Galactic became a publicly traded company through a merger with Social Capital Hedosophia in 2019, and it is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol “SPCE.”
Orbital Space Tourism Statistics
Orbital Space Tourism Market Size Statistics
- The orbital space travel and tourism market has steadily grown in recent years.
- In 2021, the market generated approximately USD 385 million in revenue, indicating the beginning of commercial interest in orbital space travel experiences.
- This growth trend continued into 2022, with revenues reaching USD 400 million. Projections for the following years remain optimistic, with expected revenues of USD 460 million in 2023 and USD 500 million in 2024.
- However, there was a slight dip in revenue to USD 475 million in 2025, followed by further stabilization at around USD 455 million in 2026.
- The market rebounded in 2027, reaching USD 470 million, and continued to ascend, with revenues coming to USD 515 million in 2028 and USD 605 million in 2029.
- The year 2030 is expected to yield revenue of approximately USD 555 million.
- These figures reflect a growing interest in orbital space tourism as more companies and individuals explore the possibilities of commercial activities in Earth’s orbit.
(Source: Statista)

Consumer Demographics of Space Tourism Statistics
- Over 55% of American adults expect that in the next 50 years, it will become common for people to travel to space for tourism.
- About 35% of those surveyed expressed interest in going into space and orbiting the Earth in a spacecraft.
- However, 65% of respondents said they would not be interested in space tourism.
- Nearly 44% of the participants believe space tourism will not become routine by 2073.
- The survey was conducted among 10,329 adults in the US between May 30 and June 4. It aimed to understand American attitudes toward space, including private space companies, NASA, and future space expectations.
- About 70% of Americans consider it essential for the United States to continue leading in space exploration. 65% believe NASA should remain involved in space exploration despite the increasing involvement of private companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin.
- A significant 69% of those surveyed worry about human-made space debris, including rockets and satellites, in the next 50 years.
- Only 58% of respondents are confident we will not discover intelligent life or build colonies on other planets in the next 50 years.
- According to the respondents, monitoring asteroids (60%) and Earth’s climate system (50%) are the top priorities for NASA. However, sending humans to the Moon or Mars is not a top priority for most Americans.
- NASA has planned the Artemis II mission for late 2024, which involves flying astronauts around the Moon. This mission is seen as important preparation for future Mars missions.
(Source: Pew Research Center Survey)
Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- SpaceX partners with Axiom Space: In 2023, SpaceX announced a partnership with Axiom Space to provide transportation services for private missions to the International Space Station (ISS). This partnership, valued at $1.5 billion, aims to support Axiom’s long-term goal of building the world’s first commercial space station.
- Voyager Space Holdings acquired The Launch Company: In mid-2023, Voyager Space Holdings acquired The Launch Company, a firm specializing in space launch logistics. The acquisition strengthens Voyager’s capabilities in supporting space tourism missions and infrastructure development.
New Product Launches:
- Virgin Galactic’s VSS Imagine: In 2023, Virgin Galactic introduced its new spaceship, VSS Imagine, which is designed to carry tourists to the edge of space. This spacecraft is part of the company’s plan to offer regular suborbital flights to space, with ticket prices starting at $450,000 per person.
- Blue Origin’s Orbital Reef project: In late 2023, Blue Origin announced its plans for the Orbital Reef. A commercial space station designed for space tourism, research, and industrial use. The project is expected to be operational by 2030 and aims to host private space tourists along with researchers.
Funding:
- Space Perspective raises $60 million in Series B funding: In 2023, Space Perspective, a space tourism company that offers balloon-based trips to the edge of space, secured $60 million in Series B funding. The funds will be used to scale production and develop more spacecraft, with commercial flights expected to begin in 2024.
- Zero 2 Infinity raises $40 million for near-space flights: In early 2024, Zero 2 Infinity, a Spanish-based space tourism startup. Raised $40 million to develop its balloon-based space tourism platform. The company plans to offer near-space experiences with an altitude of up to 40 kilometers by 2025.
Technological Advancements:
- Reusable Spacecraft Technology: The development of reusable spacecraft is reducing costs and making space tourism more accessible. By 2025. Reusable spacecraft are expected to account for 50% of commercial space tourism flights, as companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin continue to innovate in spacecraft recovery and reuse.
- AI Integration for Space Travel: AI is playing a growing role in space tourism, enhancing safety, navigation, and customer experience. By 2025, over 25% of space tourism companies are expected to integrate AI for customer support, personalized experiences, and flight safety monitoring.
Market Dynamics:
- Growth in the Space Tourism Market: This growth is driven by increasing interest from wealthy individuals. Advancements in reusable spacecraft technology, and the expansion of private space stations and tourism infrastructure.
- Rising Demand for Suborbital Flights: Suborbital flights, which offer short trips to space without entering full orbit, are becoming more popular due to their lower costs. By 2025, suborbital flights are expected to account for 60% of the space tourism market, attracting customers interested in brief space experiences.
Conclusion
Space Tourism Statistics – In conclusion, space tourism is an exhilarating frontier in the aerospace and travel sectors.
Offering civilians an unprecedented journey beyond Earth’s bounds, replete with the marvel of weightlessness and breathtaking celestial vistas.
While rooted in the visionary imaginings of the early 20th century, space tourism has burgeoned into reality through pioneering efforts by companies such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic.
These firms have notched remarkable achievements, from launching private rockets into orbit to ferrying paying passengers on suborbital and orbital flights.
The space tourism market is poised for substantial growth. Buoyed by projections of soaring revenues in the years ahead.
Nonetheless, this burgeoning industry confronts formidable challenges, encompassing safety considerations, regulatory frameworks, and ecological impacts, necessitating a delicate balance between commercial interests and responsible space exploration.
Looking to the horizon, space tourism holds the potential to revolutionize travel and usher in a new era of space exploration and habitation, thus shaping the future of humanity’s relationship with the cosmos.
FAQs
Space tourism is a commercial activity that allows private individuals to travel to space for recreational, adventure, or scientific purposes.
Key players in space tourism include SpaceX, Blue Origin, Virgin Galactic, and several emerging startups.
Ticket prices vary but can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars for suborbital or orbital spaceflights.
Suborbital space tourism involves reaching the edge of space for a brief experience of weightlessness. Orbital space tourism entails traveling to Earth’s orbit and may involve extended stays on space stations.
Safety is a top priority; companies conduct rigorous testing and adhere to safety protocols. However, space travel inherently involves risks.
Space tourists must meet specific health and fitness criteria, as space travel can be physically demanding. Requirements may include medical evaluations and physical training.
The future of space tourism looks promising, with increasing competition and technological advancements expected to make space travel more accessible and affordable in the coming years.


