Table of Contents
Report Overview
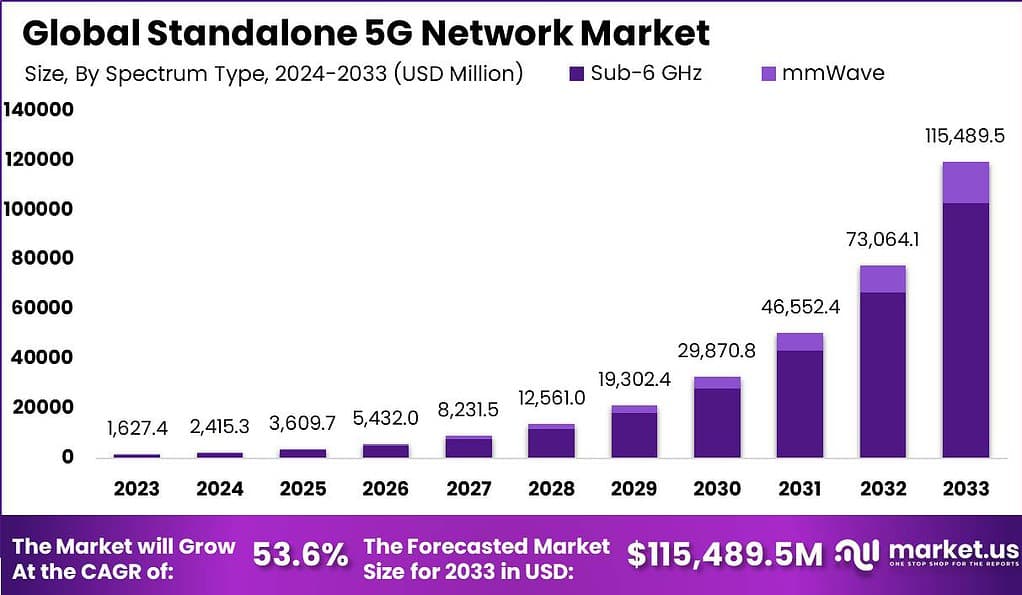
According to Market.us’s latest study, The Global Standalone 5G Network Market is set for remarkable growth, projected to reach USD 115,489.5 million by 2033, a leap from USD 1,627.4 million in 2023. This strong upward trend represents a CAGR of 53.6% from 2024 to 2033. The rapid expansion is driven by the increasing demand for high-speed, low-latency connectivity to support advanced digital services, such as IoT, smart cities, and autonomous vehicles.
In 2023, APAC led the market, capturing over 42% of the share and generating USD 683.5 million in revenue. This region’s leadership stems from extensive investment in digital infrastructure and early adoption of 5G technology, particularly in countries like China, South Korea, and Japan. These nations are pushing forward with significant 5G deployments to support growing tech ecosystems, strengthening APAC’s position in the global market.
Standalone 5G, or 5G SA, is a mobile network infrastructure that operates completely independently from previous generations. Unlike its counterpart, the non-standalone 5G that relies on existing 4G LTE core networks, standalone 5G has its own dedicated core network. This new core, known as 5G Core or 5GC, allows the network to fully utilize 5G capabilities such as improved bandwidth, ultra-low latency, and enhanced security. Standalone 5G supports innovative applications that demand quick data processing and real-time responsiveness across various sectors, including autonomous driving, industrial automation, and healthcare.
The market for standalone 5G networks is burgeoning, driven by the need for more efficient, secure, and faster network solutions that can handle the increasing volume of data and connectivity demands of modern technologies. The shift towards standalone 5G infrastructure is propelled by its ability to enable critical applications that require instantaneous communication and data transfer. One of the key growth factors for the standalone 5G network market is the rapid expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, which requires vast connectivity capabilities that only 5G can provide. Additionally, industries are pushing for digital transformation that leverages the high speed and low latency of 5G to enhance operational efficiency and introduce new services.
Technological innovations in standalone 5G include network slicing, which allows operators to create multiple virtual networks within a single physical 5G network. Each slice can be customized for specific needs, providing flexibility and optimized performance for different applications. This innovation not only boosts the efficiency of network management but also enhances security, making standalone 5G attractive for industries with stringent data protection requirements.
Key Takeaways
- The Standalone 5G Network Market is expected to see incredible growth, projected to surge from USD 1,627.4 million in 2023 to an impressive USD 115,489.5 million by 2033, achieving a staggering CAGR of 53.6% throughout 2024 to 2033. This growth is powered by global digital transformations and the increasing need for ultra-reliable, high-speed connectivity.
- In 2023, Asia-Pacific (APAC) led the market, securing over 42% market share with revenues around USD 683.5 million. APAC’s dominance stems from its early 5G rollouts and heavy investments in infrastructure.
- The Solutions segment dominated with an 81.23% share in 2023, highlighting the demand for adaptable 5G solutions that meet the diverse needs of businesses.
- On the spectrum side, the Sub-6 GHz segment captured 86.11% of the market in 2023. Sub-6 GHz frequencies are popular due to their balanced capabilities, providing both reliable speed and broad coverage, which is essential for effective urban and rural connectivity.
- The Public segment held an 86.83% share in 2023, emphasizing the significant role public carriers and government-led projects play in deploying standalone 5G networks.
- Finally, Manufacturing led the industry application segment, accounting for 23.52% of the market.
Standalone 5G Network Statistics
- The global 5G services market is on an impressive trajectory. By 2033, it’s projected to soar to approximately USD 3,299.8 billion from USD 88.5 billion in 2023. This represents a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 43.6% from 2024 to 2033.
- Similarly, the global small cell 5G network market is expected to expand significantly. Estimates suggest a growth from USD 6.2 billion in 2023 to about USD 480.5 billion by 2033. This market could see an even higher CAGR of 54.5% during the same period.
- In the realm of 5G fixed wireless access (FWA), the market size was USD 24.6 billion in 2023. Forecasters expect it will reach USD 411.5 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 38%.
- Exploring further, 115 operators across 52 countries are investing in 5G standalone networks. This equates to 21.4% of the 535 operators investing in 5G at some level. 36 of these operators have launched or are deploying public 5G standalone (SA) networks.
- The industry currently supports over 17 5G core network vendors and offers more than 89 5G SA modems and chipsets. There are nearly 1,750 device types compatible with 5G SA.
- The latest update from the GSA shows that the number of 5G devices rose by 2.4% from March to April 2023, totaling 1,942 devices. Out of these, 1,557 are commercially available, making up 80.1% of all announced devices.
- Market surveys indicate strong consumer demand for 5G, predicting that 5G products and services could represent 51% to 75% of telecom sales by 2027. Despite the enthusiasm, there are concerns over energy consumption and the high costs involved upfront.
- Technological advances are ongoing, with Open RAN and cloud-based infrastructures gaining momentum. Around 40% of survey respondents expect that Open RAN will make up half of all equipment shipments by 2025. Furthermore, 53% believe that by 2027, clouds will host 51% to 75% of 5G infrastructure. However, maintaining quality of service poses a significant challenge, according to 44% of the respondents.
- On a practical note, T-Mobile has achieved up to a 40% improvement in latency through standalone 5G testing. SA architecture allows for the full utilization of the 600 MHz spectrum, unlike the non-standalone architecture, which combines it with mid-band LTE.
- Comparatively, T-Mobile’s 5G network is more than twice the size of AT&T’s and over 10,000 times larger than Verizon’s. By 2029, 5G connections are predicted to account for over 51% of mobile connections, reaching 56% by 2030.
- As of now, global 5G subscriptions have hit the one billion mark. By the end of 2023, this figure is expected to rise to 1.5 billion and is projected to hit two billion by 2025. This rapid adoption underscores the pivotal role of 5G technology in modern telecommunications.
APAC Standalone 5G Network Market Size
In the Standalone 5G Network Market, Asia-Pacific (APAC) stands out, leading the way with a significant 42% share in 2023. This dominance is driven by rapid urbanization, massive mobile subscriber growth, and substantial investments in advanced telecom infrastructure across countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. APAC’s growth trajectory is set to remain strong, bolstered by government initiatives supporting 5G expansion.
Meanwhile, Europe holds a solid 33.2% market share, thanks to proactive 5G rollouts and strategic collaborations between telecom operators and tech companies. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK are at the forefront, fostering innovation in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and autonomous driving, all set to benefit from a robust 5G backbone.
North America captures a modest 5.8% of the market, largely fueled by the United States. Though the region’s growth is slower compared to APAC and Europe, the high demand for connected devices and the adoption of IoT technologies contribute significantly to the market. Telecom giants in the U.S. are steadily advancing their 5G networks to meet rising demand.
In Latin America, the market share is 5.6%, reflecting early-stage adoption. While countries like Brazil and Mexico are making progress in 5G deployment, the growth pace is tempered by infrastructural challenges and investment needs. However, with improving economic conditions and increasing mobile penetration, the Latin American 5G market holds promise for future expansion.

Emerging Trends
- Open RAN Implementation: The shift towards open and interoperable radio access networks (Open RAN) is revolutionizing 5G by promoting innovation and vendor diversity. This allows for more flexible and scalable networks that can meet the evolving demands of 5G services.
- Enhanced Network Slicing: Network slicing is becoming more sophisticated, enabling the creation of virtualized, isolated network segments to cater specifically to diverse applications such as high-speed broadband and IoT. This trend is set to grow as 5G Standalone networks mature.
- Advanced Automation and AI Integration: Service providers are focusing on automating network operations and integrating AI to improve efficiency and performance. This includes automating network lifecycle processes and adopting intelligent automation to reduce energy costs and CO2 emissions.
- Expanding Use of Network Digital Twins: The telecom industry is increasingly using digital twins—virtual models of network elements—to optimize network operations and maintenance. This technology helps in testing changes and implementing new services with reduced errors and outages.
- Growth of Private 5G Networks: The adoption of private 5G networks is expected to rise, particularly in enterprise settings. These networks offer tailored connectivity solutions that can dramatically enhance operational efficiency and are especially beneficial in industries like manufacturing and logistics.
Top Use Cases
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): Standalone 5G significantly boosts data speeds and capacities, enhancing user experiences across streaming, gaming, and more, thanks to its high bandwidth and low latency capabilities.
- Internet of Things (IoT): With its ability to support a vast number of connected devices per square kilometer, standalone 5G is ideal for the next generation of IoT applications, providing the connectivity backbone for smart cities and industrial automation.
- Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC): Standalone 5G is crucial for applications requiring instantaneous communication, such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgeries, and other critical services where every millisecond counts.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): The high speed and low latency of standalone 5G are perfect for powering immersive VR and AR experiences, supporting advanced use cases in gaming, training, and remote work.
- Smart Infrastructure Management: Leveraging standalone 5G networks for infrastructure management can lead to more efficient utility services and smarter management of resources, ultimately contributing to sustainable urban development.
Major Challenges
- Deployment Complexity: Transitioning from non-standalone (NSA) to standalone (SA) architectures involves significant complexities due to the need to implement entirely new 5G cores separate from existing 4G LTE networks. This shift demands substantial changes in network design and operation, which can be daunting and resource-intensive.
- High Costs: The financial burden of building out SA infrastructure is considerable, including costs associated with new equipment, software, and potential overhauls of existing systems. Managing these costs while trying to maintain competitive pricing for customers poses a substantial challenge.
- Technical Hurdles: Implementing SA requires overcoming several technical obstacles, such as ensuring interoperability between old and new technologies and achieving desired levels of performance across all network components.
- Workforce Transition: As networks evolve, there is a pressing need for skilled professionals who understand the new SA technologies. Retraining and hiring for these competencies can be a slow and costly process, impacting the speed and efficiency of SA deployments.
- Regulatory and Security Concerns: With new technologies come new regulatory challenges and security vulnerabilities. Ensuring compliance and protecting against new threats in a rapidly evolving technology landscape remains a critical concern.
Attractive Opportunities
- Enhanced Network Capabilities: SA networks offer significant improvements in speed, latency, and network efficiency, facilitating advanced applications like autonomous vehicles, remote healthcare, and more immersive AR/VR experiences.
- Innovative Business Models: The architectural flexibility of SA allows for more tailored services and business models, such as network slicing, where operators can offer customized connectivity solutions that meet the specific needs of various industries.
- Market Leadership in 5G Services: Early adopters of SA can position themselves as market leaders in offering cutting-edge 5G services, securing a competitive advantage as the demand for high-speed, low-latency services grows.
- Private Networks and Enterprise Solutions: SA facilitates the deployment of private networks that can support specific business operations, enhancing security, reliability, and performance for enterprise users.
- Long-term Cost Savings: Despite the high initial costs, SA networks are more cost-efficient in the long run due to their higher efficiency and the ability to better manage network resources.
Recent Developments
- T-Mobile has made significant strides in enhancing its standalone 5G network. In May 2023, T-Mobile collaborated with Nokia and Qualcomm to achieve record-breaking uplink speeds of over 200 Mbps using carrier aggregation, marking the first such achievement on a live U.S. 5G standalone network. This enhancement boosts applications such as video streaming, gaming, and augmented reality by transmitting data more quickly.
- In January 2024, T-Mobile selected Nokia to improve the scalability of its 5G network for high-speed internet, aiming to expand its standalone 5G capabilities. This development aligns with T-Mobile’s goal of increasing network efficiency and service reach across the U.S., setting the stage for broader 5G applications in IoT and real-time services.
- Samsung Electronics has partnered with T-Mobile to support the integration of advanced mid-band 5G channels, allowing T-Mobile to achieve speeds exceeding 3 Gbps in mid-2022. This achievement supports a high-performance standalone 5G network, enabling faster and more responsive internet connectivity across diverse applications.
Key Player Analysis
- Nokia Corporation continues to strengthen its 5G SA portfolio by partnering with global telecom providers, including T-Mobile and AT&T, to supply essential network infrastructure. The company’s recent focus has been on enhancing low-latency solutions and carrier aggregation, which has positioned Nokia as a key technology supplier in the U.S. and Europe’s 5G ecosystem. The company has also collaborated on innovations in multi-user massive MIMO and network slicing, allowing telecom providers to serve various consumer and business applications efficiently.
- Vodafone Limited has embraced 5G SA innovations, with deployments focused on Europe and the APAC region. Vodafone’s commitment to advanced 5G use cases, including cloud gaming and IoT, highlights its vision of 5G as a platform for new digital experiences. It has also launched initiatives for private 5G networks targeting industrial applications, enhancing Vodafone’s market footprint in the enterprise space as it capitalizes on low-latency and high-reliability 5G connections.
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. remains active in the 5G SA space despite regulatory hurdles in Western markets. The company’s latest offerings include enhanced 5G core solutions and green technology for energy-efficient network deployments, primarily targeted toward APAC and emerging markets. Huawei’s investments focus on facilitating large-scale 5G networks with greater energy efficiency, catering to countries emphasizing sustainable infrastructure.
- Verizon Communications Inc. has been expanding its C-band 5G SA services, focusing on urban markets. While Verizon faced a slight lag in initial 5G SA rollouts, the provider has made significant strides with upgrades to its network core and is working on mid-band spectrum enhancements to boost speed and coverage. Partnerships with Ericsson for 5G SA core infrastructure are anticipated to strengthen its competitive position in the coming years.
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. collaborates extensively with U.S. telecoms, particularly T-Mobile and Verizon, by providing network equipment and device support for 5G SA networks. Samsung’s integration of 5G functionalities, such as four-carrier aggregation on its Galaxy devices, underscores its commitment to enhancing the 5G user experience. Samsung’s R&D efforts in mmWave and mid-band spectrum technologies further support standalone 5G applications.
- AT&T Inc. has focused on expanding its 5G SA network with a primary emphasis on low-band and mid-band spectrums to enhance nationwide reach. Recent agreements with Nokia and Ericsson aim to advance AT&T’s 5G core, positioning it to compete more robustly with T-Mobile in 5G coverage and performance. AT&T’s approach to 5G includes both consumer and enterprise solutions, with applications in edge computing and connected vehicles expected to drive growth.
- Singtel leads the 5G SA rollout in Southeast Asia, deploying standalone 5G for industrial applications, including ports and smart cities. Singtel’s approach emphasizes IoT integrations and network slicing, catering to large-scale enterprises requiring low latency and high reliability. As of 2023, Singtel has expanded partnerships to support industry-specific 5G applications.
- Rogers Communications Canada Inc. continues to expand its 5G SA footprint, with investments in mid-band spectrum and collaboration with Ericsson for network infrastructure. Rogers is expected to leverage 5G SA for rural coverage enhancements and enterprise applications in Canada. The company also targets 5G applications for healthcare and remote working, catering to Canada’s unique regional needs and digital transformation goals.
Conclusion
Standalone 5G, or 5G SA, represents a significant leap forward in networking technology, operating entirely independently of legacy networks and powered by its own 5G Core. This evolution enables transformative capabilities like ultra-low latency, massive connectivity, and enhanced bandwidth, making it fundamental for emerging applications across diverse sectors such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and telemedicine.
The market for standalone 5G is poised for robust growth, driven by the escalating demands of IoT and the push for digital transformation across industries. Innovations such as network slicing further amplify its appeal, offering tailored network capabilities that optimize performance and security for various applications. As industries and technologies evolve, standalone 5G stands out as a critical infrastructure component that will enable a new wave of technological integration and innovation.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)


