Table of Contents
Introduction
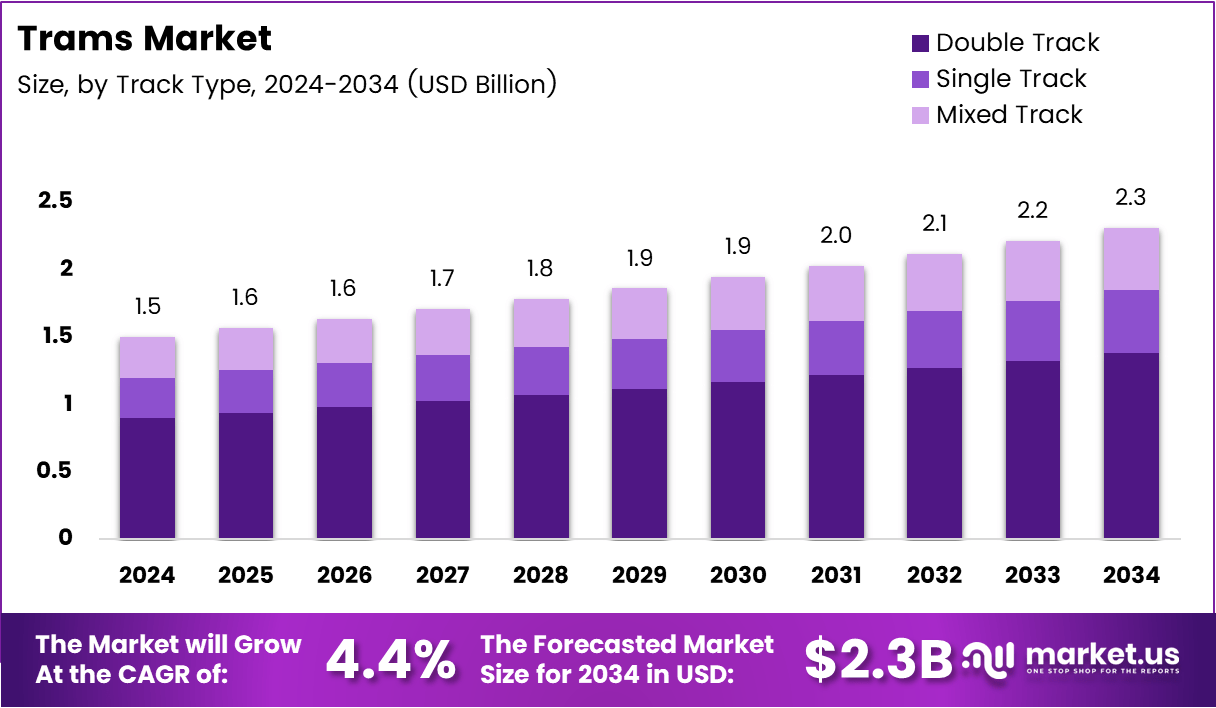
The Global Trams Market is projected to reach USD 2.3 Billion by 2034, growing from USD 1.5 Billion in 2024, at a CAGR of 4.4% between 2025 and 2034. The market is gaining momentum as urban centers worldwide shift toward sustainable and high-capacity transportation systems that reduce emissions and congestion.
Trams have become a cornerstone of modern public mobility due to their ability to integrate with metro, bus, and light rail systems. With smart ticketing, automation, and digital monitoring systems, trams enhance efficiency and accessibility while contributing to environmental sustainability.
Increased government funding, public-private partnerships, and adoption of green energy are driving modernization projects globally. Major economies in Europe and Asia Pacific are leading investments in tram infrastructure, reinforcing the market’s role in shaping smart, connected cities.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Trams Market is projected to reach USD 2.3 Billion by 2034, growing from USD 1.5 Billion in 2024 at a CAGR of 4.4%.
- 60–150 Passengers segment led the market with a 58.9% share in 2024, favored for medium-density routes and flexibility.
- Manned Trams dominated with an 89.3% share, emphasizing safety and operational control.
- Electric and Hybrid Trams captured a 67.8% share, supported by clean-energy initiatives.
- Double Track Systems accounted for 61.6% share, ensuring efficient bi-directional movement.
- Surface Trams held an 82.1% share, due to cost-effectiveness and urban compatibility.
- Asia Pacific dominated the market with 35.8% share, valued at USD 0.5 Billion.
Market Segmentation Overview
The By Type segment was led by trams with 60–150 Passenger capacity, accounting for 58.9% share in 2024. These trams offer the perfect balance between efficiency and capacity, making them ideal for medium-density cities. Compact and large-capacity trams follow, serving low and high-demand routes, respectively.
In the By Operation category, Manned Trams dominated with 89.3% share due to safety and adaptive operation. Human-driven systems allow real-time decision-making, crucial in dense traffic zones. Meanwhile, driverless trams are gaining interest through automation and AI-based monitoring, though adoption remains gradual.
By Technology, Electric and Hybrid Trams led with 67.8% share. Their dominance stems from sustainability goals, reduced carbon emissions, and government-backed electrification programs. Conventional trams persist in regions where modernization is slower but are steadily being phased out.
The By Track Type segment saw Double Track systems commanding 61.6% share, offering higher capacity and reduced delays. Single track and mixed configurations remain relevant in smaller cities and transition networks, balancing cost and performance.
Under By Infrastructure, Surface Trams captured 82.1% share. Their popularity arises from cost efficiency, accessibility, and quick construction timelines. Tunnel and bridge-based systems cater to complex terrains but involve higher capital investment.
Drivers
1. Rapid Urbanization and Expansion of Transit Networks: Global urban growth has intensified the need for sustainable, efficient public transport. Trams reduce congestion, lower emissions, and provide seamless city connectivity. Governments are investing heavily in tram systems to modernize public infrastructure and meet commuter demand.
2. Shift Toward Smart and Connected Mobility: The integration of digital ticketing, IoT sensors, and real-time passenger information is transforming urban transport. These innovations enhance safety, scheduling, and convenience, positioning trams as the backbone of next-generation urban mobility systems.
Use Cases
1. City Center Connectivity: Trams play a pivotal role in connecting central business districts with residential zones. Their consistent schedules and large passenger capacity make them ideal for intra-city commuting, especially in high-density regions like Paris, Tokyo, and Berlin.
2. Green Tourism and Urban Renewal: Many European and Asian cities use trams to boost eco-tourism and redevelop older neighborhoods. Their quiet operation and low emissions complement initiatives aimed at creating pedestrian-friendly, attractive urban spaces.
Major Challenges
1. High Infrastructure and Maintenance Costs: Building and maintaining tram networks involves large-scale capital investment for tracks, power systems, and vehicles. These costs often deter smaller cities or developing economies from rapid deployment.
2. Limited Flexibility and Operational Delays: Trams rely on fixed tracks, making them less flexible than buses. Any disruption, repair, or obstruction can halt operations, impacting service reliability and discouraging potential expansion.
Business Opportunities
1. Integration with Multimodal Smart Mobility Platforms: The convergence of trams with metro, bus, and shared mobility systems offers vast growth potential. Seamless ticketing, real-time data sharing, and unified scheduling enhance commuter convenience and network efficiency.
2. Advancements in Electric and Hydrogen Propulsion: The rise of zero-emission technologies like battery and hydrogen-powered trams opens new avenues. These innovations minimize environmental impact and attract government subsidies, creating opportunities for OEMs and technology providers.
Regional Analysis
1. Asia Pacific: Holding 35.8% of the global share valued at USD 0.5 Billion, the Asia Pacific region leads the trams market. Rapid urbanization in China, Japan, and India, along with green mobility initiatives, drives large-scale investments in electric tram networks.
2. Europe: Europe remains a mature market with advanced rail systems and strong policy backing for decarbonization. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK are upgrading infrastructure and adopting smart tram technologies to reduce urban congestion and enhance connectivity.
Recent Developments
- In December 2024, the European Investment Bank (EIB) committed €16.5 million to modernize tram systems in Kyiv, Mykolaiv, Odesa, and Ivano-Frankivsk, supporting new vehicle procurement and infrastructure upgrades.
- In April 2025, the EIB approved €400 million for Helsinki’s Crown Bridges LRT, covering new depots and tram procurement.
- In March 2025, Portugal’s Council of Ministries sanctioned €150 million to expand the Lisbon tram extension across the Odivelas–Loures corridor.
Conclusion
The Global Trams Market is evolving rapidly as cities prioritize sustainable, connected, and efficient public transit. With governments promoting electric and hybrid propulsion systems, the industry is set to witness strong growth over the next decade. Strategic collaborations, green financing, and smart infrastructure will define the next wave of tram development, enabling global progress toward carbon-neutral urban mobility.


