Table of Contents
Introduction
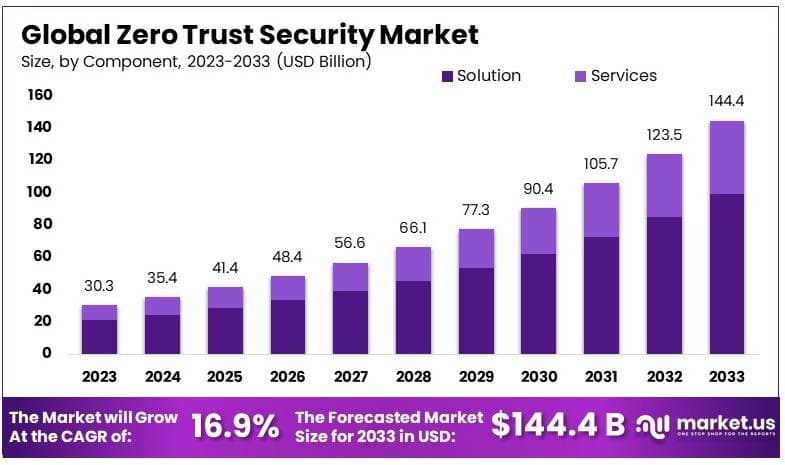
According to the Market.us, The Global Zero Trust Security Market is projected to reach approximately USD 144.4 billion by 2033, up from USD 30.3 billion in 2023, with an anticipated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.9% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity paradigm that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security models that assume everything inside an organization’s network can be trusted, Zero Trust treats all users, devices, and network flows as potentially hostile. It requires stringent identity verification for every individual and device trying to access resources on a private network, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network perimeter. This approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches by applying strict access controls and continuous authentication.
The Zero Trust Security market refers to the commercial landscape surrounding the technologies, services, and solutions that enable the implementation of the Zero Trust model. This market includes various products such as identity and access management (IAM), security orchestration automation and response (SOAR), data security, network security, and endpoint security solutions that support the rigorous and continuous verification demands of the Zero Trust approach.
The demand for Zero Trust Security solutions has surged significantly due to the increasing number of cyber threats, data breaches, and the more sophisticated nature of cyber-attacks. Organizations’ transition to cloud-based architectures and the rise of remote work scenarios have further exacerbated vulnerabilities, making traditional perimeter-based security models obsolete. This has driven organizations across various industries to adopt Zero Trust architectures as part of their core security strategy to protect sensitive data and systems.
Several factors contribute to the growth of the Zero Trust Security market. The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and their integration into corporate networks expand the attack surface, necessitating robust security measures that Zero Trust provides. Additionally, regulatory requirements for enhanced data protection across sectors such as healthcare, finance, and government enforce the adoption of stringent security frameworks like Zero Trust. Technological advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence also enable more effective implementation of Zero Trust models, further stimulating market growth.
The Zero Trust Security market presents substantial opportunities, especially in sectors where data security and privacy are paramount. Healthcare, financial services, and government are key sectors due to their need to safeguard sensitive information against rising cyber threats. Additionally, as more organizations adopt cloud computing and hybrid work models, the need for flexible and scalable security solutions that can be applied uniformly across various platforms and locations offers significant market potential for Zero Trust solutions. Moreover, partnerships and collaborations between technology providers and security firms are likely to drive innovation and adoption, providing further growth opportunities in this field.
Key Takeaways
- The Zero Trust Security Market was evaluated at USD 30.3 Billion in 2023 and is projected to ascend to USD 144.4 Billion by 2033, registering a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 16.9%. This growth trajectory is underscored by the increasing emphasis on security protocols and measures across various sectors.
- In terms of components, the Solutions segment was predominant, capturing 68.8% of the market in 2023. This dominance is primarily due to the escalating demand for comprehensive security measures that can preemptively counteract potential threats.
- Authentication methods within the Zero Trust framework also saw significant segmentation, with Multi-Factor Authentication leading at 70.6% in 2023. This is indicative of the heightened security concerns that necessitate robust authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access.
- Deployment models also showed a clear preference for On-Premise solutions, which accounted for 69.5% of the market. This preference is largely attributed to the control it offers organizations over their sensitive data, a critical factor in maintaining stringent security standards.
- By organization size, Large Enterprises were the leading consumers of Zero Trust Security solutions, holding a 68.0% share. This reflects the larger security needs and capabilities of big organizations which are often the prime targets for cyber threats.
- From an industry vertical perspective, IT and Telecommunications were at the forefront, commanding 24.9% of the market. The sector’s leadership is driven by the imperative to secure expansive and complex data networks that are inherently vulnerable to cyber threats.
- Geographically, North America was the most significant market, leading with 37.1% in 2023. This prominence can be attributed to the high levels of cyber threats in the region, which necessitate advanced and robust security solutions like those offered by the Zero Trust model.
Zero Trust Security Statistics
- The recent survey on Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) adoption indicates that only 15% of respondents have fully implemented ZTNA, while a notable 9% have no plans to pursue this security framework. However, a significant majority, 68%, are either planning or are actively working towards adopting a Zero Trust access model.
- In their journey towards implementing Zero Trust, organizations are predominantly focusing on a comprehensive security approach. 57% are prioritizing Identity and Access Management (IAM), and 52% are concentrating on securing cloud application access. This focus underscores the importance of verifying user and device identities and controlling resource access, which are fundamental principles of Zero Trust security.
- The survey also highlights that the primary security concern for many organizations has shifted to at-risk devices accessing network resources, with 48% identifying this as their highest concern—a rise to the top spot compared to the previous year.
- Furthermore, enhancing Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and improving vulnerability remediation are critical aspects, cited by 46% and 45% of respondents respectively. These priorities align with the Zero Trust principle of continuous monitoring and rapid response to emerging security threats.
- The data reveals that Zero Trust is already implemented in approximately one in five organizations (19%), with 38% planning to undertake Zero Trust access projects and another 30% having projects currently in progress. This demonstrates that a large portion of the surveyed organizations (68%) are actively pursuing Zero Trust access models.
- The shift to remote work has sharpened the focus on security for 81.4% of SME IT professionals, reinforcing the need for robust security measures.
- Organizations are also emphasizing other secure access priorities aligned with Zero Trust principles, such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) (65%), real-time threat detection (50%), and securing access from personal devices (46%).
- Lastly, while overprivileged access remains a concern, it accounted for less than 25% of security incidents in nearly half of the organizations (45%). This finding suggests that, although significant, overprivileged access is not the predominant cause of security incidents in many organizations, which represents a third (34%).
- As of 2023, 61% of organizations have reported adopting a defined Zero Trust security strategy, representing a considerable uptick in adoption over the previous two years.
- About 41% of organizations have successfully deployed a Zero Trust security architecture, contrasted with 59% that have yet to implement such measures. In both the U.S. and U.K., 58.6% of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are either actively pursuing or planning to pursue a Zero Trust program.
- The implementation of Zero Trust Security has been shown to potentially reduce the costs associated with a data breach by approximately $1 million.
- Meanwhile, the average cost of data breaches has escalated from $4.24 million in 2021 to $4.35 million in 2022, illustrating the financial repercussions of not adopting robust security measures like Zero Trust.
- There has been a 70% surge in data breaches during Q3 of 2022 compared to Q2, highlighting the pressing necessity for enhanced security frameworks.
- The typical cost of a ransomware attack stands at about $4.54 million, which does not include the average ransom payment of $170,404. This data underscores the critical importance of robust security measures to mitigate the escalating costs and risks associated with cyber threats
Emerging Trends
- Comprehensive Application Across Digital Estates: Successful organizations are applying Zero Trust principles across all layers of their digital estate to combat sophisticated attacks and improve user experiences. This includes automating policies and strengthening governance to enhance security postures and reduce management overhead.
- Integration Across Security Pillars: Zero Trust is increasingly integrated across different security pillars, including policy enforcement, threat intelligence, and attack mitigation. This highlights a shift towards more cohesive and interconnected security architectures.
- Focus on Device and User Verification: As mobile and remote work environments expand, there’s a significant push towards enhancing security protocols that verify user identities and device integrity to manage access and prevent breaches.
- Advancements in Threat Detection and Response: Organizations are leveraging more sophisticated threat detection and response mechanisms within the Zero Trust model. This includes real-time responses and advanced analytics to preemptively address security threats.
- Expansion of Zero Trust to IoT and Cloud Environments: Zero Trust principles are being extended beyond traditional IT infrastructures to include IoT and multi-cloud environments, recognizing the need to secure a broader range of devices and applications.
Top Use Cases
- Securing Remote Workforces: Implementing Zero Trust access controls for hybrid and remote workforces to ensure that all access requests are securely verified, regardless of the user’s location.
- Protection Against Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Utilizing Zero Trust strategies to mitigate risks from APTs by continuously verifying and limiting access based on stringent security protocols.
- Enhancing Identity Verification: Strengthening identity and access management processes to enforce that only verified and authorized users can access sensitive data and systems.
- Regulatory Compliance and Data Protection: Leveraging Zero Trust architectures to meet stringent regulatory requirements and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Securing IoT and Edge Devices: Applying Zero Trust principles to manage and secure IoT and edge devices, which are often used in critical infrastructure and industrial applications, to prevent exploitation and maintain system integrity.
Major Challenges
- Complex Legacy Systems: Transitioning from traditional perimeter-based security controls to a Zero Trust architecture is complicated by entrenched legacy systems, which are often incompatible with the stringent access controls required by Zero Trust strategies.
- Budget Constraints: Implementing a comprehensive Zero Trust framework can be resource-intensive, requiring significant investment in technology upgrades and employee training, which not all organizations are prepared to commit.
- Resistance to Change: There is often internal resistance within organizations, as Zero Trust requires a shift in both technology and culture. This shift necessitates ongoing education and buy-in at all levels of the organization to be effective.
- Managing Privileged Access: Balancing the need for security with the efficiency of business operations is a key challenge, as overly restrictive access controls can hinder productivity. Managing the level of access granted to users, particularly privileged users, remains a difficult task.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: In today’s interconnected digital ecosystem, securing the supply chain is particularly challenging. Zero Trust architectures need to ensure robust security measures are extended to third-party vendors and service providers, which is often complex due to the diverse nature of digital supply chains.
Top Opportunities
- Enhanced Security Posture: By assuming no trust and verifying each request, Zero Trust significantly reduces the attack surface, limiting the impact of breaches and improving the overall security posture of the organization.
- Improved Compliance and Data Protection: Zero Trust frameworks support compliance with various regulatory requirements by providing robust mechanisms for data protection and user access control, essential for protecting sensitive information and avoiding penalties.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Zero Trust principles are inherently scalable, making it easier for organizations to adapt to changing business needs and technological environments without compromising on security.
- Reduced Insider Threats: Zero Trust helps mitigate risks associated with insider threats by continuously monitoring and validating user activities, regardless of their position or level of access
- Cloud Security: As organizations continue to move to cloud-based environments, Zero Trust models offer a strategic approach to secure cloud deployments by ensuring consistent security policies are applied across all environments.
Recent Developments
- Palo Alto Networks has made significant strides by acquiring Talon Cyber Security in December 2023, aiming to enhance their Prisma SASE with the addition of Talon’s Enterprise Browser for improved security across unmanaged devices. This acquisition reinforces Palo Alto’s commitment to providing comprehensive Zero Trust security solutions.
- Okta reports a significant uptick in Zero Trust adoption, with their 2023 state report highlighting that 61% of surveyed organizations have a defined Zero Trust initiative. This reflects a growing mainstream acceptance of the Zero Trust framework.
Conclusion
In Conclusion, The Zero Trust Security model, advocating a “never trust, always verify” approach, is increasingly vital in today’s cybersecurity landscape marked by sophisticated threats and evolving work environments. As traditional security perimeters become obsolete due to the rise of remote work and cloud technologies, the demand for Zero Trust solutions is soaring. This surge is bolstered by growth factors such as the expansion of IoT devices and stringent regulatory demands across various sectors, notably in healthcare, finance, and government.
The market for Zero Trust Security offers significant opportunities, particularly as organizations seek flexible and robust security solutions that can adapt to a mix of on-premises and cloud-based infrastructures. The ongoing innovations in AI and machine learning are set to further enhance the efficacy and adoption of Zero Trust models, positioning them as indispensable components of modern cybersecurity strategies.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



