Table of Contents
Introduction
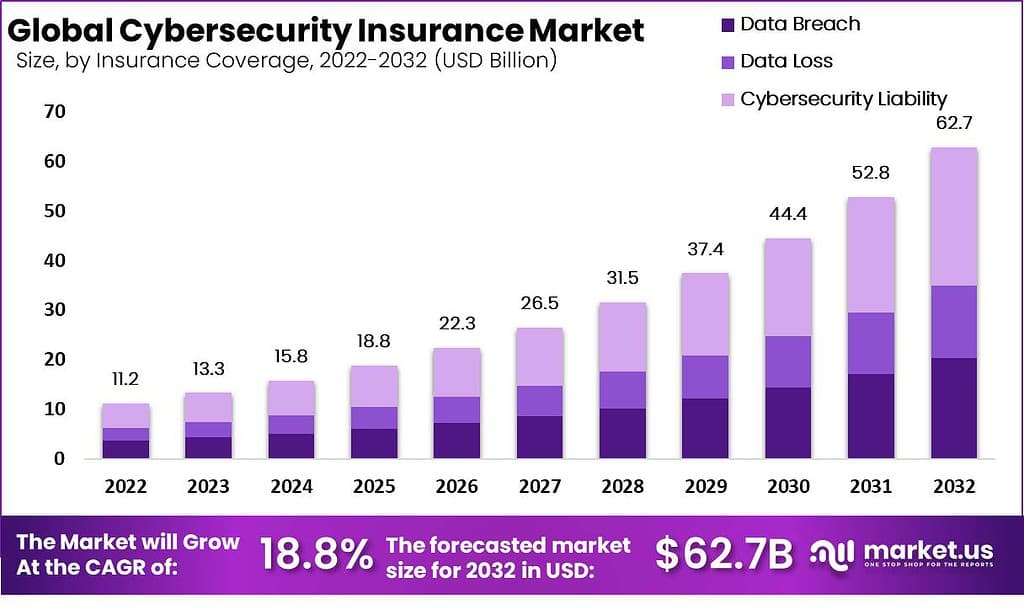
According to Market.us, The Global Cybersecurity Insurance Market is projected to experience significant growth, with its value expected to reach approximately USD 62.7 billion by 2033, up from USD 13.3 billion in 2023. This robust expansion, at a CAGR of 18.8% from 2024 to 2033, underscores the increasing awareness and importance of cyber insurance as cyber threats continue to rise.
Cybersecurity insurance, also known as cyber liability insurance, helps organizations mitigate financial risks associated with cyber incidents. This form of insurance covers losses from data breaches, cyberattacks, ransomware, and other digital threats. Policies typically cover expenses related to investigation, legal fees, notification costs, and fines, assisting businesses in financial recovery and risk management from cyber disruptions.
The major drivers propelling the growth of the cybersecurity insurance market include the escalating frequency of cyberattacks, the stringent regulatory requirements concerning data protection, and the increasing awareness among businesses about the financial impacts of cyber incidents. Additionally, as companies continue to integrate digital technologies into their operations, the risk of cyber exploitation grows, thereby driving the demand for comprehensive cyber insurance solutions.
The demand for cybersecurity insurance is particularly strong in sectors like technology, healthcare, and financial services, where the potential damage from cyberattacks can be severe. The market is also expanding globally, with significant growth in regions such as North America, which holds the largest market share due to robust cybersecurity and data protection regulations. Europe and Asia Pacific are also seeing significant market expansions due to increased digitalization and regulatory changes.
Technological advancements are also shaping the cybersecurity insurance market. Innovations in cyber risk assessment tools and the incorporation of artificial intelligence to better predict and mitigate risks are becoming more prevalent. These advancements enhance the ability of insurers to assess threats and customize insurance solutions, making them more effective and appealing to businesses looking to protect themselves from cyber threats.
Opportunities in the cybersecurity insurance market are emerging from the continuous development of new insurance products tailored to evolving cyber risks. Insurance companies are increasingly offering cyber risk management services and innovative coverage options like parametric insurance, which provides payouts based on the occurrence of specified events rather than the actual financial loss incurred. This adaptability and expansion of services are likely to drive market growth further.
Key Takeaways
- The global cybersecurity insurance market is projected to expand by USD 62.7 billion by 2032, achieving a strong CAGR of 18.8%. This growth reflects the rising need for protection against increasing cyber threats globally.
- Cybersecurity liability insurance holds a leading position, capturing a revenue share of 44.6%. This segment’s dominance is driven by companies seeking coverage against potential financial losses from cyber incidents.
- Standalone insurance types are notably in high demand, commanding the largest revenue share of 63.6%. This preference highlights the desire for tailored cyber insurance solutions that address specific needs without bundling with other policies.
- The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) segment stands out, holding a significant revenue share of 26.4%. The sector’s exposure to sensitive data makes it highly vulnerable to cyber risks, fueling the demand for specialized insurance coverage.
- North America leads the market with a dominant revenue share of 39.6%. The region’s proactive stance on cybersecurity, robust insurance infrastructure, and strict regulatory landscape strengthen its position in the global market.
Cybersecurity Insurance Statistics
- According to the Munich Re Cyber Risk and Insurance Survey 2024, 87% of global decision-makers believe their companies are not adequately protected against cyber-attacks.
- 4o
- In 2024, the average cost of a data breach reached a record high of $4.88 million, marking the most expensive average to date for organizations managing cyber incidents.
- 88% of cybersecurity breaches stem from human error, underscoring the critical role of employee awareness and training in protecting against cyber threats.
- Chubb Ltd Grp stands as one of the largest insurers in the industry, with premiums written amounting to $404,144,104 and capturing a 14.7% market share in the cybersecurity insurance domain.
- Ransomware continues to be a major driver of claims, causing 81% of those involving recovery expense losses, highlighting its costly impact on organizations’ operational resilience.
- Data breach claims are often impacted by exclusions in insurance packages, with 27% of breach claims and 24% of first-party claims resulting in non-payouts or partial payouts due to these limitations.
- 1,153 cyber insurance claims in 2022 were attributed to business email compromise scams, reflecting the prevalent risks tied to email security and phishing attacks.
- Targeting small and medium businesses (SMBs) has become the norm, with over 56% of cyber insurance claims arising from these businesses, showing their vulnerability to cyber threats.
- It takes an average of 194 days to identify a breach, while the average lifecycle of a breach — from identification to containment – spans 292 days, indicating the prolonged exposure period organizations face.
- Cyber fatigue has become a notable challenge, affecting 42% of companies, where the frequency of threats leads to reduced proactive defenses and a higher risk of successful attacks.
- A surprising 64% of Americans have never checked if they were affected by a data breach, pointing to a gap in public awareness and personal cyber hygiene practices.
- The U.S. remains a prime target for cyberattacks, with 46% of global attacks aimed at American organizations in 2020 – more than double the percentage of any other country.
- 56% of Americans are unaware of what steps to take if they experience a data breach, underscoring the need for clearer guidance and resources for consumers.
- Since the Russia-Ukraine war began in 2022, 97% of organizations report an increase in cyber threats, illustrating how geopolitical tensions amplify cyber risks.
- Over 56% of claims are reported from small businesses with revenue under $25 million, highlighting the widespread cyber exposure within this business segment.
- Only 19% of organizations carry cyber insurance with coverage exceeding $600,000, suggesting that the majority remain underinsured for substantial cyber incidents.
Emerging Trends
- Increasing Focus on Disinformation Risks: With major elections like the US presidential election and others globally, there is a heightened focus on protecting against disinformation and malinformation, which can significantly impact public opinion and the integrity of these processes.
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies are becoming integral in detecting and responding to threats quickly and efficiently. This shift emphasizes the need for cyber insurance to adapt to the technological advancements in threat detection.
- Ransomware Proliferation: Ransomware remains a dominant threat, with attackers using more sophisticated methods. The increase in ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) makes it necessary for businesses to secure insurance that covers these evolving risks.
- Expanded Coverage for New Threats: Cyber insurance is expected to offer broader coverage options to include emerging risks such as pixel tracking and other privacy violations that are not traditionally covered.
- Focus on Supply Chain Risks: With the increase in supply chain attacks, there is a growing demand for insurance solutions that address these specific vulnerabilities.
Top Use Cases
- Data Breach Response and Recovery: Cybersecurity insurance is crucial for managing the costs associated with data breaches, which can include legal fees, forensic analysis, and customer notifications.
- Extortion and Ransom Negotiations: As ransomware attacks increase, insurance policies that help manage the financial and negotiation aspects of these threats are critical.
- Regulatory Compliance: With varying global regulations on data protection, cybersecurity insurance helps businesses manage the costs of compliance and fines associated with breaches.
- Business Interruption Losses: Insurance can cover losses due to operational disruptions caused by cyberattacks, which are becoming more frequent and severe.
- Third-party Litigations: Coverage extends to lawsuits brought by third parties affected by breaches, a common issue as cyber incidents increase.
Major Challenges
- Evolving Threats: Ransomware continues to be a primary concern, with attackers shifting tactics from encryption to data destruction and pretense of data theft for extortion. These sophisticated threats, including ransomware-as-a-service, are targeting cloud infrastructure more frequently, creating significant challenges for cybersecurity and insurance industries.
- Regulatory Compliance: As cyber threats grow, so do regulatory requirements. There is an increasing expectation for organizations to comply with stringent cybersecurity standards. These include managing data breaches and privacy legislation which adds complexity and pressure on the ability to insure against these risks.
- Sophistication of Attacks: Cybercriminals are employing more advanced tactics, such as reconnaissance-as-a-service, making it harder for traditional cyber defenses to keep pace. This increases the difficulty for insurers to assess and insure against such dynamically evolving risks.
- Insurance Market Volatility: The cyber insurance market is experiencing a flux with increasing premiums, growing exclusions, and a more selective insurance issuance process. This trend reflects the market’s response to the heightened risk and the challenges in accurately pricing the cyber insurance products.
- Underwriting Challenges: Insurers are facing difficulties due to a lack of consistent, reliable data to assess risks adequately. This has led to challenges in the underwriting process where insurers are forced to become more selective and demand higher standards of cybersecurity from their clients.
Attractive Opportunities
- Better Risk Quantification: As the industry matures, insurers are gaining access to better data, allowing them to quantify risks more clearly. This improved understanding can lead to more tailored cyber insurance solutions that align closely with individual organization needs.
- Investment in Cybersecurity as a Business Enabler: Recognizing cybersecurity investments not just as a cost but as a vital component of business strategy can transform how businesses approach cyber risks. This perspective helps in fostering more resilient digital operations.
- Expansion of Cyber Insurance Services: There is an opportunity for the development of new insurance products that consider the nuances of cyber risks in various sectors. This includes policies that offer “a la carte” options to better meet the specific needs of different businesses.
- Innovation in Underwriting Practices: Using sophisticated underwriting methods, such as third-party scanning technologies, allows insurers to identify and endorse specific vulnerabilities. This helps in enhancing the precision of cyber risk management and insurance coverage.
- Partnerships and Education: There’s significant potential for insurers to partner with cybersecurity firms to provide comprehensive risk management solutions. Educating clients about cybersecurity best practices and the importance of maintaining robust security measures can also reduce the frequency and severity of cyber incidents.
Recent Developments
- May 2024: CyberArk announced plans to acquire Venafi, a company specializing in machine identity management, for approximately $1.5 billion. This acquisition aims to enhance CyberArk’s capabilities in securing both human and machine identities.
- June 2024: Zurich Insurance Group agreed to acquire AIG’s travel insurance business for $600 million. This strategic move is expected to boost Zurich’s global market share in travel insurance to approximately 10%.
- March 2024: Aon plc acquired the technology assets and intellectual property of Humn.ai, an AI-powered platform. This acquisition is intended to enhance Aon’s commercial fleet proposition.
- April 2024: Arch Capital Group’s North American unit announced the acquisition of Fireman’s Fund Insurance’s businesses from Allianz for $450 million in cash. This deal includes Allianz’s U.S. MidCorp and Entertainment insurance businesses.
Conclusion
The cybersecurity insurance market is poised for substantial growth, driven by escalating digital threats and increased awareness of cyber risks. As organizations globally face heightened cyber vulnerabilities due to rapid digital transformation, the demand for cybersecurity insurance is rising significantly. Market expansion is supported by the development of innovative insurance products and enhanced risk assessment tools that leverage technological advancements such as artificial intelligence.
North America currently leads the market, supported by stringent data protection regulations, while regions like Europe and Asia Pacific are experiencing strong growth due to regulatory changes and increased digitalization. The market is projected to continue its upward trajectory, propelled by evolving cyber threats, regulatory demands, and the critical need for financial protection against cyber incidents. This dynamic sector offers numerous opportunities for growth, making it a crucial area for businesses to consider as part of their risk management strategies.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



