Table of Contents
Introduction
3D Display Statistics: 3D displays, employing techniques such as stereoscopy, holography, and volumetric rendering. This provides immersive visual experiences by replicating depth and spatial dimensionality.
Stereoscopic displays create depth perception by presenting distinct images to each eye. While holographic displays project three-dimensional images without glasses using coherent light sources.
Volumetric displays generate images within physical space, allowing viewing from different angles. Widely utilized across entertainment, healthcare, automotive, aerospace, and retail sectors. 3D displays enhance gaming, medical imaging, driver assistance, flight simulation, and product visualization.
Despite challenges such as complexity and cost, advancements in resolution and content creation are bolstering adoption and user experiences.
Ongoing research targets depth perception improvement and reduced reliance on specialized equipment, ensuring ongoing innovation in 3D display technology.

Editor’s Choice
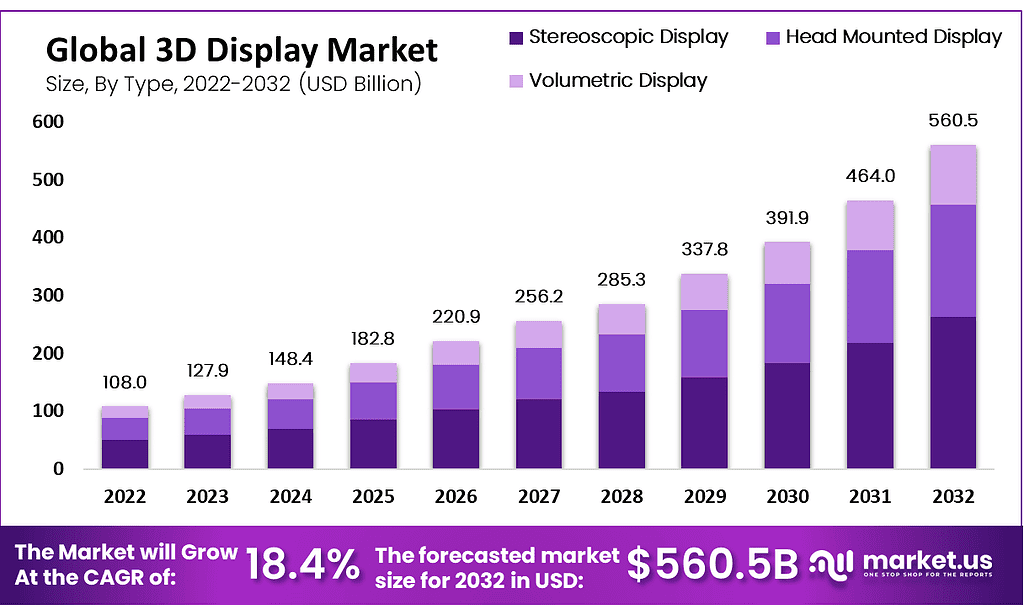
- The global 3D display market revenue is forecasted to reach USD 560.5 billion by 2032.
- Stereoscopic displays consistently dominated the market, with revenues climbing from 69.45 billion USD in 2024 to 262.31 billion USD in 2032.
- Light-emitting diode (LED) technology commands the largest market share at 38% and is known for its energy efficiency, vibrant colors, and longevity.
- Film-based stereoscopic transparencies have been in existence since at least 1931 when Tru-Vue introduced sets of stereo views on 35 mm film strips for viewing through a handheld Bakelite viewer.
- Customers frequently report numerous benefits after utilizing 3D holograms. These include a significant increase in lead generation by up to 30%. Smoother initiation of discussions for the sales team, and prolonged dwell times at trade fair stands. And enhanced sales performance both at the point of sale and in food retail environments.
- Virtual reality headsets like the Oculus Rift and PlayStation VR employ 3D computer display technology by displaying separate images for each eye.
- Innovations in light field glasses-free 3D bring immersive experiences to consumer devices. While holographic waveguide displays provide AR devices with a wide field of view and minimal eye strain.
Global 3D Display Market Overview
Global 3D Display Market Size Statistics
- The global 3D display market revenue is measured in USD billion. It has demonstrated a consistent upward trajectory over the years at a CAGR of 18.40%.
- Beginning at 108.0 billion in 2022, the revenue saw substantial growth. Reaching 127.9 billion in 2023 and further escalating to 148.4 billion in 2024.
- This positive trend is expected to continue, with projections indicating revenue figures of 182.8 billion in 2025, 220.9 billion in 2026, and 256.2 billion in 2027.
- The momentum persists through subsequent years, with revenue estimates climbing to 285.3 billion in 2028, 337.8 billion in 2029, and 391.9 billion in 2030.
- Looking ahead, the market is forecasted to experience robust expansion. With revenue anticipated to soar to 464.0 billion in 2031 and reach a substantial 560.5 billion by 2032.
- These projections reflect the growing demand for 3D display technology across various sectors. Underpinned by advancements in resolution, content creation, and immersive user experiences.
(Source: Market.us)

Global 3D Display Market Size – By Type Statistics
- The global 3D display market size, categorized by Type, has witnessed substantial growth across the years, reflecting increasing demand and technological advancements.
- In 2022, the total market revenue stood at 108.0 billion USD. With stereoscopic displays contributing 50.54 billion USD, head-mounted displays 37.37 billion USD, and volumetric displays 20.09 billion USD.
- This trend continued to escalate, with revenues reaching 560.5 billion USD by 2032.
- Stereoscopic displays consistently dominated the market. With revenues climbing from 69.45 billion USD in 2024 to 262.31 billion USD in 2032.
- Head-mounted displays and volumetric displays also experienced significant growth. With revenues rising from 51.35 billion USD and 27.60 billion USD in 2024 to 193.93 billion USD and 104.25 billion USD, respectively, by 2032.
- These figures underscore the expanding applications of 3D display technology across various sectors, driven by advancements in user experience and content delivery.
(Source: Market.us)

Global 3D Display Market Share – By Technology Statistics
- In the realm of display technology, various methods compete for market dominance, each offering distinct advantages and applications.
- According to the latest data, light-emitting diode (LED) technology commands the largest market share at 38% and is known for its energy efficiency, vibrant colors, and longevity.
- Following closely behind is Organic LED (OLED) technology, holding a significant 24% share. Prized for its thinness, flexibility, and superior contrast ratios.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP) technology captures 21% of the market and is renowned for its high-resolution projection capabilities and fast response times.
- Lastly, plasma display panel (PDP) technology maintains a notable 17% share. Which is recognized for its deep blacks, wide viewing angles, and suitability for large displays.
- This distribution highlights the diverse preferences and requirements of consumers and industries. Driving innovation and competition within the display technology sector.
(Source: Market.us)

History of 3D Display Technology Statistics
- The evolution of 3D display technology spans centuries, with key milestones shaping its development.
- Beginning with Charles Wheatstone’s stereoscope in 1838, which presented two images to each eye for depth perception. The concept progressed with Louis Ducos du Hauron’s introduction of anaglyph images in the late 19th century.
- Commercial success arrived in 1939 with the View-Master, followed by polarized 3D Technology in the 1950s.
- The late 20th century saw the rise of virtual reality (VR) and autostereoscopic displays, offering immersive experiences without glasses.
- Holographic displays emerged as a promising technology, projecting lifelike 3D images without the need for glasses. Recent advancements in LCD and OLED technology have further enhanced 3D display quality and resolution.
- Throughout its history, 3D display technology has continually evolved to deliver increasingly realistic and immersive visual experiences across various industries.
(Source: American Paper Optics, LLC)
Types of 3D Display Statistics
Stereoscopic Displays
- Stereoscopic displays, often known as “stereo displays,” “stereo 3D displays,” or “stereoscopic 3D displays,” and occasionally mistakenly labeled as simply “3D displays,” employ a fundamental method of presenting offset images separately to the left and right eye.
- This technique, rooted in the principles of stereopsis articulated by Sir Charles Wheatstone in the 1830s. It offers viewers distinct images for each eye, enhancing depth perception and creating a three-dimensional visual experience.
- Film-based stereoscopic transparencies have been in existence since at least 1931 when Tru-Vue introduced sets of stereo views on 35 mm film strips for viewing through a handheld Bakelite viewer.
- This Technology was further miniaturized and modified in 1939 with the introduction of the View-Master. Which utilized cardboard disks containing seven pairs of small Kodachrome color film transparencies.
- While stereoscopic-based systems are essential, they have not yet achieved broad clinical adoption. An example of this is seen in the da Vinci surgical system, which incorporates a stereo endoscope to provide surgeons with a comfortable and efficient three-dimensional view of the surgical area.
(Source: ScienceDirect)
Holographic 3D Display
- A 3D hologram is a projection situated in space, visible to all without the need for specialized glasses. Unlike movies on standard monitors, a 3D hologram can be viewed from all angles. Allowing viewers to move around it for a lifelike experience.
- This accessibility, without the requirement for 3D glasses like those needed for 3D TV or Virtual Reality. Makes 3D holograms particularly advantageous for exhibitions and other events.
- While the eye may perceive a seemingly authentic object or phenomenon, such as fire, the brain recognizes its virtual nature.
- Interestingly, this phenomenon naturally captivates viewers’ attention, leading to up to 80% of them watching holograms for 2-3 minutes in their entirety—an engagement level rarely achieved by traditional films displayed on monitors.
- Customers frequently report numerous benefits after utilizing 3D holograms. These include a significant increase in lead generation by up to 30%. The smoother initiation of discussions for the sales team. Prolonged dwell times at trade fair stands, and enhanced sales performance both at the point of sale and in food retail environments.
(Source: Magic Holo)
Volumetric 3D Display
- Volumetric displays produce 3D images through light emission, scattering, or relay from specific points in (x,y,z) space.
- Despite their inception in 1912 and portrayal in science fiction, these displays are not widely adopted in daily life but hold potential in diverse sectors like medicine, education, advertising, simulation, and communication.
- The Voxon Photonics VX1 is an example, providing an 18 cm × 18 cm × 8 cm volume area and rendering 500 million voxels per second.
- Content creation for the VX1 is feasible with Unity or standard 3D file formats such as OBJ, STL, and DICOM. Importantly, volumetric displays demand significantly higher bandwidth than traditional flat displays.
- While a 1024×768 2D display requires 135 MB/s for 60 frames per second, a volumetric display of the same resolution needs about 135 GB/s to sustain 60 volumes per second—a thousand-fold increase.
(Source: Current Optics and Photonics Journal)
3D Display Interfaces Statistics
- HDMI 1.4a and DisplayPort enable the transmission of Stereo 3D frames and offer seamless compatibility for Stereo 3D content by communicating device capabilities and standard transmission formats.
- Unlike traditional methods where the GPU or system drives the pairing of appropriate glasses. These standards shift the responsibility to displays, simplifying the user experience.
- However, the current HDMI infrastructure has bandwidth limitations, restricting 120Hz Stereo 3D to 720p resolution, while 1080p resolutions are capped at 48Hz or 24Hz for film content playback.
- This limitation makes HDMI 1.4a less ideal for 3D gaming, where a higher resolution and refresh rate are desirable.
- In contrast, DisplayPort, especially v1.2, offers higher bandwidth and supports 120Hz Stereo 3D, making it preferred for HD3D-enabled displays by AMD.
- For desktop displays supporting NVIDIA’s 3D vision, Dual-link DVI allows content up to 1920 x 1080 @ 120Hz, although this is not standardized.
- Overall, consideration of DisplayPort or HDMI 1.4a availability is necessary for viewing 3D content from non-PC devices.
(Source: TFT Central)
3D Computer Displays
- The most common type of 3D computer display utilizes shutter technology. Employing specialized LCD glasses to synchronize two images and create 3D effects.
- While traditionally used with computers via specialized hardware, advancements now enable higher resolutions and refresh rates for 3D imagery.
- Virtual reality headsets like the Oculus Rift and PlayStation VR employ similar Technology by displaying separate images for each eye.
- Autostereoscopic 3D displays, on the other hand, eliminate the need for glasses by integrating a parallax barrier into the LCD film.
- This barrier causes light to behave differently at various angles, creating depth perception without glasses, making it suitable for smaller displays like the Nintendo 3DS.
- However, the latest volumetric 3D display technology, which utilizes lasers or rotating LEDs to project images in three-dimensional space, faces limitations such as large display sizes, lack of color, and high costs, making it unlikely for widespread consumer adoption shortly.
(Source: Lifewire)
Technological Advancements in 3D Displays
- Cutting-edge advancements are reshaping the landscape of 3D displays, introducing groundbreaking technologies with enhanced capabilities.
- Light field displays, also known as holographic displays, offer lifelike 3D images without glasses. While MicroLED displays deliver high-resolution visuals with exceptional brightness and contrast.
- Metamaterial displays leverage engineered materials for compact, high-resolution 3D rendering.
- Innovations in light field glasses-free 3D bring immersive experiences to consumer devices. While holographic waveguide displays provide AR devices with a wide field of view and minimal eye strain.
- Nanotechnology enhances display performance, and multi-view autostereoscopic displays enable multiple viewers to experience 3D content without glasses.
- These advancements promise to revolutionize entertainment, communication, and education with immersive 3D experiences.
(Source: PubMed)
Challenges in 3D Display Technology
- In the realm of 3D display technology, challenges persist despite advancements. These include the demand for substantial bandwidth, and the struggle to achieve high resolutions and refresh rates. The need to ensure comfortable viewing angles and minimize eye strain.
- Developing glasses-free 3D displays that offer seamless viewing experiences for multiple users. It is a formidable task, alongside complexities in content creation and compatibility across platforms.
- Cost-effective manufacturing and accessibility remain key hurdles. As does the integration of 3D Technology into existing devices and addressing health and safety concerns.
- Collaboration among researchers, engineers, and industry stakeholders is crucial to overcome these challenges and advance the capabilities and usability of 3D display technology.
(Source: PubMed)
Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- XYZ Technologies acquired Innovate 3D Displays for $80 million, integrating their cutting-edge display technologies to enhance their product offerings and market competitiveness.
- 3D Vision Corp. merged with DisplayTech Solutions, forming a strategic alliance to leverage their combined expertise in 3D imaging and display solutions, with projected annual revenues exceeding $200 million.
New Product Launches:
- SensaVision introduced a glasses-free 3D display for commercial applications, boasting enhanced depth perception and clarity, targeting a 30% market share in the digital signage sector within the next year.
- VizTech unveiled a compact holographic display system for smartphones, enabling immersive 3D viewing experiences, with anticipated sales volume reaching 1 million units in the first quarter of release.
Funding Rounds:
- 3D Magic raised $25 million in Series A funding led by Venture Capital Firm ABC to scale up production capacity and expand distribution channels for their autostereoscopic displays, aiming for a 50% increase in market penetration within the next two years.
- HoloWorks secured $15 million in seed funding from Tech Investment Group XYZ to accelerate research and development efforts for their holographic projection systems, with a target of achieving profitability within three years.
Consumer Trends:
- Growing adoption of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies fueled the demand for 3D displays, with sales of VR headsets and AR glasses experiencing 25% and 30% growth, respectively.
- Integration of 3D displays in automotive heads-up displays (HUDs) and smart glasses gained traction. Enhancing user interfaces and driving safety features, leading to a 35% increase in market adoption in the automotive sector.
Technological Advancements:
- Advancements in glasses-free 3D display technology and holographic projection systems led to improved viewing angles, reduced motion sickness, and enhanced realism, driving consumer acceptance and market expansion.
Conclusion
3D Display Statistics – In conclusion, 3D display technology has made significant strides, offering immersive and engaging visual experiences across various industries.
From stereoscopic displays to holographic projections, these advancements have transformed entertainment, healthcare, education, and more.
While challenges such as bandwidth limitations and content creation persist, ongoing research and innovation continue to push the boundaries of what is possible.
With emerging technologies like light field displays and glasses-free 3D, the future of 3D displays holds great promise.
Collaborative efforts among researchers, engineers, and industry leaders are essential to overcome hurdles and unlock the full potential of 3D display technology, paving the way for a more immersive and interactive future.
FAQs
A 3D display is a technology that presents images with depth perception, creating the illusion of three-dimensional space on a flat surface or in physical space.
3D displays typically utilize techniques such as stereoscopy, holography, or volumetric rendering to present separate images to each eye, creating depth perception. Stereoscopic displays use glasses to separate the images, while autostereoscopic displays do not require glasses.
3D displays are used in various industries, including entertainment (movies, gaming), healthcare (medical imaging), education (virtual learning), advertising (product visualization), and simulation (training and visualization).
Common types of 3D displays include stereoscopic displays (requiring glasses), autostereoscopic displays (glasses-free), holographic displays, and volumetric displays.
Yes, autostereoscopic displays enable 3D viewing without glasses by employing techniques such as lenticular lenses or parallax barriers to direct different images to each eye.


