Table of Contents
Overview
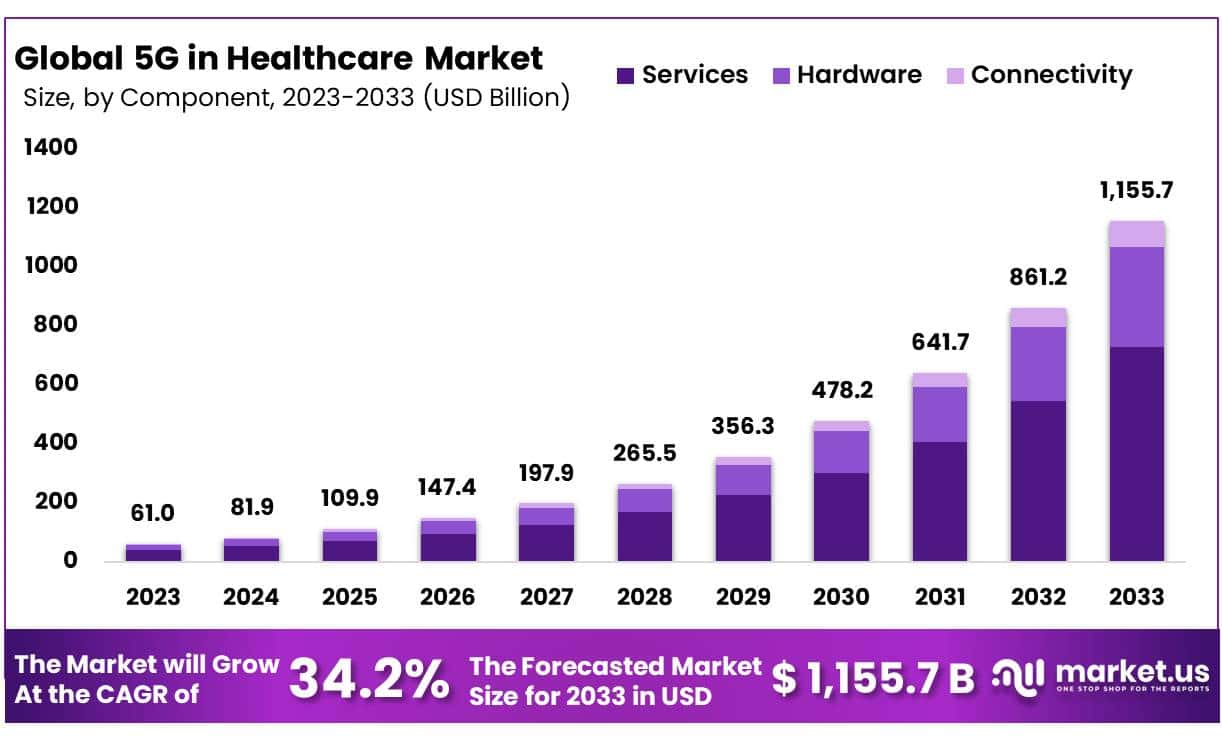
New York, NY – Feb 02, 2026 – The Global 5G in Healthcare Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1,155.7 Billion by 2033 from USD 61.0 Billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 34.2% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The integration of 5G technology into the healthcare sector is being recognized as a significant advancement in digital health infrastructure. With ultra-low latency, high data speeds, and enhanced network reliability, 5G is enabling faster, more efficient, and more connected healthcare services across the value chain.
5G supports real-time data transmission, which is critical for applications such as remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and virtual consultations. High-definition video communication and instant data sharing are improving clinical decision-making and expanding access to quality healthcare, particularly in remote and underserved regions. The growth of connected medical devices and wearables is also being accelerated, allowing continuous tracking of patient vitals and proactive care management.
In hospital environments, 5G is facilitating the adoption of smart healthcare systems. Automated workflows, connected equipment, and advanced imaging solutions are benefiting from stable and high-capacity networks. In addition, emerging use cases such as remote-assisted surgery, robotic procedures, and augmented reality–based medical training are being supported by 5G’s low-latency capabilities.
From a data perspective, 5G is strengthening healthcare data management by enabling faster integration of electronic health records, cloud-based analytics, and artificial intelligence platforms. This is contributing to improved operational efficiency and personalized treatment approaches.
Overall, the adoption of 5G in healthcare is expected to enhance patient outcomes, optimize healthcare delivery, and support the ongoing digital transformation of the global healthcare industry.
Key Takeaways
- The Global 5G in Healthcare Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1,155.7 Billion by 2033 from USD 61.0 Billion in 2023..
- The market growing at a CAGR of 34.2% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
- By component, the services segment accounted for a significant market revenue share of 63.2%, thereby dominating the global 5G in healthcare market in 2023.
- By application, the connected medical devices segment held a substantial market share of 58.4%, driven by its role in transforming patient care delivery and treatment approaches.
- By end user, healthcare providers emerged as the leading segment, commanding a dominant market share of 61.3% in the global 5G in healthcare market.
- Regionally, North America remained at the forefront of the global 5G in healthcare market in 2023.
- The increasing adoption of 5G-enabled remote patient monitoring is strongly reinforcing the growth trajectory of the global 5G in healthcare market.
Regional Analysis
North America leads the global 5G in healthcare market throughout the forecast period, accounting for a strong revenue share of 39.6% in 2023. The region’s leadership is supported by multiple growth factors. These include the rising prevalence of coronary artery disorders, an expanding geriatric population, and continuous product innovations introduced by key market participants. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, nearly 20 million people in the United States were affected by coronary artery disorder in 2020, reinforcing the demand for advanced digital healthcare solutions.
Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness notable growth during the forecast period. This expansion is largely driven by increasing adoption of 5G-enabled medical devices, supportive government initiatives, improving network infrastructure, and the growing integration of IoT-enabled medical equipment across healthcare systems.
Emerging trends in 5G for healthcare
5G is being used for “real-time” clinical work where delay matters
- Clinical pilots have reported ~23–30 ms latency with stable links while sending high-quality medical imaging/video, which supports remote specialist guidance during procedures.
- In telesurgery research, one-way latency around ~73 ms with zero packet loss has been reported in a long-distance trial, which is important for safe control and reliable video.
Robot-assisted tele-surgery is moving from concept to early clinical trials
- Recent studies report ~18 ms motion latency and ~350 ms video delay in a 5G robot-assisted setup that enabled key surgical tasks (cutting, dissection, transfer).
- Other clinical work has reported ~19 ms measured video latency during a remote robotic-assisted procedure.
- At the same time, evidence suggests performance can worsen when delays rise to ~100–200 ms, so engineering focus is being placed on keeping delays low and stable.
Connected ambulances and pre-hospital care are being tested with 5G links
- In the UK, a formal research summary describes 5G-enabled “connected ambulances” aimed at linking paramedics to hospitals and remote doctors for improved pre-hospital decision-making.
- A public case study from the West Midlands shows a remotely located clinician conducting an ultrasound via a haptic interface while interpreting findings in real time (showing the direction of travel for emergency diagnostics).
Network slicing and “quality guarantees” are being designed for clinical reliability
- Healthcare-focused 5G architectures are increasingly being designed around dedicated slices to help guarantee quality of service (QoS) for different medical traffic types (video, vitals, imaging, alerts).
- This is being driven by the need to keep critical data streams stable, rather than only “fast.”
More hospitals are evaluating private 5G for secure, controlled coverage inside buildings
- Research is reporting that private 5G can coexist with existing hospital wireless systems when engineered correctly, supporting the direction toward hospital-controlled networks for clinical workloads.
- This trend is being strengthened by the hospital reality that indoor coverage and interference control matter as much as headline speed.
Use Cases of 5G for healthcare
Remote imaging and tele-ultrasound in emergency care
- Remote scanning and guidance can be supported when latency stays in the tens of milliseconds; one reported setup showed 23–30 ms latency while transmitting clinical-quality visuals.
- Connected ambulance trials have already demonstrated remote clinician involvement in ultrasound workflows in the field.
Robot-assisted telesurgery and remote expert operation
- Early evidence shows surgical tasks can be performed with ~18–19 ms motion/video latency in some 5G-enabled systems, while longer-distance setups have reported ~73 ms one-way latency with zero packet loss in a trial context.
- It is also indicated that keeping delay below ~100–200 ms is important because precision can degrade beyond that range.
Continuous remote patient monitoring using wearables (inside and outside hospitals)
- Reviews of 5G in wearables describe its role in continuous monitoring for chronic disease management and clinical decision support, where stable connectivity is needed for frequent data uploads and alerts.
- Recent work in real-time monitoring architectures is also being built around 5G URLLC concepts and encrypted data flows for vital signs.
AR/VR support for remote assistance, training, and “virtual” ward rounds
- AR/VR-based clinical assistance is being positioned for scenarios that need high-quality video and low delay (for example, remote step-by-step support in procedures). This is highlighted in healthcare-focused 5G deployment guidance as a practical direction.
- The value is strongest when the connection is stable enough to avoid motion sickness, dropped frames, and instruction lag (so performance engineering is central).
Hospital operations: connected devices, tracking, and faster internal data movement
- 5G is being used as a backbone for large numbers of connected devices (medical IoT) and fast movement of clinical data inside facilities, supported by 5G capability targets such as very high throughput (up to multi-Gbps in eMBB scenarios) and large connection capacity concepts.
- Private 5G feasibility work in hospitals supports the direction that mission-sensitive applications (device connectivity, alarms, telemetry) can be carried on controlled wireless infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions on 5G in Healthcare
- How does 5G improve patient care?
Patient care is improved through ultra-low latency communication, enabling real-time remote consultations, faster diagnostics, continuous patient monitoring, and rapid data exchange between connected medical devices, clinicians, and healthcare facilities across diverse care environments. - What role does 5G play in telemedicine?
5G enhances telemedicine by supporting high-definition video consultations, real-time imaging transmission, and uninterrupted connectivity, allowing physicians to perform accurate remote diagnosis, treatment planning, and follow-up care with minimal network delays. - How does 5G support remote surgeries?
Remote surgeries are supported by 5G through ultra-reliable low-latency communication, enabling precise control of robotic surgical systems, real-time video feedback, and seamless data exchange, which reduces procedural risks and expands access to advanced surgical expertise. - Is 5G technology secure for healthcare data?
Healthcare data security is strengthened through advanced encryption, network slicing, and secure authentication mechanisms in 5G networks, helping protect sensitive patient information while meeting regulatory requirements for data privacy and cybersecurity compliance. - What factors are driving market growth?
Market growth is driven by rising demand for telehealth services, increasing adoption of connected medical devices, expanding digital health initiatives, and the need for faster, more reliable data transmission to support advanced healthcare applications. - Which applications dominate the 5G in healthcare market?
Key applications include telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, connected ambulances, smart hospitals, and robotic-assisted surgeries, with telehealth and real-time monitoring accounting for a significant share due to widespread adoption and cost efficiency. - What regions show strong growth potential?
Strong growth potential is observed in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, supported by advanced telecom infrastructure, increasing healthcare digitalization, favorable government initiatives, and growing investments in smart healthcare systems and 5G deployment.
Conclusion
The integration of 5G technology is reshaping the global healthcare ecosystem by enabling real-time connectivity, ultra-low latency, and reliable data transmission across clinical workflows. Its impact spans telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, smart hospitals, and emerging applications such as robotic-assisted surgery and AR/VR-based training.
Market growth is being reinforced by rising digital health adoption, increasing use of connected medical devices, and supportive infrastructure investments, particularly in North America and Asia-Pacific. Overall, 5G is positioned as a foundational enabler of digital health transformation, contributing to improved patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and more accessible, data-driven healthcare delivery worldwide.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



