Table of Contents
- Regional Analysis
- Endpoint Security Adoption Statistics
- The Occurrence of Endpoint Attacks
- Endpoint Attack Methods
- Ransomware
- The Cost of an Endpoint Breach
- Current Endpoint Security Trends Statistics
- Most Common Endpoint Security Threats Statistics
- The Different Methods of Endpoint Security Statistics
- Benefits of Endpoint Security Statistics
- Future of Endpoint Security Statistics
- Extra Endpoint Security Statistics
- Recent Developments
- Conclusion
- FAQ’s
Endpoint Security Statistics: Endpoints are net-connected computing devices that can communicate with other network points and devices. Such gadgets can range from PCs, tablets, and smartphones to smart automobiles and light bulbs.
While these devices are network endpoints, they are frequently the starting point of a cyberattack. Which is why endpoint security is critical. This is especially important in a corporate setting when sensitive company information is at stake.
Antivirus software, endpoint detection and response, EDR, software and services, and multi-factor authentication are examples of endpoint security or protection solutions.
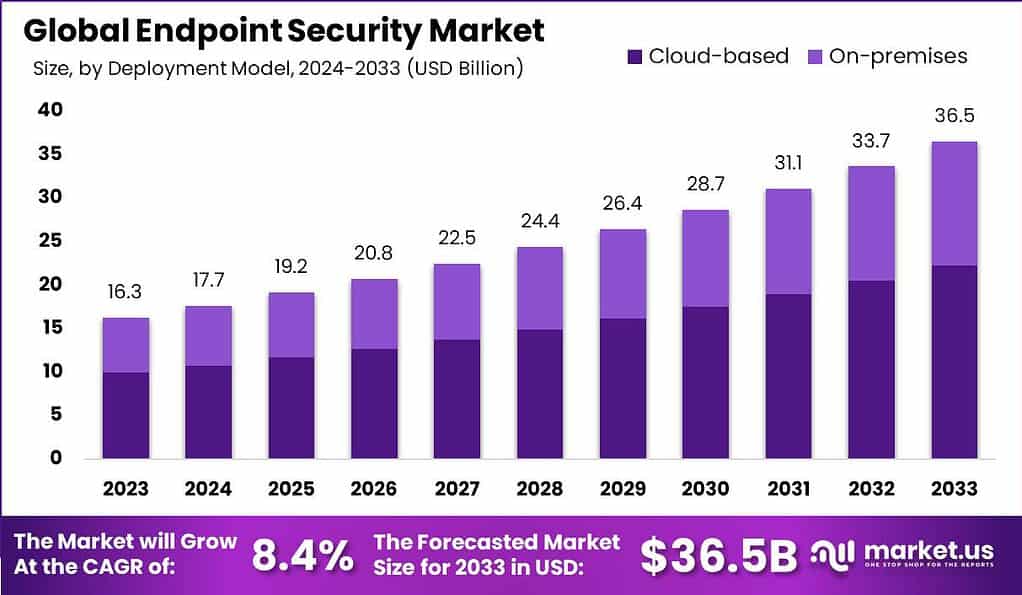
The global endpoint safety market is expected to reach USD 11 billion in 2022 and continue to expand as cybersecurity becomes increasingly important to enterprises today.
The Global Endpoint Security Market is anticipated to be USD 36.5 billion by 2033. It is estimated to record a steady CAGR of 8.4% in the Forecast period 2024 to 2033. It is likely to total USD 16.3 billion in 2023.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America, which includes the United States and Canada, is a mature and technologically advanced endpoint security industry.
Because of the region’s major presence of huge enterprises, financial institutions, and government bodies, there is a high emphasis on cybersecurity.
This region has a high rate of adoption of advanced endpoint security solutions and practices. The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber-attacks, and tight regulatory requirements. Growing awareness of the necessity for robust endpoint protection is driving the market.
Europe
Europe is another big endpoint security market. Countries with a well-established cybersecurity landscape include the United Kingdom, Germany, France, and the Nordic countries.
The region features rigorous data protection requirements. Such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which has pushed endpoint security solutions adoption.
Furthermore, the growing number of cyber threats and high-profile data breaches has fueled demand for enhanced endpoint security technology and services.
Asia-Pacific
Because of increased company digitization, expanding IT infrastructure, and an increase in cyber threats, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing tremendous growth in endpoint security.
China, Japan, India, and South Korea are major contributors to the market. Because the region contains both developed and growing economies, the adoption of endpoint security solutions varies.
Government measures, such as data protection legislation and cybersecurity policies, also have an impact on industry growth.
Latin America
Endpoint security is a growing sector in Latin America. Countries such as Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina are seeing an increase in cyber-attacks and data breaches. Raising awareness about the importance of comprehensive endpoint protection.
The increasing adoption of mobile devices and cloud computing. As well as the growing importance of data privacy legislation, is driving market expansion.
Challenges such as limited cybersecurity expenditures and a lack of awareness of advanced endpoint security solutions, on the other hand, can stymie industry growth.
Middle East and Africa
Endpoint security is becoming increasingly important in the Middle East and Africa region. Countries such as the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa are increasing their investments in cybersecurity infrastructure.
The region presents unique problems, including a diversified threat landscape, geopolitical tensions, and limited resources.
However, increased digitization, mobile device penetration, and government cybersecurity initiatives are projected to fuel the endpoint security market in this area.

Endpoint Security Adoption Statistics
Endpoint protection suites are being adopted by businesses of all sizes and across industries. Here are some key adoption trends
- Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are increasingly adopting endpoint protection suites, as they become more affordable and easier to deploy.
- The healthcare and finance industries are among the leading adopters of endpoint protection suites, due to their stringent security requirements.
- Endpoint protection suites are also being adopted by governments and public sector organizations, as they look to secure their sensitive data and networks.
The Occurrence of Endpoint Attacks
According to Ponemon Institute research, 68% of firms had suffered one or more endpoint assaults that successfully compromised data and/or IT infrastructure. In the same research, 68% of IT experts believe that the rate of endpoint attacks has increased over the previous year.
According to an additional Ponemon study, assaults against endpoints were among the most common that respondents have encountered. With 81% of firms having an attack, including some type of malware and 28% experiencing attacks involving hacked or stolen equipment.

Ransomware is one of the most frequent and destructive types of malware in use today. Once downloaded to the victim’s device. The malware locks users off of company data or encrypts it until the target firm pays a ransom. In 2021, 53% of organizations saw a successful ransomware assault, with approximately 23% experiencing multiple attacks.
Sadly, this figure indicates that ransomware is on the rise. According to a recent SonicWall analysis, recorded ransomware incidences last year constituted a startling 148% year-on-year increase over 2020. A separate Check Point study found that the weekly average of ransomware attacks targeting business networks grew by 50% in 2021 compared to 2020.
With that in mind, it’s no wonder that 69% of CISOs anticipate at least one ransomware assault in 2022.
Endpoint Attack Methods
Malware is one of the most popular methods by which attackers target endpoints, and it can be put on the victim’s device in a variety of ways.
According to Verizon, the use of password dumpers, allows attackers to steal credentials saved on a compromised device. It is the most common sort of malware intrusion, accounting for almost 40% of all breaches. Following password dumpers are application data capture and ransomware.
According to the same survey, Windows apps and Office documents are among the most common file types containing malware, and email and the web are the favored virus distribution mechanisms.
According to Webroot research, 83% of malware threats are kept in one of four locations: %tmp%, %appdata%, %cache%, and %desktop%.
Malware can also be installed by “juice jacking,” which involves altering USB ports to put malware on the victim’s device. In public places, these ports are frequently disguised as free chargers. This installation approach is one to keep an eye out for in firms with a large number of remote workers or people who travel frequently as part of their work. 79% of business travelers have linked their devices to a public USB port or charging station, inadvertently allowing a potential attacker access.
Malware, however, is not only a threat to your company’s endpoints. “SIM swapping” is a sort of cybercrime in which the attacker calls their target’s mobile phone provider while impersonating that target and asks them to change their target’s phone number to one that they own.
This allows the attacker to divert all phone calls and text messages from their target. Since 2016, swapping SIM card attacks on mobile endpoints have more than doubled year on year. The number of people utilizing personal cell phones for work has surged.
Ransomware
Ransomware is among the most common types of malware. According to research by Sophos the most likely (29%) to be introduced into an organization through files downloaded or emails with an infected link.
The phishing method is followed by remote attacks on the server. Which account for 21% of ransomware attacks, and emails with malicious attachments make up 16% of attacks.
The numbers are verified by research done recently in recent times by SonicWall and SonicWall that shows that Ryuk ransomware. Which is typically distributed via TrickBot and Emotet’s phishing campaigns is responsible for approximately one-third of ransomware-related attacks.
However, where do your data be after the ransomware is in place?
Well, 59% of ransomware-related attacks where data is encrypted are stored in public cloud systems like Office 365 or Amazon Web Services (AWS). This is about the location where the data was stolen from and how the attacker utilizes the data.
The majority of attackers send stolen data to an authentic cloud-based storage provider, making the crime harder to trace. Google Drive, Amazon S3, and Mega. nz are the most commonly used cloud storage solutions to store data that has been stolen.
The typical data breach costs $4.27 million, according to IBM. Ransomware and malicious assaults that delete or wipe data destructively cost an average of $4.62 million and $4.69 million. Respectively, while the cost of a successful endpoint attack has risen from $7.1 million to $8.94 million.
According to Coveware analysis, the average compensation of ransomware attacks remained fairly steady between Q2 and Q3 2021. However, the median reward more than doubled. This could be due to attackers avoiding larger targets. Which could result in a national political or law enforcement response, and instead focus on mid-market firms.
The Cost of an Endpoint Breach
In addition to the financial cost of a ransomware attack, there is the (increasingly prevalent) consequence of data loss: in Q3 2021, more than 80% of ransomware assaults included a threat to exfiltrate data.
When data is at the center of every organization, it’s no surprise that, despite law enforcement warnings. An increasing number of companies are choosing to pay the ransom: In the third quarter, 47.8% of corporations elected to pay, rising to 59.6% in the fourth quarter.
Another significant consequence of ransomware attacks is downtime; in Q4 2020, the average organization attacked by ransomware saw around 21 days of outage.
When responding to a ransomware assault, it is usually safer to try to restore your data from backups rather than pay the attacker’s ransom, if backups are available. According to Sophos’ research, more than twice as many firms (56%) recovered their data through backups than by paying the ransom (26%).
Paying the ransom does not always guarantee that you will receive your data back; after all, you are dealing with a cybercriminal. Another 1% paid the ransom but did not receive it back.
Furthermore, according to Sophos’ study, paying the ransom increases the expense of dealing with a ransomware attack.
This cost averages 761,106 USD globally; 505,827 USD for businesses with 100-1,000 people; and 981,140 USD for businesses with 1,000-5,000 employees.
So you know not to pay the ransom, but if you want further information on how to recover from a ransomware assault, see our ransomware recovery guide.
Current Endpoint Security Trends Statistics
Right now, around 58% of enterprises worldwide work telework environment. Remote working allows employees to be more flexible, but it also poses various security risks. When asked which of these security issues they are most concerned about, Ponemon survey respondents responded:
- Lack of physical security in the workspace (47%)
- Risk of malware infection (32%)
- Criminals are gaining control over remote devices to steal sensitive data (24%)
- Securing external comms (23%)
- Securing the network (20%)
- Criminals leveraging devices to gain network access (17%)
- Phishing and social engineering attacks (15%)
- Devices being lost or stolen (12%)
- Securing external access to internal resources (8%)
As we observe, four of the leading nine worries include endpoint assaults. This is hardly surprising given that, since the beginning of the epidemic. 51% of enterprises report that exploits and malware have eluded their intrusion detection systems, and 49% report that exploits and malware have evaded their antivirus software.
Top 11 Endpoint Security Solutions for Business Statistics
- ESET Endpoint Security
- Heimdal™ Threat Prevention Endpoint
- Avast Small Business Solutions
- Bitdefender GravityZone
- Trend Micro
- Crowdstrike Falcon
- Trellix Endpoint Security
- Microsoft Defender Advanced Threat Protection
- SentinelOne
- Sophos Endpoint Protection
- Symantec Endpoint Protection
Top 10 Antivirus Software for Small Businesses
- ESET Endpoint Security
- Heimdal™ Next-Gen Endpoint Antivirus
- Avast Small Business Solutions
- AVG Business
- Bitdefender GravityZone Business Security
- Norton Small Business
- Sophos Intercept X
- Trellix Endpoint Security (ENS)
- Trend Micro Worry-Free Business Security
- WithSecure Elements Endpoint Protection
Most Common Endpoint Security Threats Statistics
- Malware: Malware is any malicious programming that is designed to penetrate a private network. Malware is frequently composed of embedded software or code that accesses a network to extract critical business data. Cybercriminals can employ malware to corrupt data, steal login passwords, or hold critical information hostage.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is a type of virus that uses encryption to hold a victim’s data hostage for a fee. Ransomware encrypts the user’s important data, databases, and apps and refuses to release them until the victim meets the cybercriminal’s demands. It is designed to spread swiftly, crippling an entire company.
- IoT devices: The Internet, or IoT, is the rapidly expanding system of interconnected objects that communicate in real time over embedded networks. Examples include smart appliances, lighting, thermostats washing machines, as well as many smart appliances. In 2022, your dishwasher can send out a tweet, however, this also means that it will be compromised. Despite its ease of use, IoT can play into the attacks of cyber criminals by enhancing the vulnerability of your business.
- Phishing: Phishing refers to a method of cybercrime that uses deceit to obtain login credentials and gain access to sensitive data. This is also among the most prevalent security threats to endpoints. Phishing scams typically are initiated through email links and can be incredibly obvious, but also coordinated and well-planned-out attacks.
- Remote devices: The emergence of COVID-19 in the coronavirus pandemic has given rise to several organizations implementing work-from-home policies and managing employee health care. Remote-based connections are a terrific way for hackers to obtain access, allowing them to abuse your systems for business, then your network, and finally the entire firm.
The Different Methods of Endpoint Security Statistics
- URL filtering This filtering goal is designed to block users from accessing unauthorized websites and apps. URL filtering systems evaluate URLs that are entered into a search engine against an accept or reject list compiled by your IT managers. It also helps keep employees from working on websites that are not productive. Although it’s efficient, URL filtering can be avoided by using VPNs, or virtual private networks (VPN).
- Internet Access Control (NAC): Imagine network Access Control as a gate that blocks access by anyone who is not authorized by your company. Network Access Control (NAC) stops any intrusion into the private network of your company. Only devices that fully comply with your policies regarding data are permitted access. The bigger your network gets; the more devices you’ll be able to have. The more endpoints you’ve got the more requirement for a strong network Access Control. One of the advantages of NAC is its ability to block any malware-prone devices. This reduces infection by malware and assists in determining the primary reason behind any security breach.
- Endpoint Protection Platform: An Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP) is an integrated, centrally-located security protocol for endpoints. The platform is central, which means that it was specifically designed to address the security of your computer by itself and give your company the freedom to concentrate on its primary business operations and expand.
Other Methods of Endpoint Security Statistics
- Insider Threat Monitor: It is essential to keep an eye on and guard against cyber security threats that originate from within your business. If there’s malicious intent or not, employees may divulge confidential information to cybercriminals if they’re not cautious. Set up strict training and monitoring procedures to stop this from occurring. Through Managed IT by Computers Nationwide, we can educate your employees on the best practices to secure sensitive data. We can install software to monitor threats so that you are aware of any security threats coming into your organization.
- Sandboxing When the business you work for has an innovative product or program it must run in a secure environment, it’s an excellent idea to test your program in the security of a separate environment. Sandboxing is an effective method to detect any security risks before when an application or product goes live.
- Endpoint encryption: Endpoint encryption involves the process of encrypting data. Anyone who doesn’t have the encryption key cannot open the file. Data files that are important to you will be encrypted or encrypted to restrict their access within a designated network. Encryption is the final security measure to protect your data in the event of a cyber-attack.
- Secure email gateways They are an essential element of business communication between one another and with each other daily. Phishing emails are the most frequent type of malware, therefore it’s essential to have a strategy in place to block access to emails with potentially dangerous content, or ransomware.
Benefits of Endpoint Security Statistics
- When the endpoints of your SMB are secured, you’re safeguarding your customers, employees as well as your bottom line and your reputation! Who would want to do business with you if they aren’t able to ensure that their data is secure within your control? Let’s talk about the ways that investing in security for your endpoints will help your business grow to new levels…
- One central, single system for managing the security of endpoints: For a long time, IT security is approached by siloed point solutions. Security is managed by each endpoint of a company. This leaves a lot of security gaps at the endpoint. Modern methods to counter threats to security at the endpoint are to create a central endpoint management system. It works from a variety of angles, making security holes much easier to find and resolve.
- Simpler management of security: If the security of your endpoints is centrally managed and well-lit, it decreases administrative costs. Manual administration and auditing tasks that can slow your business can be streamlined, which gives you more time to manage the more important business functions.
Endpoint Security More Benefits Statistics
- Increase resilience of your business Increase business resilience: As we have discussed in the data, there is a good chance that your company is likely to be the victim of any kind of security breach. Each comprehensive security plan for endpoints should include plans for contingency on steps to take in the case of an endpoint security breach. Your system must be able to identify risks before they become apparent as well as create backups in the case of data loss, or corruption, and also recovery options in the situation of an emergency.
- Secure your reputation and your earnings: It’s not a secret that data breaches can be costly for companies. The total cost of an attack by ransomware will be $4.62 million, which is a bit higher than the median data breach which costs $4.24 million. However, that number is small when compared to the damage the breach could cause to your reputation. It is estimated that 60 percent of businesses fail within the first six months following an incident of data loss. Furthermore, estimates place the average share value that is destroyed in a data breach at 7% or more. The level of confidence that efficient security software on endpoints provides is measured both in the bottom line as well as in terms of reputational value.
Future of Endpoint Security Statistics
- More widespread adoption of Artificial Intelligence as well as Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies play an increasing role in security for endpoints. These technologies provide advanced security capabilities for detection and response to threats as well as behavioral analysis and anomaly detection. They help to detect and combat new threats in real time. AI and ML additionally enable automation as well as the capability to learn and adapt to new threats, which makes the security of endpoints more efficient and efficient.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Integration The endpoint detection and reaction (EDR) methods are growing in recognition in cyberspace. EDR concentrates on detecting, analyzing, and combating advanced threats that evade conventional security methods. Shortly, EDR capabilities will likely be integrated into more comprehensive security solutions for the endpoint, providing companies with complete protection and visibility across their devices.
- Cloud-based Endpoint Security With the rising popularity of cloud-based services and remote workplaces cloud-based security solutions are becoming more popular. They provide central management, scalability, as well as real-time threat analysis that allow organizations to safeguard their endpoints no matter their geographical location. Cloud-based solutions also allow for quick updates and patch management to ensure that endpoints are secure against new threats.
Extra Endpoint Security Statistics
- Zero Trust Security: The idea of Zero Trust Security, which believes that no device or user device can be trusted automatically is growing in popularity. With Zero Trust the endpoints are constantly checked for authenticity, and access controls are continuously adjusted in response to the user’s behavior, the health of the device, and the network’s conditions. This method reduces the threat surface and also helps to prevent access by unauthorized users even when an endpoint has been compromised.
- Integration with Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR): Endpoint security statistics solutions are expected to be connected to Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms. SOAR platforms offer an automated incident response as well as threat intelligence integration and simplified workflows. Through integration with SOAR security solutions for endpoints. These solutions make use of automation to swiftly respond to security threats, investigate incidents, and fix security vulnerabilities.
- The focus is on user-centric security: As the traditional security perimeter of networks becomes less clear because of the increasing use in mobile and remote working, security for endpoints will be increasingly focusing on user-centric approaches. This means securing the identity of the user and providing the security of access to resources, regardless of the device or network employed. Technologies like multi-factor authentication Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), as well as Identity and Access Management (IAM), are going to play crucial aspects in this new user-centric approach.
- Privacy and Privacy and Data Protection: Privacy regulations like the GDPR, as well as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Have highlighted the importance of safeguarding personal information. Future security solutions for endpoints will have to take into consideration privacy concerns and offer robust security measures for data. Data loss prevention, encryption, (DLP), and other privacy-focused features will become an integral part of the cybersecurity solutions for endpoints.
Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- SentinelOne acquired Attivo Networks in a deal worth $616 million. Aiming to enhance its capabilities in detecting and responding to cyber threats.
- McAfee completed its acquisition of Light Point Security, integrating its browser isolation technology to bolster its endpoint protection solutions.
New Product Launches:
- CrowdStrike introduced its Falcon Fusion platform, designed to provide unified management and response capabilities across endpoints, workloads, and identities.
- Carbon Black unveiled its Predictive Security Cloud 2.0, incorporating advanced analytics and threat intelligence to deliver proactive endpoint protection.
Funding Rounds:
- Tanium secured $300 million in Series G funding, valuing the company at $9 billion, to further develop its endpoint security and management solutions.
- Cybereason raised $275 million in Series F funding. Enabling the company to expand its endpoint detection and response platform and global presence.
Partnerships and Collaborations:
- VMware partnered with CrowdStrike to integrate its endpoint security capabilities with VMware Carbon Black Cloud. Providing customers with enhanced threat detection and response.
- Cisco collaborated with SentinelOne to combine its endpoint security solutions with the Cisco SecureX platform. Offering comprehensive visibility and protection across the network.
Conclusion
Endpoint Security Statistics – In the end, endpoint security is an essential component of cybersecurity that focuses on protecting devices or endpoints from a variety of dangers.
Security for devices is experiencing substantial growth across the globe due to the growing number and sophistication of cyber-attacks and the increasing number of connected gadgets. As well as the rising awareness of the necessity for powerful endpoint protection.
The main factors that drive the use of security solutions for endpoints. Include strict regulatory requirements high-profile data breaches and the digitalization of business across all industries.
Companies are investing more and more in cutting-edge security solutions for endpoints and methods to protect their confidential data, intellectual property, and customer data.
FAQ’s
Endpoint security refers to the practice of securing individual devices or endpoints, such as laptops, desktops, servers, and mobile devices, from various threats. Including malware, unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cybersecurity risks.
Endpoint security is crucial because endpoints are often the entry points for cyberattacks. Securing these devices helps protect sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access. Detect and block malware, and ensure the overall integrity and confidentiality of an organization’s network and data.
Common threats to endpoints include malware (viruses, ransomware, spyware), phishing attacks, zero-day exploits, unpatched software vulnerabilities, insider threats, and physical theft or loss of devices.
Endpoint security solutions typically include antivirus and anti-malware software, firewall protection, intrusion detection/prevention systems, device control, data encryption, vulnerability assessment, endpoint detection and response (EDR), and security management consoles for centralized monitoring and control.
Yes, many endpoint security solutions offer centralized management consoles that allow administrators to monitor and manage endpoints from a single location. This enables better visibility, control, and the ability to enforce security policies consistently across all endpoints in an organization.
No, endpoint security is relevant for both businesses and individuals. While businesses need to protect their network and sensitive data. Individuals also need to secure their devices to prevent identity theft, financial fraud, and unauthorized access to personal information.


