Introduction
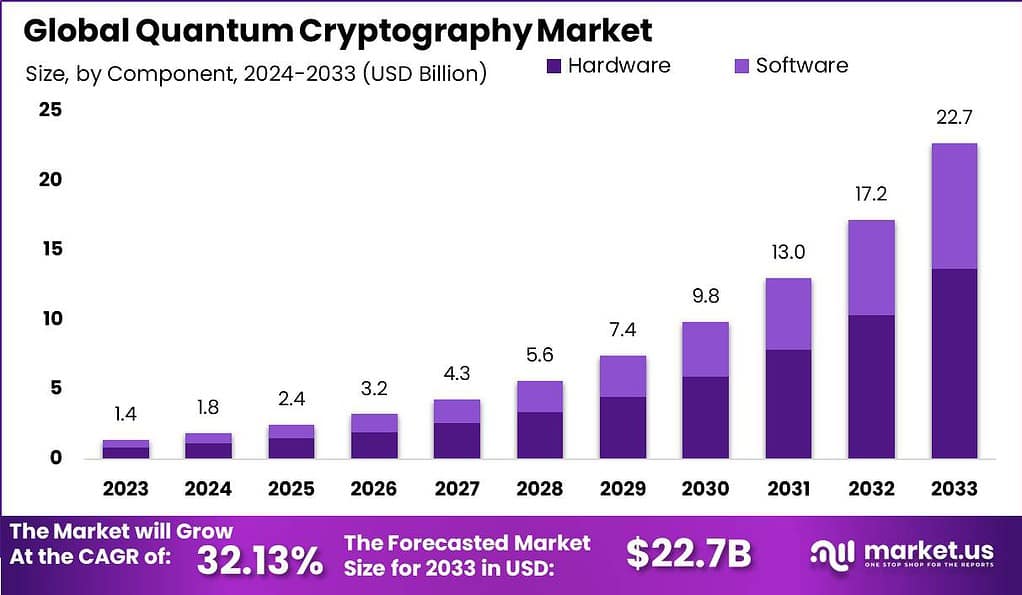
The Quantum Cryptography Market is positioned at the forefront of cybersecurity innovation, leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to fortify the security of digital communications against the most sophisticated cyber threats. With a projected market size of USD 1.8 billion in 2024, this sector is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 32.13%, reaching USD 22.7 billion by 2033. This remarkable growth trajectory is underpinned by the escalating prevalence of cyberattacks and the increasing demand for next-generation security solutions across various sectors, including IT, telecommunications, BFSI, government, defense, and healthcare.
The market’s dynamic landscape is shaped by several key players, including QuintessenceLabs, Crypta Labs, ID Quantique, MagiQ Technologies, Inc., and NuCrypt, who are at the forefront of driving innovation in Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and other quantum encryption technologies. Recent developments in the field have seen significant partnerships, such as that between ID Quantique and CryptoNext Security, aiming to enhance Quantum-Safe Communication Solutions for mobile users, and collaborations between Oxford Ionics and Infineon Technologies, targeting the industrial production of quantum processing units.
Comparative insights with adjacent markets, such as Quantum Computing and Cloud Encryption, reveal a broader technological ecosystem experiencing robust growth, with the Cloud Encryption market exhibiting a particularly strong CAGR of ~30% through 2033. This reflects a burgeoning landscape of digital transformation where quantum cryptography plays a crucial role in securing data against the potential future threats posed by quantum computing advancements.
To learn more about this report – request a sample report PDF
Key Takeaways
- The global quantum cryptography market is projected to reach a substantial value of USD 22.7 billion by 2033, showing a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate of 32.13% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
- Arqit, a company specializing in quantum encryption solutions, achieved a market capitalization of approximately $1.7 billion on April 14, 2022, after going public in 2021 through a SPAC merger.
- China leads in quantum cryptography patents, with over 4,000 applications reported by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), indicating significant research and development activity in the country.
- According to a survey by the Cloud Security Alliance, it is projected that 66% of organizations will adopt quantum-safe cryptography by 2030 to mitigate the threats posed by quantum computing.
- The U.S. Department of Energy granted $74 million in 2022 to accelerate the commercialization of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and other quantum networking technologies, demonstrating government support for quantum-safe solutions.
- A report by Entrust reveals that 81% of organizations believe there would be a medium to high business impact if their current encryption and security solutions are compromised by quantum computers, highlighting the importance of adopting quantum-safe encryption.
- Thales report indicates that 53% of cybersecurity professionals believe that quantum computers will be capable of breaking current public key cryptography within the next 10 years, creating a sense of urgency for investing in quantum-safe security measures.
- North America leads the quantum cryptography market, holding over 31.6% share in 2023, driven by robust technological infrastructure, research and development activities, and collaborations between academia, government, and private sectors.
- The hardware segment, particularly quantum key distribution (QKD) systems, held a dominant market position in 2023, capturing over 60.3% share, indicating the critical role of hardware in ensuring the secure transmission of information.
- Network security emerged as the dominant application segment, accounting for more than 53% of shares in 2023, driven by escalating threats to data transmission and increasing demand for secure communication channels.
- In 2023, the Government and Defense segment held a dominant market position in the quantum cryptography market, capturing more than a 36% share, driven by the escalating demand for advanced security solutions against increasing cyber threats and espionage activities targeting sensitive government and military communications.
- The quantum cryptography market faced a significant restraint in the form of high implementation costs, which can be prohibitively expensive for many organizations, especially smaller entities and emerging markets.
- The quantum cryptography market is poised to benefit from a spur in demand for security solutions across various industry verticals, driven by the increasing awareness and concern for advanced data protection mechanisms.
- A critical challenge in the quantum cryptography market is its commercialization, as translating theoretical advantages into practical, widely available solutions has been slow due to technological complexity, lack of standardization, and high implementation costs.
Trends
- Transition to Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: The threat posed by quantum computing to current encryption standards, such as RSA and elliptic-curve cryptography (ECC), catalyzes the transition to quantum-resistant cryptography. This shift is becoming a mainstream discussion in boardrooms, especially within large enterprises in sensitive industries like finance, healthcare, and military contracting. The focus is on developing roadmaps for deploying post-quantum cryptography (PQC) to safeguard assets and operations against new computing paradigms. This trend is supported by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology’s (NIST) development of quantum-resistant encryption standards. (Source: siliconrepublic.com)
- Global Standards and Governance for Post-Quantum Cryptography: NIST is in the process of standardizing encryption algorithms that can resist quantum computer attacks. With three new algorithms expected to be ready for use in 2024, this standardization effort marks a critical step toward global readiness for quantum-resistant encryption. These developments are vital for organizations worldwide to integrate these tools into their encryption infrastructure, protecting sensitive information against future threats. (Source: nist.gov)
- Quantum-Safe Cryptography Standards and Implementation: The commercial realization of quantum technology is prompting organizations to adopt quantum-safe cryptography standards before quantum computing becomes widely accessible. IBM and other entities are leading the way in developing quantum-safe schemes, emphasizing the urgency of preparing for quantum threats to secure today’s data against tomorrow’s challenges. The newly developed NIST standards aim to enable organizations to mitigate future quantum threats effectively. (Source: esecurityplanet.com)
- Guidance on Migrating to Post-Quantum Cryptography: The US government, through CISA, NSA, and NIST, has published guidance encouraging organizations to proactively prepare for migrating to quantum-resistant cryptographic standards. This includes creating a quantum-readiness roadmap, assessing reliance on quantum-vulnerable cryptography, and beginning quantum risk assessment processes and vendor engagement. (Source: securityweek.com)
- Formation of the Post-Quantum Cryptography Alliance (PQCA): To facilitate the adoption of post-quantum cryptography, the PQCA has been established, engaging in technical projects such as the development of software for evaluating, prototyping, and deploying post-quantum algorithms. This initiative underscores the collaborative effort required to ensure the security of digital protections in the face of quantum computing advancements. (Source: securityweek.com)
Facts About Quantum Cryptography
- Security Evaluation of Current Public Key Cryptography
- RSA and elliptic curve cryptography rely on mathematical problems like integer factorization and discrete logarithms for security.
- Security strength is measured in bit lengths, with 128-bit security considered standard.
- Quantum computers pose a threat to current cryptography due to their ability to perform complex computations exponentially faster.
- Quantum Computer’s Evolution
- Quantum computers utilize quantum mechanics phenomena like superposition and entanglement for computation.
- While quantum computers are evolving rapidly, their practical application for breaking cryptographic algorithms remains limited due to noise and instability.
- Companies like Alphabet and IBM have made significant strides in quantum computer development, with IBM projecting advancements up to 4,158 qubits by 2025.
- Selection of Post Quantum Cryptography
- NIST initiated a standardization project for Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC) in 2016.
- CRYSTALS Kyber, CRYSTALS Dilithium, FALCON, and SPINCS+ were selected as standard algorithms in 2022.
- Parameters like algorithm security strength and mathematical foundations differentiate PQC algorithms from traditional ones.
- Post Quantum Security for Symmetric Key Cryptography
- Grover’s algorithm highlights the reduced security strength of symmetric key algorithms against quantum computers.
- Selecting longer key lengths and hash function outputs ensures post-quantum security for symmetric key cryptography.
- World Trends for Post Quantum Cryptography
- Open source projects like PQClean and PQCRYPTO offer software libraries for post-quantum algorithms.
- IT companies are developing beta versions of post-quantum cryptography for TLS.
- Governmental organizations like CISA and ENISA advocate for the adoption of post-quantum cryptography to ensure long-term security.
- Conclusion
- Post-quantum cryptography is essential for maintaining digital security in the face of advancing quantum computing.
- Standardized algorithms provide a framework for secure communication in the post-quantum era.
- Continued research and collaboration are necessary to implement robust post-quantum cryptographic solutions effectively.
Recent Developments
- Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations: Companies in the quantum cryptography sector are engaging in strategic partnerships to enhance their capabilities and expand their market presence. For example, Amazon Web Services introduced skill development programs for quantum computing in India, collaborating with academic institutions to integrate Amazon Braket, a quantum computing service. Another notable collaboration includes the International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad partnering with Synergy Quantum India to develop quantum technologies.
- Innovations and Technological Advancements: The field has seen the introduction of new quantum key distribution (QKD) technologies and cryptographic chips aimed at securing IoT device communications, as demonstrated by SK Telecom & ID Quantique. European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) published a Protection Profile for the security assessment of QKD modules, marking a step forward in standardizing quantum cryptography.
- Expansion and Growth in Asia Pacific: The Asia Pacific region is experiencing substantial growth in quantum cryptography, driven by the increasing adoption of quantum technologies, rising cybersecurity threats, and the need for secure communication channels. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are leading this advancement, with significant investments in quantum cryptography solutions.
- Regional Dominance and Startup Growth: North America continues to dominate the market, buoyed by an increase in research projects and quantum communications (QComms) startups, especially in the U.S. and Canada. The number of QComms startups in the U.S. grew from 5 in 2015 to 19 in 2021.


