Table of Contents
Introduction
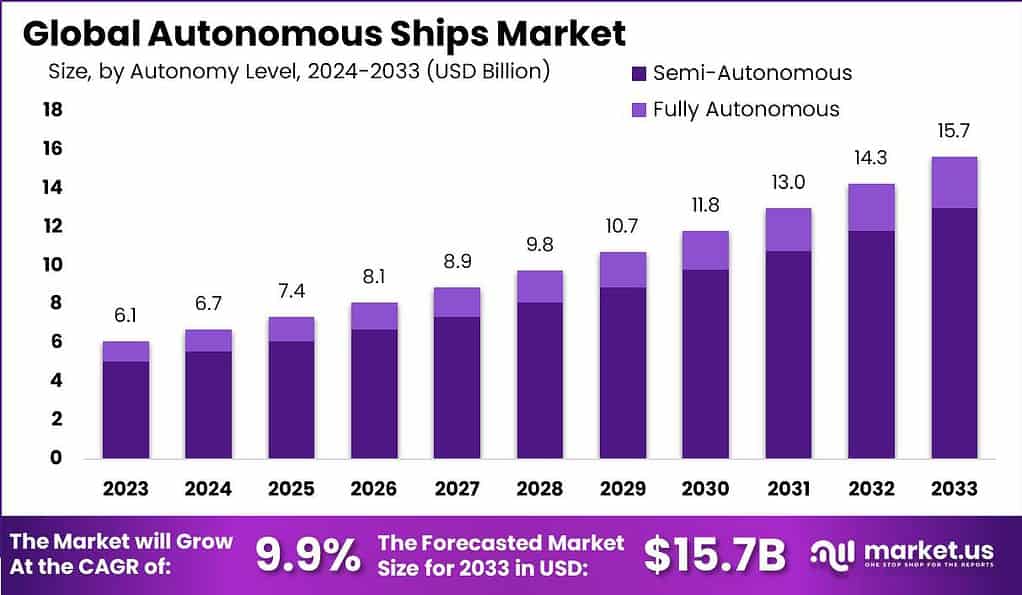
According to Market.us report, the worldwide market for Autonomous Ships is projected to grow from USD 6.1 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 15.7 billion by 2033. This growth indicates a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.9% from 2024 to 2033. The autonomous ships market is entering an exciting phase as technology advances, making self-navigating ships a reality. These vessels, equipped with sensors, AI, and other technologies, can operate without human intervention, promising to revolutionize maritime transport by increasing safety and efficiency.
One of the key drivers of growth in this market is the push for enhanced safety and efficiency in maritime operations. Autonomous ships minimize human error, which is a leading cause of maritime accidents. Additionally, they optimize fuel consumption and voyage planning, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact. The growing advancements in AI and machine learning technologies also fuel the market’s expansion, enabling more sophisticated navigation and operational systems onboard.
Despite these advantages, several challenges could slow market growth. Regulatory hurdles are significant, as international maritime laws currently require vessels to be manned by crews. Technological limitations, such as the need for reliable communication systems to operate ships remotely, also pose challenges. Moreover, cybersecurity risks are a critical concern, with the potential for hacking posing threats to the safety of autonomous operations.
Nevertheless, the opportunities in the autonomous ships market are vast. The technology opens up new possibilities for shipping companies to operate more cost-effectively and with fewer human crew members, potentially reshaping labor dynamics in the industry. The technology enables new services such as unmanned cargo delivery and specialized tasks like oceanographic monitoring or underwater cable repairs, creating new market opportunities within the maritime industry. Additionally, these ships can access dangerous or remote areas without risking human life, useful for research and rescue operations in harsh environments.
Key Takeaways
- The Autonomous Ships market is poised for robust growth, anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 9.9% from 2024 to 2033, ultimately reaching a market valuation of USD 15.7 billion by 2033, up from USD 6.1 billion in 2023.
- In the segmentation by operational capability, the Semi-Autonomous segment notably led the market in 2023, securing an impressive 82.9% share of the total market.
- Regarding technology components, the Hardware segment was predominant in 2023, accounting for a significant 77.5% share of the overall market.
- From a usage perspective, the Commercial segment was the largest in 2023, capturing a substantial 64.2% share of the market.
- Regionally, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) area maintained a leading position in 2023, with a 43.0% market share. This dominance is attributed to robust investments in maritime infrastructure, a thriving shipbuilding industry, and considerable government backing for autonomous ship initiatives.
Autonomous Ships Statistics
- Nippon Yusen is set to conduct the world’s first trial of an autonomous ship on a 236-mile route, notable for its high marine traffic. This pioneering endeavor is a significant milestone in maritime innovation.
- The global autonomous ships market is poised for significant growth over the next decade, with projected market valuations rising from $6.1 billion in 2023 to $15.7 billion by 2033. This robust expansion is characterized by a steady compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.9%, reflecting increasing investments and advancements within the sector.
- From the onset in 2023 with a market size of $6.1 billion, there is a consistent year-over-year increase.
- By 2024, the market size is expected to grow to $6.7 billion, followed by a rise to $7.4 billion in 2025.
- The growth trend continues with the market reaching $8.1 billion in 2026 and $8.9 billion in 2027.
- As we approach the end of the decade, the increments become more pronounced with the market size reaching $9.8 billion in 2028, $10.7 billion in 2029, and $11.8 billion in 2030.
- The growth trajectory steepens further in the early 2030s, culminating at $15.7 billion by 2033.
- Further, the Nippon Foundation forecasts that the integration of technologies like artificial intelligence, which is expected to enhance operational efficiencies, could contribute around $9 billion to Japan’s economy by 2040 through the development of unmanned ships. These advancements are anticipated to significantly influence the economic landscape, pushing the boundaries of traditional maritime operations.
Emerging Trends
- Increased Adoption of AI and Big Data: The integration of artificial intelligence and big data analytics is becoming more prevalent, allowing for improved navigational safety and operational decision-making in autonomous ships.
- Enhanced Remote Control Capabilities: There is a growing trend towards developing ships that can be controlled remotely, reducing the need for crew on board and enhancing operational efficiency.
- Focus on Environmental Sustainability: Autonomous ships are increasingly being designed with eco-friendly technologies such as electric and hybrid propulsion systems to minimize maritime emissions and comply with global environmental standards.
- Government and Defense Applications: There is significant interest from governmental and defense sectors in deploying autonomous ships for various applications, including surveillance and remote operations, supported by initiatives like the Norwegian Forum for Autonomous Ships (NFAS) and other national projects.
- Collaboration Between Tech and Shipbuilding Industries: Partnerships between technology firms and traditional shipbuilding companies are on the rise, aiming to bridge the gap between current marine vessels and future autonomous operations.
Top Use Cases for Autonomous Ships
- Commercial Cargo Transport: Autonomous ships are increasingly used in commercial sectors for transporting goods and cargo, leveraging automation to improve efficiency and reduce operational costs.
- Environmental Monitoring: These vessels are employed for environmental monitoring and data collection, utilizing advanced sensors and systems to assess maritime conditions without human presence.
- Military and Defense: Autonomous ships are utilized in military operations for tasks such as patrolling, surveillance, and reconnaissance, providing a strategic advantage by conducting operations without direct human risk.
- Search and Rescue Operations: The ability to operate in hazardous conditions makes autonomous ships ideal for search and rescue missions, offering reliable assistance in emergency situations.
- Scientific Research: They are also crucial in scientific research, allowing for the exploration of underwater and surface marine environments that are otherwise challenging and risky for crewed ships.
Major Challenges
- Regulatory Frameworks: Existing maritime regulations were not designed with autonomous ships in mind, leading to significant challenges in integrating these technologies into current legal frameworks. Both the U.S. and international regulations need adaptation to better accommodate unmanned vessels and automated systems, which involves complex legal considerations about vessel control and crew responsibilities.
- Technological Reliability: Building trust in autonomous technology is critical, as stakeholders must believe in the system’s reliability and safety. Trust develops over time as the technology proves itself through consistent performance. However, initial skepticism and the need for extensive testing pose significant barriers to adoption.
- Social and Labor Impacts: The potential reduction in crew due to automation raises concerns about job losses. While some officers might find comparable positions ashore, it’s less likely for lower-rated crew members, contributing to resistance from maritime labor communities
- Technical Integration Challenges: As autonomous technologies evolve, integrating them into existing ship architectures and systems poses significant challenges. This includes ensuring compatibility with current vessel designs and port operations, where automation must seamlessly interact with traditional elements.
- Security and Cyber Threats: With increased reliance on digital systems, autonomous ships face heightened risks from cyber threats. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures are in place is crucial to protect against potential hacks that could jeopardize operational safety and data integrity.
Market Opportunities for Autonomous Ships
- Enhanced Safety and Efficiency: Autonomous ships offer the potential for increased safety by reducing human error, which is a leading cause of maritime accidents. Additionally, automation can enhance operational efficiency, optimizing fuel use and reducing transit times.
- Cost Reduction: Over the long term, autonomous ships could significantly lower operational costs, primarily through reduced labor expenses and optimized maintenance through predictive analytics and automated systems.
- Expansion into New Markets: The ability of autonomous ships to operate in challenging environments without risking crew life could open up new markets. These include remote research, deep-sea mining, and accessing hazardous areas.
- Innovative Shipping Models: The advent of fully autonomous vessels can lead to new business models and services within the maritime industry, such as on-demand shipping, which could further enhance market dynamics and customer service offerings.
- Compliance with Environmental Regulations: Autonomous ships are well-positioned to align with increasing environmental regulations in the shipping industry. They can be equipped with advanced technologies to minimize emissions and operate more sustainably, thereby supporting industry compliance with global environmental standards.
Recent Developments
- ABB Ltd.:
- January 2024: ABB acquired Sevensense, a Swiss start-up specializing in AI-enabled 3D vision navigation technology for autonomous mobile robots. This acquisition is part of ABB’s strategy to enhance its capabilities in autonomous systems, including applications in autonomous ships.
- June 2024: ABB launched the OmniCore, an advanced robotics control platform designed to integrate AI, sensor, cloud, and edge computing systems. This platform enhances the automation and autonomy of various robotic applications, which can be applied in the maritime sector.
- Wärtsilä Oyj Abp:
- April 2023: Wärtsilä introduced its new autonomous navigation system, the Wärtsilä SmartMove Suite, which enables ships to navigate autonomously, avoiding obstacles and optimizing routes. This development aims to improve safety and efficiency in maritime operations.
- November 2023: Wärtsilä signed a collaboration agreement with Kongsberg Gruppen to jointly develop autonomous maritime solutions, combining their expertise in marine technology and autonomous systems.
- Rolls-Royce Holdings plc:
- May 2023: Rolls-Royce launched its latest autonomous ship control system, known as the Intelligent Awareness System, which integrates AI and advanced sensors to provide enhanced situational awareness and decision-making capabilities for autonomous vessels.
- September 2023: Rolls-Royce entered a partnership with Sea Machines Robotics to integrate their autonomous control systems with Rolls-Royce’s marine propulsion technology, aiming to create more efficient and reliable autonomous ships.
- Kongsberg Gruppen:
- March 2023: Kongsberg announced the completion of the first autonomous voyage of its Yara Birkeland, the world’s first fully electric and autonomous container ship. This milestone marks a significant step forward in the commercialization of autonomous shipping technology.
- August 2023: Kongsberg launched its new Remote Operation Center (ROC), enabling operators to monitor and control autonomous vessels from shore, enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
- L3Harris Technologies Inc.:
- July 2023: L3Harris unveiled its new autonomous surface vessel (ASV) technology, designed for a range of applications including maritime security, environmental monitoring, and offshore operations. This technology leverages advanced AI and sensor fusion to enable fully autonomous operation.
- December 2023: L3Harris acquired a minority stake in Sea Machines Robotics, further strengthening its position in the autonomous maritime technology market.
- Siemens AG:
- February 2023: Siemens launched its new autonomous ship energy management system, which uses AI to optimize energy consumption and reduce emissions. This system is part of Siemens’ broader strategy to support sustainable maritime operations.
- October 2023: Siemens collaborated with RH Marine to develop integrated autonomous navigation and energy management solutions for commercial shipping, aiming to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of maritime operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the autonomous ships market is poised for significant growth and transformation in the coming years. The industry is witnessing a shift towards autonomous technologies driven by the need for improved efficiency, safety, and sustainability in maritime transportation. With advancements in artificial intelligence, connectivity, and automation, autonomous ships offer a promising solution to enhance operational capabilities and reduce human error.


