Table of Contents
Introduction
The pace of AI adoption in manufacturing has increased as firms seek higher efficiency and improved accuracy in daily operations. The interest in AI has been supported by the ability to process large volumes of data and extract actionable insights that were previously unreachable through traditional systems. The adoption journey has been influenced by rising operational pressures and the need to maintain consistency in competitive markets. As a result, AI is being positioned as a foundational technology that strengthens decision making and supports long term productivity gains.
The integration of AI into factories has also been motivated by the demand for safer work environments and better resource utilization. The industry has recognized that machines equipped with learning capabilities can reduce downtime and ensure smoother operations. Studies show that more than 70% of global manufacturers now consider AI essential for digital transformation, reflecting a structural shift in how factories operate. This shift demonstrates that AI is no longer viewed as an optional upgrade but as a strategic requirement for modern manufacturing.
Request AI Impact Analysis on the Manufacturing Industry Market in – PDF Brochure
Market Outlook
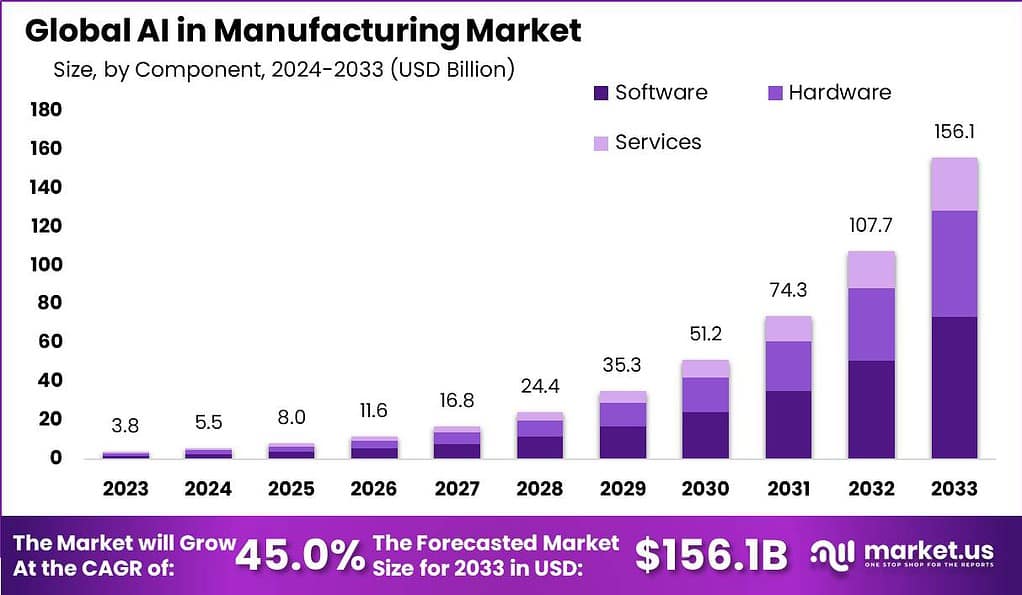
The global AI in manufacturing market is expected to reach approximately USD 156.1 billion by 2033, rising from about USD 3.8 billion in 2023 at a CAGR of 45% from 2024 to 2033. This trajectory reflects rapid adoption of AI driven automation, predictive maintenance, and intelligent quality control across manufacturing sectors.
According to a groundbreaking study, AI adoption in manufacturing has reached a meaningful milestone, with 35% of companies already integrating AI into their operations. The financial outlook is also strong, as the market value of AI in manufacturing is expected to rise from USD 3.8 billion in 2023 to nearly USD 24.4 billion by 2028.
Insights from the Manufacturing Institute indicate that AI driven decision support systems can improve manufacturing efficiency by up to 20%, reinforcing AI’s role as a practical tool rather than a theoretical concept. The study further shows that manufacturers primarily use AI in maintenance and quality functions, with about 29% relying on AI for maintenance. Predictive maintenance supported by AI can reduce machinery maintenance costs by up to 25% and lower breakdowns by nearly 70%, highlighting substantial operational benefits.
AI Impact Analysis
Transformation of Production Processes
Production processes have been transformed as AI provides the ability to automate complex tasks, identify inefficiencies, and improve throughput. Manufacturers have relied on AI driven systems to coordinate production flows, reduce bottlenecks, and maintain consistency at scale. This transformation has supported the industry’s shift from traditional linear workflows to more dynamic and adaptive production models that respond quickly to changing demands. The resulting gains have increased operational stability and reduced manual errors across multiple production lines.
The adoption of AI enabled systems has also improved decision making on shop floors. Real time data analysis helps teams evaluate machine performance, energy use, and material consumption. Nearly 64% of manufacturers report improvements in operational planning after deploying AI based production tools. This improvement signals that production processes are moving toward greater precision, where each step is optimized to reduce waste and improve output quality.
Predictive Maintenance and Asset Reliability
Predictive maintenance supported by AI has increased equipment reliability by identifying failures before they interrupt production. Sensors embedded across machines collect continuous performance data, helping identify unusual patterns that indicate possible faults. This approach has allowed operators to schedule repairs proactively, preventing costly breakdowns and extending the life of machinery. Many firms report that unplanned downtime decreases by over 30% when predictive maintenance systems are implemented, showing a clear benefit to asset management.
Reliability has improved further as AI models learn from each maintenance event and continuously refine predictions. This learning process supports a preventive strategy rather than a reactive one, creating a stable environment for high volume manufacturing. As accuracy increases, maintenance resources are used more efficiently, with fewer interventions and better allocation of repair teams. This improvement strengthens continuity in operations and reduces long term maintenance expenses.
AI Driven Quality Inspection and Defect Detection
Quality inspection practices have shifted as AI tools detect defects faster and with greater accuracy than manual inspection. High resolution imaging systems supported by AI models evaluate products in real time, allowing immediate identification of deviations from required standards. This capability has been especially helpful for industries with strict precision requirements. Research indicates that AI inspection systems can reduce defect rates by nearly 50%, improving overall customer satisfaction.
The continuous learning nature of AI models ensures deeper recognition of subtle patterns that human eyes may miss. As datasets grow, the system becomes more capable of identifying microscopic or complex flaws. This accuracy helps manufacturers maintain uniformity across large production volumes and ensures compliance with strict regulatory standards. The improved inspection process strengthens brand trust and lowers the financial burden of product recalls or rework.
Supply Chain Optimization and Forecasting Improvements
AI has strengthened supply chain management by improving demand forecasting, inventory accuracy, and logistics planning. Manufacturers rely on AI to track real time supply conditions and identify disruptions before they affect production. This oversight reduces uncertainty and helps maintain a smooth flow of materials. Studies show that forecasting accuracy improves by nearly 40% with AI driven planning tools, enabling better procurement and distribution decisions.
Furthermore, AI supports risk mitigation by analyzing supplier performance, market volatility, and transportation constraints. The system generates simulation models that help teams evaluate alternative strategies and maintain supply resilience. These insights have supported faster responses to global disruptions and allow firms to operate with greater confidence. The improved visibility across supply chains has become critical as manufacturers handle growing complexity in sourcing and distribution.
Automation and Robotics Integration
AI has strengthened automation by enabling robots to perform complex tasks with precision and adaptability. AI guided robots handle repetitive, labor intensive, and hazardous activities, allowing human workers to focus on tasks that require judgement or creativity. Research shows that nearly 43% of high performing factories now operate with advanced robotic systems trained through AI, improving both accuracy and consistency. This shift has supported safer work environments and reduced workforce strain.
Integration of AI with robotics has also enabled real time decision making on production floors. Robots learn from continuous input and adjust to variations in materials or workflows without manual intervention. As capabilities grow, robotic units become more flexible and suitable for high mix production environments. This transformation provides manufacturers the agility needed to respond to shifting customer requirements and shorter product life cycles.
Challenges Slowing AI Adoption
Despite the benefits, adoption has been slowed by the lack of skilled professionals who can manage and operate AI systems. Many factories face training gaps, making it difficult to deploy advanced models at scale. This skills shortage affects integration, monitoring, and long term maintenance of AI infrastructure. Studies reveal that nearly 45% of manufacturers cite workforce readiness as the primary barrier to AI expansion.
Financial constraints also challenge smaller firms, as implementation requires investment in data systems, sensors, and specialized software. These costs make adoption difficult for organizations operating with tight budgets. As a result, adoption rates vary widely across regions and company sizes. Until these constraints are eased, AI deployment will continue to progress unevenly across the global manufacturing landscape.
Ethical and Governance Considerations
Ethical concerns have influenced AI adoption in manufacturing. Firms are required to ensure that automated decisions remain transparent and fair, free from unintended bias. Governance frameworks must address data privacy, accountability, and traceability of AI decisions. Surveys show that over 52% of manufacturing leaders view ethical governance as a priority for long term AI acceptance.
The industry also faces concerns regarding workforce displacement. Although AI creates opportunities for higher skilled roles, there is persistent worry about reduction of traditional labor. Clear communication, reskilling programs, and responsible transition strategies are required to maintain trust among workers. Ethical deployment ensures that AI becomes a supportive tool rather than a disruptive force.
Opportunities for Innovation and Future Growth
Significant opportunities are emerging as firms use AI to develop new product lines, enhance customization, and improve sustainability. AI enables deeper insight into material behavior, production energy use, and design optimization. These capabilities support the creation of lightweight, durable, and environmentally friendly products. Research indicates that more than 60% of manufacturers see AI as key to future product innovation.
There is also strong potential for new business models such as on demand manufacturing and distributed production networks. AI tools help coordinate small batch production with high precision, reducing waste and shortening innovation cycles. Manufacturers adopting such models are positioned to respond quickly to changing market expectations and achieve long term differentiation.
Future Outlook for AI Enabled Manufacturing
The future outlook indicates that AI will become a central component of every major manufacturing function. Increased maturity of algorithms and wider availability of operational data will make AI systems more accurate and dependable. Over 80% of industrial leaders expect AI to be fully embedded in production planning, maintenance, and quality control within the next decade. This expectation reflects a steady shift from experimentation to full scale integration.
The manufacturing ecosystem will evolve as firms adopt connected platforms that integrate robotics, analytics, and predictive intelligence into unified operations. As adoption broadens, the industry will benefit from stronger resilience, reduced operational uncertainty, and more efficient use of resources. AI enabled factories are expected to operate with greater autonomy and maintain higher adaptability in dynamic global markets.
Conclusion
AI has reshaped manufacturing by improving production efficiency, strengthening asset reliability, and enabling higher accuracy in quality assessment. Its role in optimizing supply chains and supporting advanced robotics has created measurable gains in operational performance. The journey toward widespread adoption continues, supported by growing confidence in AI’s ability to deliver stable and long term benefits.
Although challenges remain, the opportunities for innovation and improvement are substantial. Ethical governance, workforce training, and careful planning will guide responsible adoption as the industry evolves. As AI capabilities expand, manufacturers are expected to achieve stronger competitiveness, improved sustainability, and higher overall productivity in the years ahead.
Related Report
Global AI in Manufacturing Market By Component (Software, Hardware, Services), By Technology (Machine Learning, Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Other Technologies), By Application (Process Optimization, Production Planning, Predictive Maintenance, Quality Control and Inspection, Supply Chain Management, Other Applications), By End-Use Industry (Automotive, Food & Beverage , Electronics & Semiconductor, Chemicals, Pharmaceuticals, Metal & Heavy Machinery, Other End-Use Industries), By Region And Key Companies – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends And Forecast 2024-2033


