Table of Contents
- Robotic Parcel Inductor Market Size
- Market Overview
- Key Industry Highlights
- Performance and Efficiency Insights:
- Drivers Impact Analysis
- Risk Impact Analysis
- Restraint Impact Table
- Driver Analysis
- Restraint Analysis
- Opportunity Analysis
- Challenge Analysis
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Investor Type Impact Matrix
- Technology Enablement Analysis
- Key Market Segments
Robotic Parcel Inductor Market Size
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2024) | USD 274.3 Mn |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 1,891.6 Mn |
| CAGR(2025-2034) | 21.3% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historic Period | 2020-2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
Market Overview
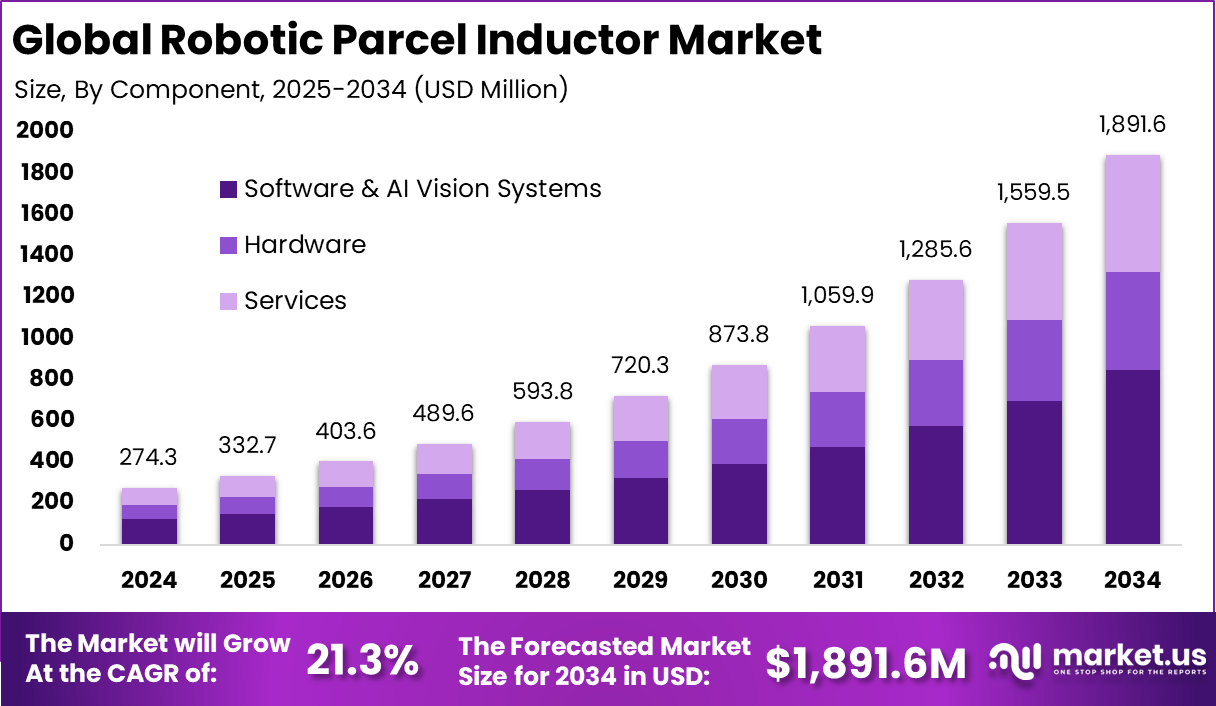
The global Robotic Parcel Inductor market generated USD 274.3 million in 2024 and is expected to grow significantly over the forecast period. Market revenue is projected to rise from USD 332.7 million in 2025 to approximately USD 1,891.6 million by 2034, registering a strong CAGR of 21.3% throughout the forecast span. This growth is driven by the increasing need for automation in logistics and parcel sorting, improving efficiency, reducing labor costs, and enhancing operational scalability.
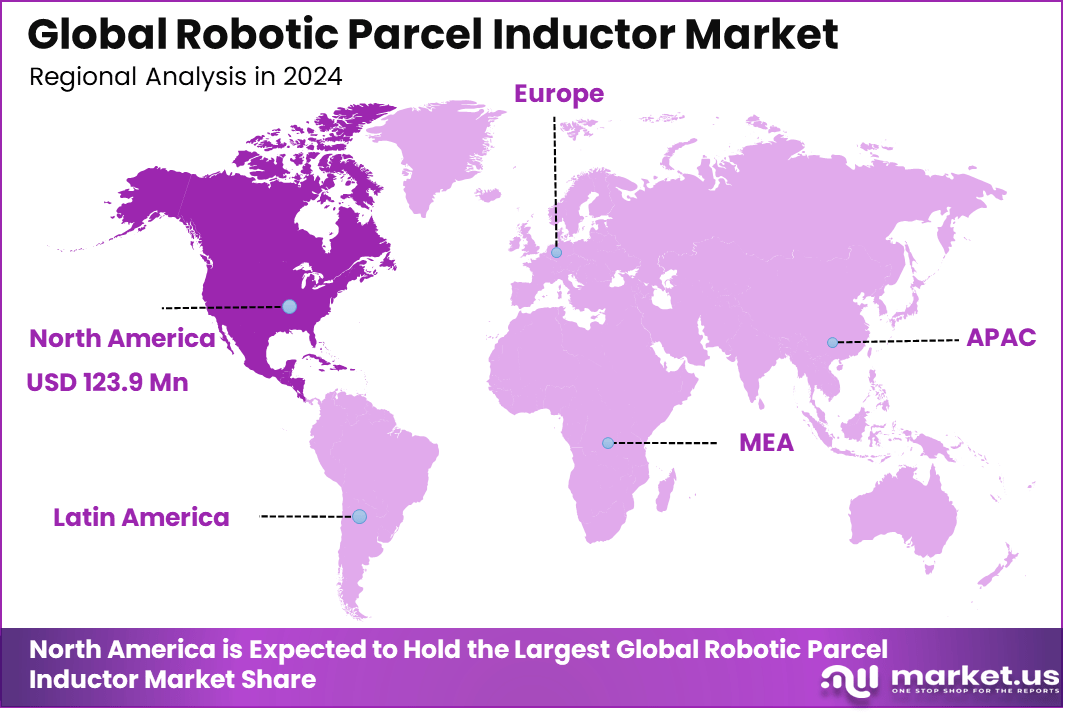
In 2024, North America held a dominant position in the global market, capturing more than 45.2% of total revenue. The region generated around USD 123.9 million, supported by high demand for advanced robotics in logistics and distribution centers. North America’s early adoption of automation technologies and its robust infrastructure for e-commerce fulfillment further strengthened its leadership in the market. As a result, North America continues to lead the growth and development of robotic parcel induction systems.
Key Industry Highlights
- Software and AI vision systems lead the market with a 44.8% share, emphasizing the use of intelligent vision, automation software, and machine learning for precise parcel handling.
- Courier, Express, and Parcel hubs represent 39.6%, driven by the need to manage high parcel volumes and fast sorting requirements in the growing e-commerce sector.
- Logistics and transportation sectors dominate end-use adoption with 54.3%, as operators invest in automation for improved speed, accuracy, and labor efficiency.
- North America holds a 45.2% market share, supported by advanced logistics infrastructure and early adoption of robotic automation.
- The U.S. market reached USD 112.8 million, reflecting strong deployment in major distribution and fulfillment hubs, with a CAGR of 19.47%, driven by rising parcel volumes, labor shortages, and demand for high-throughput automated systems.
Performance and Efficiency Insights:
- Robotic parcel induction systems can handle over 2,500 picks per hour, significantly outperforming manual processes.
- Automation reduces reliance on repetitive manual labor and helps mitigate employee turnover.
- AI-driven vision systems offer over 99% picking accuracy, even with randomly placed or unidentified parcels.
- Systems are capable of identifying and rejecting non-inducible items, ensuring smooth operations.
- Operational picking costs can decrease by 40% to 70% after deploying robotic induction systems.
- E-commerce volume growth is a key demand driver, with projections of 256 billion parcels annually by 2027.
- Mid-size warehouses processing 2 million parcels yearly could save nearly USD 400,000 in labor and error costs.
- Many operators achieve ROI within a year, driven by labor savings and enhanced accuracy.
| Segment Type | Dominant Segment | Segment Share (%) | Segment Value (USD Mn) | Market Influence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| By Component | Hardware | 64.7% | USD 177.6 Mn | Critical |
| By Application | E-commerce & Logistics | 54.8% | USD 150.3 Mn | Critical |
| By End-User | Warehouses and Distribution Centers | 68.2% | USD 186.7 Mn | Critical |
| By Technology | Vision-Based Systems | 48.4% | USD 132.4 Mn | Critical |
| By Deployment Mode | On-premise | 71.6% | USD 196.2 Mn | Critical |
Segment values are calculated from the global market size of USD 274.3 Mn in 2024.
Drivers Impact Analysis
| Driver Category | Key Driver Description | Estimated Impact on CAGR (%) | Geographic Relevance | Impact Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growing e-commerce sector | Increased parcel volumes driving demand for automation | ~7.6% | Global | Short Term |
| Demand for operational efficiency | Reduction of labor costs and faster throughput | ~6.4% | North America, Europe | Short Term |
| Advancements in AI and robotics | Enhanced accuracy and sorting capabilities | ~5.8% | Global | Mid Term |
| Need for faster sorting and delivery | Meeting same-day delivery expectations | ~5.2% | Global | Mid Term |
| Labor shortages in logistics | Automation to counteract workforce challenges | ~4.1% | Global | Long Term |
Risk Impact Analysis
| Risk Category | Risk Description | Estimated Negative Impact on CAGR (%) | Geographic Exposure | Risk Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High initial investment | Significant upfront costs for automation systems | ~5.1% | Emerging Markets | Short to Mid Term |
| Technical challenges | System integration and compatibility with existing infrastructure | ~4.3% | Global | Short to Mid Term |
| Dependence on AI and robotics | Performance limitations under certain conditions | ~3.6% | Global | Mid Term |
| Cybersecurity concerns | Risk of data breaches and system vulnerabilities | ~2.9% | Global | Mid Term |
| Regulatory uncertainties | Inconsistent regulations regarding automation | ~2.4% | Global | Long Term |
Restraint Impact Table
| Restraint Factor | Restraint Description | Impact on Market Expansion (%) | Most Affected Regions | Duration of Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High system setup cost | Expensive hardware and installation | ~6.3% | Emerging Markets | Short to Mid Term |
| Lack of skilled workforce | Need for experts to operate and maintain robots | ~5.4% | Global | Mid Term |
| Integration with legacy systems | Compatibility issues with older sorting systems | ~4.8% | Global | Mid Term |
| Data privacy and security | Concerns over data handling in automated systems | ~3.2% | North America, Europe | Long Term |
| Limited consumer awareness | Slow adoption in non-commercial sectors | ~2.7% | Global | Long Term |
Driver Analysis
The robotic parcel inductor market is being driven by the rapid growth of e‑commerce, rising parcel volumes, and the need for faster, more accurate sorting operations in distribution centres and fulfilment hubs. Traditional manual induction processes create bottlenecks in parcel flow and expose workers to repetitive strain, limiting throughput and increasing error rates.
Robotic parcel inductors automate the transfer of parcels from inbound streams onto conveyor belts or automated sortation systems, reducing cycle times and improving operational consistency. As retailers and logistics providers prioritise speed, reliability, and cost efficiency, investment in intelligent induction systems continues to strengthen.
Restraint Analysis
A significant restraint in the robotic parcel inductor market relates to high implementation costs and system integration complexity. These systems involve sophisticated robotic arms, vision systems, control software, and safety enclosures that represent substantial upfront expenditure, particularly for mid‑sized operators.
Integrating inductors with existing conveyor networks, warehouse control systems, and order management platforms requires careful engineering and testing to ensure seamless coordination. Organisations with constrained capital budgets or legacy infrastructure may delay automation investments due to perceived cost‑benefit uncertainty.
Opportunity Analysis
Emerging opportunities in the robotic parcel inductor market are linked to the expansion of automated fulfilment strategies, scalable robotics fleets, and data‑driven optimisation. As distribution environments become more interconnected through sensors, cloud analytics, and real‑time monitoring, robotic inductors can support adaptive workflows that respond to fluctuating demand, seasonal peaks, and dynamic order profiles.
There is also opportunity for modular, mobile, and collaborative robotics that can be redeployed across induction, pick‑and‑place, and sortation tasks, increasing utilisation and return on investment. Service‑oriented automation offerings such as rental or robot‑as‑a‑service models can attract smaller operators by reducing capital barriers and spreading costs over time.
Challenge Analysis
A central challenge confronting this market involves maintaining high performance and reliability across diverse parcel sizes, weights, and packaging types. Robotic inductors must quickly and accurately identify, grasp, and position irregular items without causing damage, which demands advanced vision systems, adaptive grippers, and real‑time control logic.
False detections, mis‑grips, or collision events can disrupt parcel flow and reduce overall efficiency. Ensuring consistent performance in busy, high‑throughput environments requires rigorous system tuning, quality sensing, and continuous monitoring, which can increase operational complexity.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in the robotic parcel inductor landscape include the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance object recognition, grasp planning, and motion control for varied parcel profiles. Combined AI and vision systems allow robots to classify items, predict optimal pickup points, and adapt grip strategies to minimise errors.
Another trend is the integration of collaborative robots that work safely alongside human operators, supporting mixed workflows where automation handles high‑volume induction and humans focus on exception handling. Software‑defined fleets that allow centralised orchestration and fleet‑wide optimisation are also gaining traction.
Growth Factors
Growth in the robotic parcel inductor market is supported by expanding global parcel volumes, heightened customer expectations for rapid delivery, and rising labour costs in logistics operations. Retailers, third‑party logistics providers, and postal operators are prioritising automation to enhance throughput, accuracy, and worker safety.
Advances in robotics hardware, sensor fidelity, and real‑time control algorithms improve system capability and reliability, reducing barriers to adoption. As fulfilment networks modernise and scale to meet competitive pressures, robotic parcel induction solutions remain central to achieving high‑speed, low‑error sorting and distribution operations.
Investor Type Impact Matrix
| Investor Type | Adoption Level | Contribution to Market Growth (%) | Key Motivation | Investment Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce companies | Very High | ~54.8% | Improving efficiency and throughput | Long-term capital investment |
| Warehousing and logistics firms | High | ~40.2% | Optimizing sorting and reducing operational costs | Strategic adoption of automation |
| Robotics technology companies | Moderate | ~13.7% | Providing hardware and software solutions | R&D focused investments |
| Government and regulatory bodies | Low | ~3.1% | Support automation and infrastructure policies | Policy and regulation shaping |
Technology Enablement Analysis
| Technology Layer | Enablement Role | Impact on Market Growth (%) | Adoption Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial intelligence | AI-driven sorting and decision-making | ~7.8% | Growing |
| Vision-based systems | Real-time tracking and parcel identification | ~6.4% | Mature |
| Machine learning models | Self-optimizing sorting and induction processes | ~5.7% | Growing |
| Robotics hardware | Automated parcel induction mechanisms | ~4.3% | Mature |
| Cloud computing | Data storage and processing for analytics | ~3.9% | Mature |
Key Market Segments
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Application
- E-commerce Fulfillment Centers
- Courier, Express & Parcel (CEP) Hubs
- Postal & Logistics Sorting Centers
- Retail & Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Warehouses
- Others
By End-User Industry
- Logistics & Transportation
- Retail & E-commerce
- Manufacturing
- Others
Top Key Players in the Market
- ABB, Ltd.
- KUKA AG
- FANUC Corporation
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation (Motoman)
- Dematic GmbH
- Honeywell Intelligrated
- Vanderlande
- Beumer Group
- Siemens AG
- Toshiba Infrastructure Systems & Solutions Corporation
- Okura Yusoki Co., Ltd.
- Plus One Robotics, Inc.
- RightPick
- Berlinger & Co. AG
- ULMA Handling Systems
- Others


