Table of Contents
Strategic Green Technology Investment Perspective
The Global AI-Powered Recycling Robot Market represents an attractive sustainable technology investment opportunity, expanding from USD 1.7 billion in 2025 to nearly USD 6.7 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 14.8%. North America’s dominant market position, capturing more than 38.6% share and USD 0.64 billion in revenue, underscores strong regional leadership in environmental automation and long-term value creation for impact-focused investors.
AI-powered recycling robots are automated machines equipped with artificial intelligence systems that can recognise, classify and physically sort waste materials into recyclables and non-recyclables. These robots typically use computer vision, machine learning models and robotic arms to handle waste streams with high precision and speed, improving processes that were traditionally performed by human workers. The integration of deep learning and advanced sensors allows these systems to identify different material types such as plastics, metals, glass and paper within mixed waste, supporting more effective recycling processes.
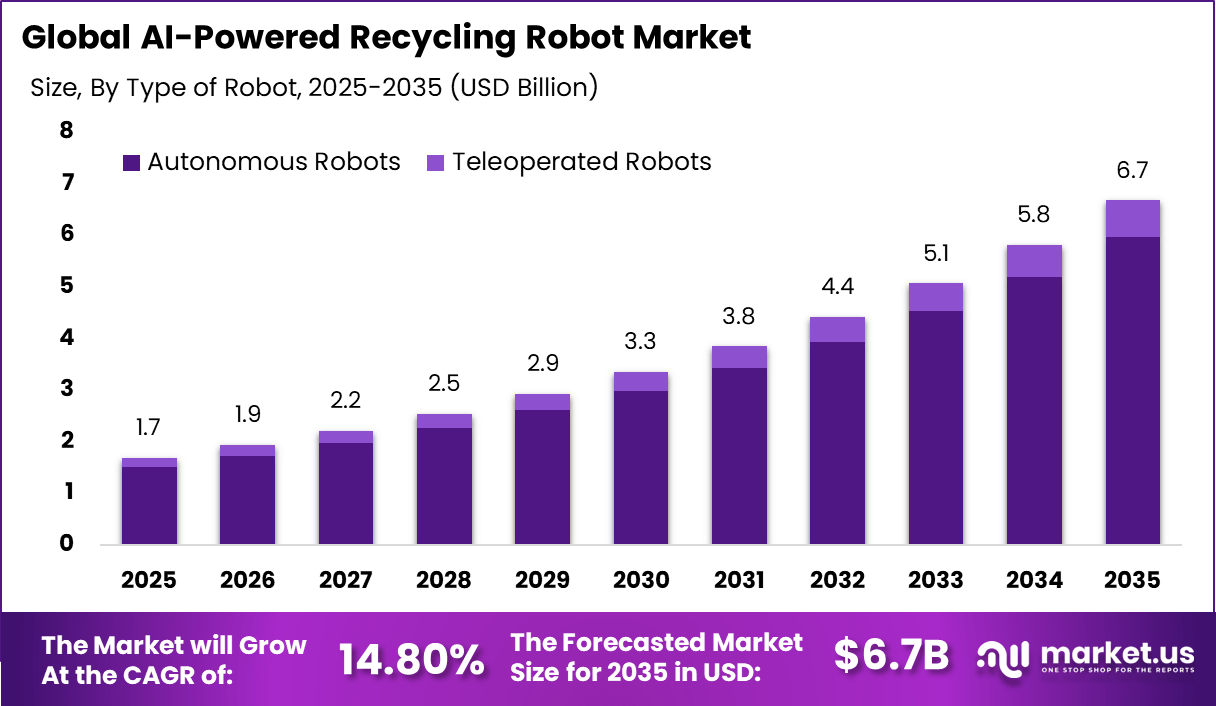
The core operation of an AI-powered recycling robot involves capturing visual and sensor data from waste on conveyor systems, then applying trained algorithms to detect and separate targeted items. This approach reduces reliance on manual sorting, increases throughput, and can handle complex item blends that are difficult to distinguish by humans alone. As recycling facilities face growing volumes of waste and stricter quality requirements for sorted materials, the adoption of these robotic systems addresses operational bottlenecks and enhances overall waste management performance.
A major driving factor for the AI-Powered Recycling Robot market is the rapid increase in municipal solid waste and recyclable materials. Global environmental data indicates that more than 2.2 billion metric tons of waste are generated annually, placing pressure on existing recycling systems. Manual sorting methods are no longer sufficient to manage this scale while maintaining material quality. Intelligent robotic systems help facilities process higher volumes with greater consistency and lower error rates.
Another key driver is the strengthening of environmental regulations and recycling targets across many countries. Governments are setting higher recovery and diversion requirements to reduce landfill use and environmental impact. Compliance with these regulations requires improved sorting accuracy and traceability, which automated systems can deliver more reliably than manual processes. As a result, recycling operators are increasingly adopting AI-based solutions to meet regulatory expectations.
Top Market Takeaways
- By robot type, autonomous robots accounted for 89.3% of the AI powered recycling robot market, as they operate continuously without human input and improve sorting efficiency.
- By application area, municipal waste management held 72.4% share, driven by the need to process large waste volumes generated by cities and landfills.
- By material stream, plastic sorting captured 47.8%, reflecting focus on recovering high value recyclable materials using AI based separation.
- By technology, computer vision led with 60.2%, using cameras and image recognition to identify materials by shape, color, and texture.
- By size of operation, medium scale facilities represented 62.5%, as they balance automation benefits with manageable investment costs.
- By end user, waste management companies accounted for 51.4%, using AI robots to reduce labor dependence and improve recovery rates.
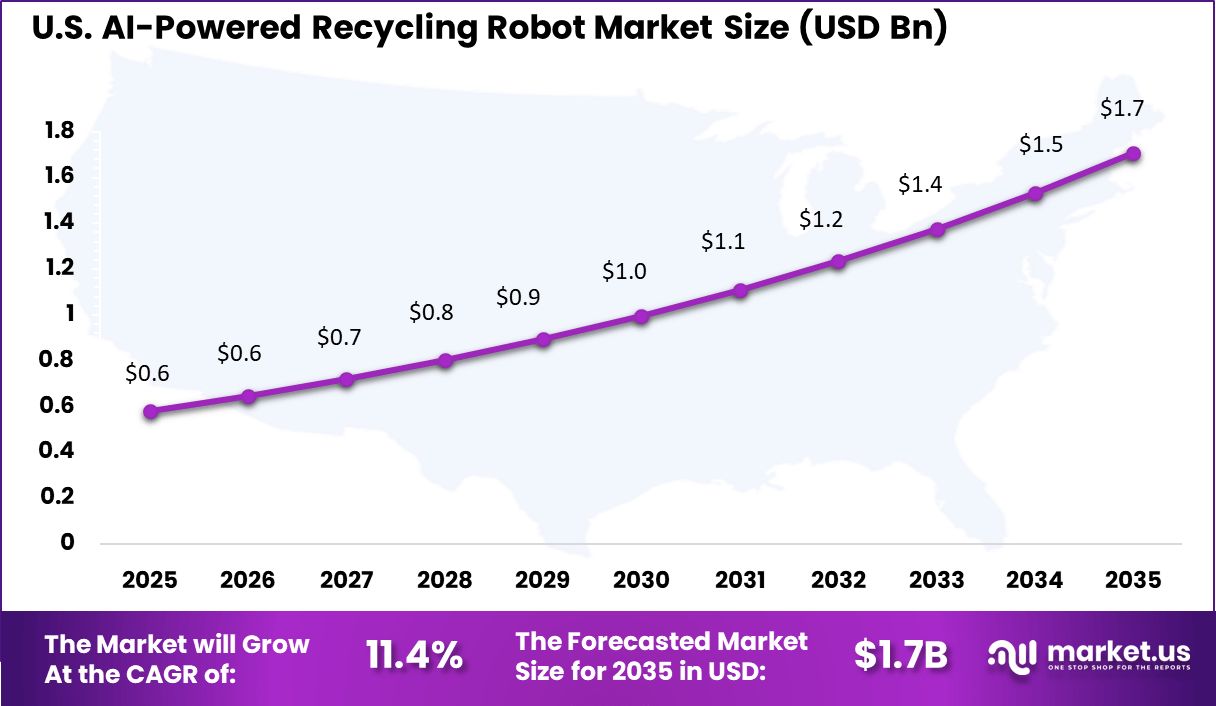
- North America held 38.6% of the global market, with the US valued at USD 0.58 billion in 2025 and growing at an 11.4% CAGR.
Key Insights Summary
Operational Performance
- AI powered robots achieve over 80 picks per minute, compared with 30 to 40 picks per minute by human workers.
- Facilities using AI robotics report around 60% improvement in overall operational efficiency.
- Material identification accuracy reaches 99%, supporting consistent and reliable sorting.
- Bale purity improves by 8% to 12% after AI robot deployment.
- Installing robots at the final sorting stage increases total material recovery by 40% to 70%.
Economic and Labor Impact
- Manual labor costs decline by 59% to 60% after AI robotics integration.
- Robots operate with over 99% uptime, enabling round the clock waste processing.
- Large recovery facilities can generate up to USD 400,000 in additional annual revenue by capturing missed recyclables.
- Worker injuries decrease by around 35%, improving safety in waste processing facilities.
Environmental Impact
- AI driven sorting systems reduce carbon emissions by more than 26,000 tons of CO₂ per year in large scale deployments.
- Contamination in recycled material streams falls by nearly 40%, reducing rejection rates and landfill disposal.
- Expansion of AI infrastructure may increase global e waste by 3% to 12% by 2030, highlighting the importance of sustainable system design.
Segmentation Impact Table
| Segment Type | Dominant Segment | Segment Share (%) | Segment Value (USD Bn) | Market Influence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| By Component | Robotic systems and AI software | 63.4% | USD 1.08 Bn | Critical |
| By Sorting Type | Vision based material sorting | 41.7% | USD 0.71 Bn | Critical |
| By Waste Type | Municipal solid waste | 39.6% | USD 0.67 Bn | Critical |
| By Deployment | Fixed recycling facilities | 58.2% | USD 0.99 Bn | Critical |
| By End User | Waste management companies | 51.4% | USD 0.87 Bn | Critical |
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in the AI-powered recycling robot landscape include the adoption of multimodal sensing that combines hyperspectral imaging, near-infrared spectroscopy, and high-speed cameras to enhance material recognition accuracy. AI models that continuously learn from new waste samples, leveraging deep learning and feedback loops, are improving adaptability to changing waste compositions.
Another trend is the deployment of autonomous mobile robots that navigate recycling facilities and assist with dynamic sorting tasks, reducing dependence on fixed conveyor systems. Integration of robotics with data analytics platforms further enables detailed performance tracking and continuous process improvement.
Growth Factors
Growth in the AI-powered recycling robot market is supported by global policy emphasis on waste reduction, recycling targets, and circular economy initiatives that compel municipalities and private operators to modernise waste processing infrastructure. Increasing urbanisation and rising volumes of municipal and industrial waste are driving demand for automation that can handle high throughput while maintaining sorting precision.
Advances in artificial intelligence, machine vision, and sensor technologies are reducing technical barriers and enabling scalable deployment across varied facility types. Continued investment in robotics and data-driven management systems reinforces the appeal of AI-powered solutions as essential tools for efficient and sustainable recycling operations.
Investment Opportunities
Investment opportunities in the domain of AI-powered recycling robots are expanding as waste management systems modernise. Investors may consider funding technology development that enhances computer vision, sensor integration and adaptive learning models tailored to local waste compositions. Deployment of innovative robotics in facilities can generate competitive advantage for operators who need to meet stringent sustainability benchmarks.
Furthermore, partnerships between municipal authorities and technology providers present potential for scalable implementation projects. Such collaborations can drive infrastructure upgrades that improve recycling system resilience while creating avenues for long-term returns on capital through improved material recovery and reduced disposal costs.
Business Benefits
Business benefits arising from the use of AI-powered recycling robots include significant reductions in operational costs through automation and efficiencies gained in sorting performance. Facilities that adopt these systems can redirect human labour to higher-value tasks, lowering risk exposure while accelerating throughput.
Another benefit is enhanced environmental performance. Robots that achieve higher sorting accuracy contribute to increased recycling rates and reduced landfill reliance, which aligns with sustainability commitments and regulatory compliance objectives. This improvement in environmental outcomes strengthens corporate reputations and appeal to stakeholders prioritising responsible waste management.
Regional Analysis
North America accounted for 38.6% share, supported by growing focus on waste management efficiency and sustainability initiatives across municipalities and industrial facilities. AI powered recycling robots have been adopted to automate material sorting and improve recovery rates in recycling plants.
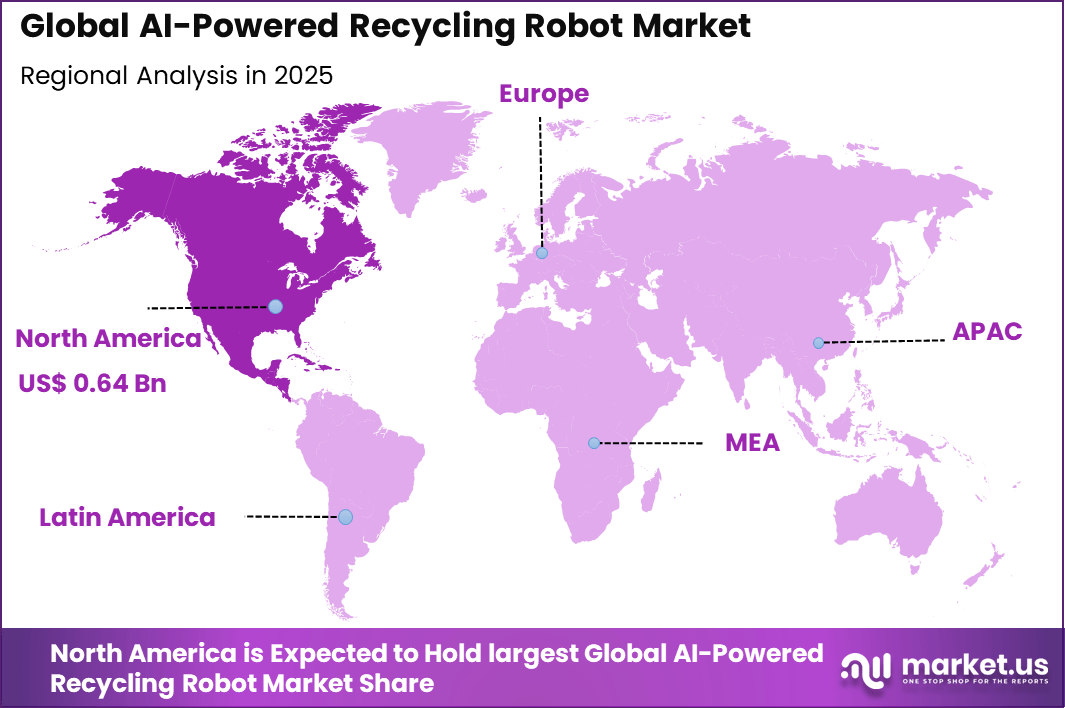
The U.S. market reached USD 0.58 Bn and is projected to grow at an 11.4% CAGR, reflecting steady adoption across municipal recycling centers and private waste management companies.
Key Market Segments
By Type of Robot
- Autonomous Robots
- Teleoperated Robots
By Application Area
- Industrial Waste Management
- Municipal Waste Management
By Material Stream Sorted
- Plastics
- Paper & Cardboard
- Metals
- E-Waste
- Others
By Technology
- Machine Learning Algorithms
- Computer Vision
- Others
By Size of Operation
- Small Scale Operations
- Medium Scale Operations
By End-User
- Recycling Facilities
- Waste Management Companies
- Municipalities
- Others
Top Key Players in the Market
- ZenRobotics
- AMP Robotics
- Sadako Technologies
- Waste Robotics
- Machinex Industries Inc.
- Bulk Handling Systems (BHS)
- Tomra Systems ASA
- General Kinematics Corporation
- Greeen Creative
- Pellenc ST
- Recycling Equipment Inc.
- MSS Inc.
- Optical Sorting Systems (OSS)
- Eagle Vizion
- Others
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2025) | USD 1.7 Bn |
| Forecast Revenue (2035) | USD 1.9 Bn |
| CAGR(2025-2035) | 14.80% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historic Period | 2020-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2035 |


