Table of Contents
Overview
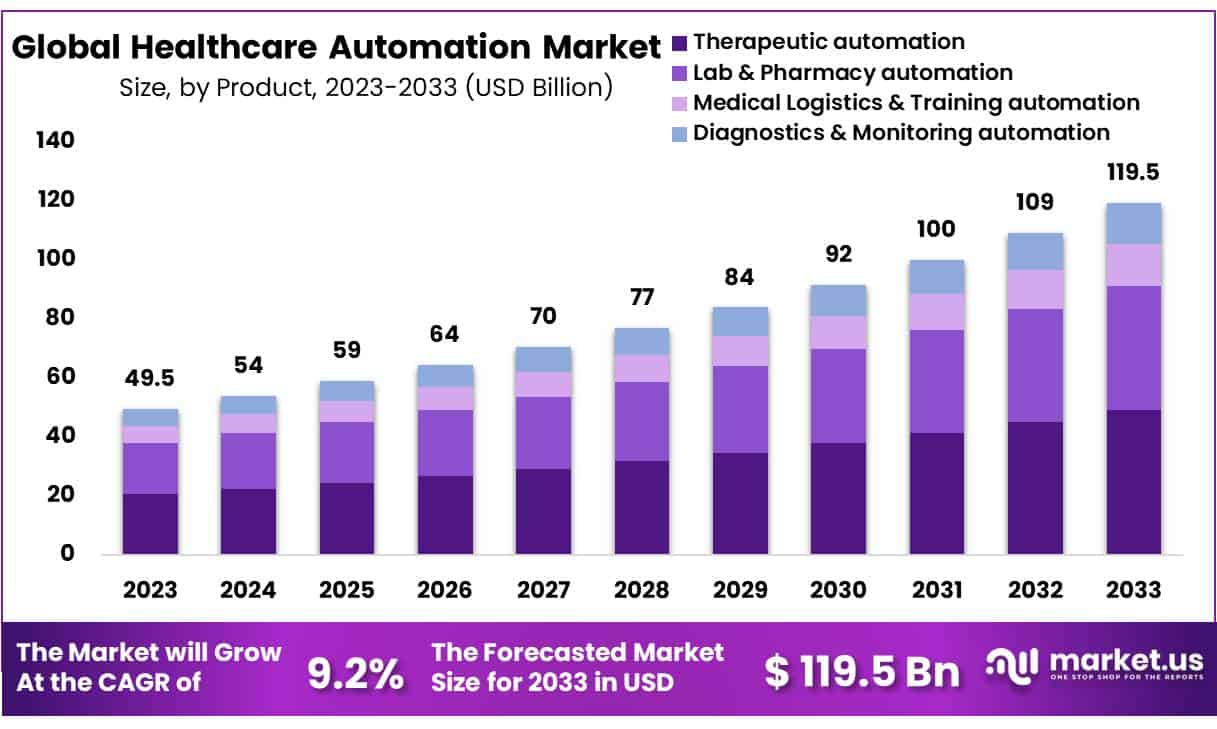
New York, NY – Jan 28, 2026 – The Global Healthcare automation Market size is expected to be worth around USD 119.5 Billion by 2033 from USD 49.5 Billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 9.2% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The adoption of healthcare automation is increasingly being recognized as a foundational step toward improving operational efficiency, clinical accuracy, and patient outcomes across healthcare systems. Healthcare automation refers to the use of digital technologies, software platforms, and intelligent systems to streamline routine, administrative, and clinical processes that were traditionally performed manually.
Automation solutions are being widely implemented in areas such as patient scheduling, electronic health records management, billing and claims processing, diagnostic support, and remote patient monitoring. The integration of automated workflows is enabling healthcare providers to reduce administrative burden, minimize human error, and improve compliance with regulatory standards. As a result, healthcare professionals are able to allocate more time to direct patient care and critical decision-making.
The growth of healthcare automation can be attributed to rising patient volumes, increasing healthcare costs, and the need for data-driven decision-making. In addition, advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing are supporting the development of scalable and secure automation platforms. These technologies are also facilitating real-time data access, predictive analytics, and personalized care delivery.
Overall, healthcare automation is positioned as a strategic enabler for modern healthcare systems. Its continued adoption is expected to support sustainable healthcare delivery models, enhance service quality, and strengthen system resilience in an evolving healthcare environment.
Key Takeaways
- Market Size: The healthcare automation market is projected to reach approximately USD 119.5 billion by 2033, rising from USD 49.5 billion in 2023.
- Market Growth: The market is anticipated to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.2% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
- Product Analysis: The therapeutic automation segment accounted for a significant 56.2% share of the market in 2023, reflecting strong adoption across clinical applications.
- End-Use Analysis: Hospitals and diagnostic centers emerged as the leading end-use segment, capturing 52.4% of the total market share in 2023.
- Regional Analysis: North America dominated the global healthcare automation market, holding a substantial 42.3% share of total revenue in 2023.
- Cost Reduction: Automation contributes to cost efficiency by reducing human error, accelerating operational workflows, and optimizing resource utilization, resulting in measurable cost savings for healthcare providers.
- Technological Innovations: Continuous advancements in robotic systems, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are strengthening automation capabilities in surgery, diagnostics, and patient management, thereby supporting overall market growth.
Regional Analysis
North America dominated the global healthcare automation market, accounting for a substantial 42.3% share of total market revenue in 2023. This strong regional position can be largely attributed to advanced healthcare infrastructure and the widespread integration of information technology across healthcare systems.
The growth of the market in North America is further supported by increasing adoption of automation solutions within the healthcare sector, along with sustained investments in research and development activities. Continuous technological innovation and favorable funding initiatives are accelerating the deployment of automated systems across hospitals, laboratories, and diagnostic centers.
Moreover, rapid improvements in healthcare infrastructure, combined with growing patient awareness of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer, are driving the demand for efficient and accurate healthcare solutions. As a result, healthcare providers across the region are increasingly implementing automation technologies to enhance operational efficiency, improve clinical outcomes, and support large-scale patient management.
What role does automation play in enabling personalized and value-based care models?
Automation plays a critical role in enabling personalized and value-based care models by supporting data-driven decision-making and efficient care coordination. The integration of automated systems allows large volumes of clinical, operational, and patient-generated data to be collected, analyzed, and applied in real time. This enables care pathways to be tailored based on individual patient profiles, medical histories, and risk factors.
Automation also supports predictive analytics and population health management, helping providers identify high-risk patients and intervene earlier. In value-based care models, automated workflows improve care quality while controlling costs by reducing manual errors, minimizing administrative burden, and improving outcome tracking. As a result, healthcare providers are better positioned to deliver measurable, patient-centric outcomes aligned with reimbursement performance metrics.
Use Cases
Revenue cycle automation (claims, denials, payment posting)
- Routine billing steps (claim creation, eligibility checks, denial sorting, status follow-ups) can be automated using RPA and AI so that fewer claims need manual review.
- Reported results include first-pass acceptance above 95%, up to 50% faster payment turnaround, and ~80% reduction in manual review time in an RPA-driven workflow.
- In a revenue-cycle AI program at scale, documentation time fell by ~40%, turnaround time fell by ~50%, and accuracy reached ~99.5% (measured on automated document processing).
- HFMA-linked evidence also points to 1,500–3,000 staff hours saved per year for hospitals using RPA for repetitive revenue-cycle tasks, and ~40% lower average claim processing time using machine learning in claims workflows.
Prior authorization automation (faster approvals, fewer delays)
- Prior authorization is paperwork-heavy, so automation is used to collect documents, validate policy rules, submit requests, and track payer responses.
- One large insurer announced it will remove about one-third of prior authorization requirements for outpatient services by January 1, 2026, and committed to deciding within one business day for at least 95% of complete electronic prior authorization requests by 2026.
- AI support for prior authorization has been reported to deliver around a 30% reduction in processing time and 35% reduction in appeals/reconsiderations in described implementations.
AI patient triage and digital front desk (access, appointment routing, call reduction)
- Automation can collect symptoms, route patients to the right care level, and reduce the “phone rush” at clinics.
- An NHS-backed evaluation of an AI triage system reported 73% reduction in GP waiting times.
- Additional reporting on the same type of trial noted 47% reduction in calls at peak hours, supporting measurable admin workload reduction.
Medication dispensing automation in hospitals (lower errors, faster turnaround)
- Automated dispensing cabinets (ADCs) reduce manual dispensing steps and add control checks, which helps reduce medication errors and delays.
- A peer-reviewed study reported prescription/dispensing error reductions (example: 3.03 → 1.75 per 100,000 prescriptions, and 3.87 → 0 per 100,000 dispensations in the reported setting), plus large reductions in certain error categories (75% in some types).
- Another hospital-focused study reported 83% reduction in turnaround time from order to administration, productivity increases >40% (majority of nurses/pharmacists), and an estimated US$4.1 million annual saving in that implementation.
Automated clinical documentation and document understanding (coding support, faster processing, higher accuracy)
- AI can read and structure unstructured documents (denial letters, medical records, lab notes) to speed coding, audits, and back-office decisions.
- In a large operational deployment, automation processed 100+ million transactions since 2020, saving 15,000+ employee hours per month, with ~99.5% accuracy reported for document processing, and ~30% ROI stated for clients.
Conclusion
Healthcare automation has emerged as a critical enabler of efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability across modern healthcare systems. By streamlining administrative, clinical, and operational workflows, automation reduces manual errors, accelerates decision-making, and allows healthcare professionals to focus on direct patient care.
Strong market growth reflects rising patient volumes, cost pressures, and the demand for data-driven and value-based care models. Advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic systems continue to strengthen automation capabilities across revenue cycle management, diagnostics, medication management, and patient engagement. Overall, healthcare automation is positioned as a long-term strategic investment supporting improved outcomes, cost control, and system resilience.


