Table of Contents
Overview
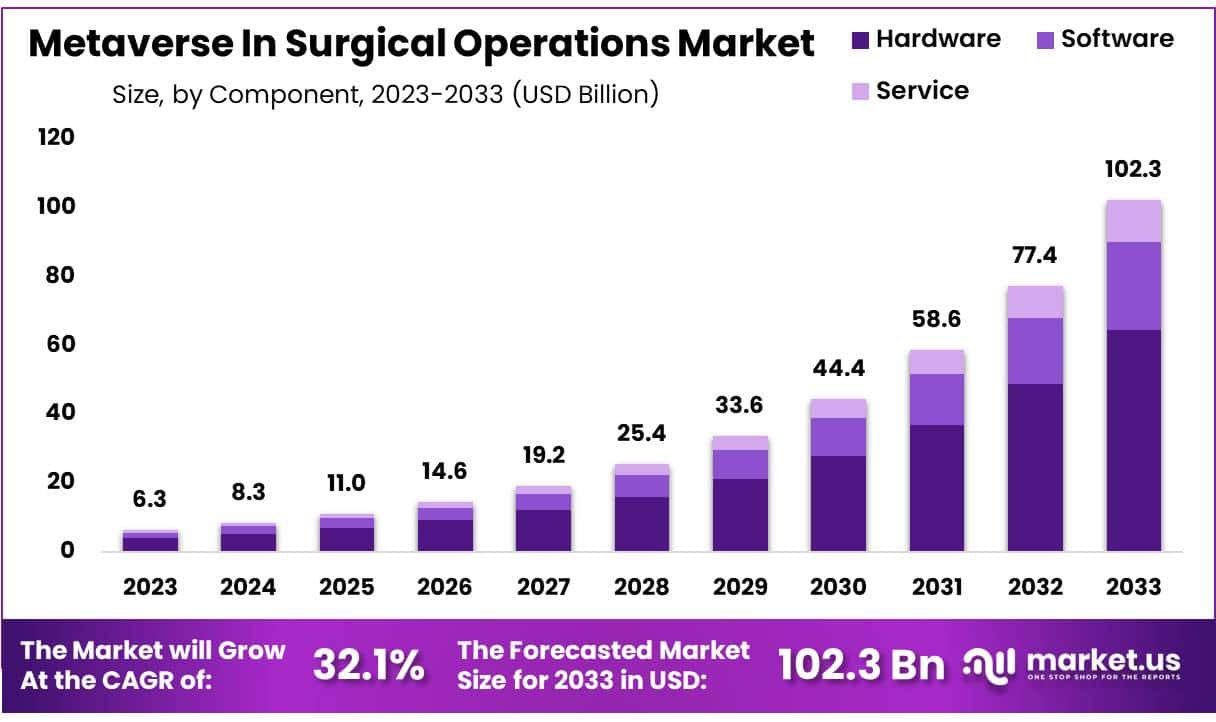
New York, NY – Feb 02, 2026 – The Global Metaverse In Surgical Operations Market size is expected to be worth around USD 102.3 Billion by 2033 from USD 6.3 Billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 32.1% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The integration of the metaverse into surgical operations is emerging as a significant advancement in modern healthcare delivery. By combining immersive technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), artificial intelligence (AI), and digital twins, the metaverse is enabling a new standard of precision, collaboration, and efficiency in surgical care.
Through metaverse-based platforms, surgeons can perform advanced pre-operative planning using three-dimensional, patient-specific anatomical models. This approach allows complex procedures to be simulated in a virtual environment before entering the operating room, reducing surgical risks and improving clinical outcomes. During live procedures, AR-enabled overlays can support real-time visualization of critical structures, enhancing accuracy and decision-making.
The metaverse is also transforming surgical training and education. Medical professionals can participate in realistic, risk-free simulations, enabling consistent skill development across geographic boundaries. Additionally, remote collaboration within virtual operating environments allows expert surgeons to provide guidance in real time, supporting hospitals with limited access to specialized expertise.
The adoption of metaverse technologies in surgical operations is being driven by the growing demand for minimally invasive procedures, improved patient safety, and data-driven healthcare solutions. As digital health infrastructure continues to mature, the metaverse is expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of surgery, supporting better outcomes, operational efficiency, and global accessibility to high-quality surgical care.
Key Takeaways
- Market Size: The Metaverse in Surgical Operations Market is projected to reach approximately USD 102.3 billion by 2033, expanding from USD 6.3 billion in 2023.
- Market Growth: The market is anticipated to register a strong compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.1% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
- Component Analysis: Hardware components dominate the market landscape, contributing nearly 63% of the total market share.
- Application Analysis: Surgical training represents the leading application segment, accounting for about 42% of the market share.
- Technology Analysis: Virtual Reality (VR) remains the most widely adopted technology, securing 46% of the overall market share.
- End-User Analysis: Hospitals and surgical centers constitute the largest end-user segment, collectively holding 48% of the market share.
- Regional Analysis: North America leads the global market, capturing approximately 43% of total revenue share.
Segmentation Analysis
- Component Analysis: Hardware dominates the Metaverse in Surgical Operations Market with a 63% share, reflecting strong dependence on VR headsets, AR devices, and haptic systems. These tools deliver realistic visuals and tactile feedback essential for accurate surgical simulation and procedural training.
- Application Analysis: In 2023, surgical training led applications with a 42% share, driven by demand for safe, immersive practice environments. The metaverse enables realistic procedure simulations, skill refinement, and error reduction without patient risk, strengthening surgeon preparedness and clinical confidence.
- Technology Analysis: Virtual Reality accounted for 46% of the market in 2023, supported by its ability to deliver fully immersive surgical environments. VR enables repeated practice of complex procedures, while AR and MR enhance real-time guidance and preoperative visualization accuracy.
- End User Analysis: Hospitals and surgical centers held a 48% market share in 2023, reflecting strong adoption of metaverse technologies for training and planning. Medical institutes and telemedicine providers also benefit by enabling risk-free education and remote surgical collaboration across regions.
Regional Analysis
In 2023, North America accounted for the largest revenue share, representing 43% of the Metaverse in Surgical Operations Market. This strong market position was supported by the convergence of multiple growth drivers. The region benefits from a highly developed healthcare infrastructure and strong technological capabilities, which collectively facilitate the rapid adoption of metaverse-based solutions in surgical environments.
Furthermore, the concentration of prominent technology firms and advanced medical institutions across North America continues to stimulate innovation and promote collaborative development. These factors are accelerating the integration of immersive technologies into surgical workflows, reinforcing the region’s leadership in the global market.
Emerging trends
VR-based surgical skill training is being validated with hard performance gains
- In a randomized, blinded study on laparoscopic cholecystectomy training, operating performance was 29% faster after VR training, and errors were 1.19 vs 7.38 per case (about 6× fewer).
- This is pushing hospitals toward “always-on” simulation labs where rare events and difficult steps can be repeated safely.
AR guidance in the operating room is moving from demos to measurable accuracy
- In spinal deformity surgery using AR navigation, 257 screws were placed with 98% overall accuracy; first-attempt accuracy was 97.4% (thoracic) and 100% (lumbar).
- This supports a trend where surgeons see critical alignment lines and planned paths directly in their field of view, instead of looking away at separate monitors.
Mixed reality is being tested for workflow impact, not only “cool visuals”
- In total hip arthroplasty, a comparative study (n=411) reported mean operative time of 89.2 minutes with MR vs 89.6 minutes without MR (no significant increase).
- The direction is clear: MR tools are expected to deliver guidance without slowing the OR, because time is a primary cost driver in surgery.
Patient-specific “digital twins” are being positioned as the next layer above imaging
- “Digital Twin–Assisted Surgery” is being described as a way to create a virtual copy of the patient that can be updated with data and used for planning, guidance, and decisions across the perioperative pathway.
- Early clinical-style implementations already use patient-specific 3D/360° models for planning and intraoperative overlays (example: 49 cases reported in a neurosurgery case series).
Remote surgical support is shifting from simple video calls to AR-enabled mentoring and low-latency networks
- A 2025 scoping review found 21 studies on telementoring using dynamic AR cues (such as gestures, tools, and pointers overlaid on the surgeon’s view).
- For remote robotic surgery feasibility, reported network latency values include ~140 ms in a 5G-enabled setup referenced in a clinical feasibility paper.
- This supports a “metaverse OR” model where expertise can be delivered remotely with shared 3D context, not only voice/video.
Use Cases
Pre-operative rehearsal on a “virtual patient”
- Imaging can be converted into interactive 3D models so the procedure can be rehearsed before incision. A case series described VR planning using custom models across 49 patients.
- Operational value is created through fewer surprises and clearer step planning for complex anatomy.
Intra-operative navigation overlays for precision steps
- AR navigation can be used for tasks where millimeters matter (for example, pedicle screw trajectories). Reported first-attempt accuracy reached 97.4%–100% in one spinal deformity surgery study.
- Clinical value is typically positioned around fewer misplacements and fewer revisions.
Remote proctoring and real-time expert mentoring
- Dynamic AR cues (hand gestures, pointers, tool overlays) allow a remote mentor to guide a surgeon in real time; evidence across 21 studies was summarized in a 2025 review.
- This supports faster upskilling, especially when new devices or techniques are introduced.
Skills onboarding and credentialing for minimally invasive surgery
- VR simulation can be used to standardize training and confirm readiness using objective metrics. In the randomized trial, VR-trained residents were 29% faster and had ~6× fewer errors during real OR performance.
- Operational value is created through reduced learning risk on patients and more consistent performance across trainees.
Procedure planning + team alignment in a shared 3D workspace
- A “metaverse-style” room can be used to bring surgeons, radiology, anesthesia, and nursing into a shared 3D view of anatomy and the planned steps, improving the team’s shared understanding. Evidence supporting improved 3D understanding and safe intraoperative overlay use was reported in the neurosurgery case series (for example, gross total resection achieved in 34/40 surgeries in that report).
- This use case is most relevant in tumor resections, vascular cases, and complex revisions where planning quality strongly affects outcomes.
Conclusion
The Metaverse in Surgical Operations Market is positioned as a transformative force in modern healthcare, driven by measurable clinical performance gains, strong adoption across hospitals, and rapid advances in immersive technologies. Evidence from VR training, AR-guided surgery, mixed reality workflows, and digital twin applications demonstrates clear improvements in accuracy, efficiency, and surgical preparedness without disrupting operating room productivity.
As demand rises for minimally invasive procedures, remote expertise, and data-driven decision-making, metaverse-enabled surgical platforms are expected to move from pilot programs to standard clinical infrastructure. Over the next decade, these technologies are likely to redefine surgical planning, training, collaboration, and patient outcomes on a global scale.


