Table of Contents
Overview
New York, NY – Feb 10, 2026 – Global 3D Printed Brain Model Market was valued at USD 42.8 million in 2024 and is anticipated to register substantial growth of USD 227.8 million by 2034, with 18.2% CAGR. In 2023, North America led the market, achieving over 34% share with a revenue of US$ 14.5 Million.
A basic 3D printed brain model has been developed to demonstrate the fundamental anatomical structure of the human brain using advanced additive manufacturing techniques. The model has been designed to represent key regions of the brain with accurate proportions, focusing on overall morphology rather than microscopic detail.
The formation process begins with a standardized digital brain template created using medical imaging references and anatomical datasets. This digital file is optimized for 3D printing to ensure structural stability and dimensional accuracy. Once finalized, the model is produced layer by layer using high-resolution 3D printing technology, allowing precise replication of major brain components such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
The use of 3D printing enables consistent quality, repeatability, and cost-effective production compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Materials selected for the basic model are lightweight, durable, and suitable for handling in educational and demonstration environments. The surface finish is intentionally simplified to highlight primary brain regions, making the model easy to understand for a broad audience.
This 3D printed brain model is intended for use in educational institutions, research demonstrations, and medical training environments. The development reflects the growing adoption of 3D printing in healthcare and life sciences, where rapid prototyping and anatomical visualization are increasingly supporting learning, communication, and innovation.
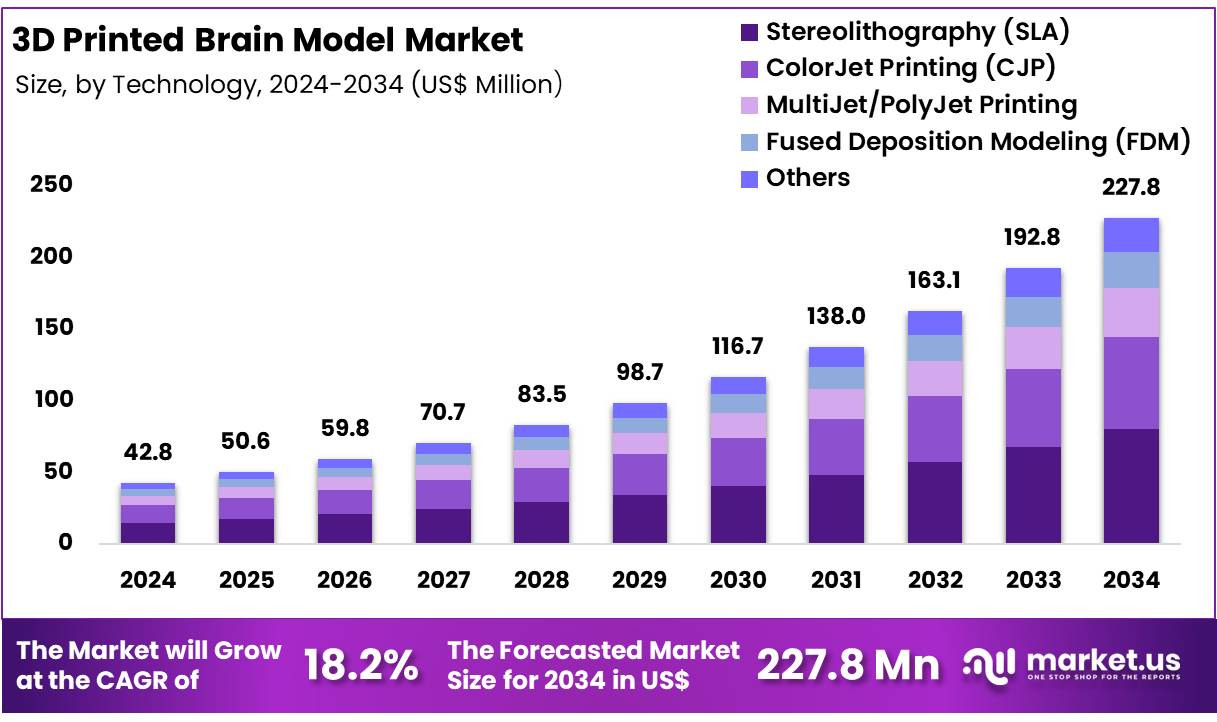
Key Takeaways
- The global 3D printed brain model market was valued at USD 42.8 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 227.8 million by 2034, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.2%.
- In 2024, the plastic segment dominated the global market, accounting for approximately 42% of total revenue.
- The fused deposition modeling (FDM) segment emerged as the leading technology, capturing around 26% of the global revenue share.
- North America retained its dominant position in the global market, contributing more than 34% of total revenue.
Regional Analysis
North America accounted for approximately 34% of the global 3D printed brain model market, supported by a combination of advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong investment in medical technologies, and increasing demand for personalized healthcare solutions. The region benefits from early adoption of innovative technologies and a well-developed ecosystem for medical research and education.
The United States and Canada, supported by mature healthcare systems, have witnessed widespread integration of 3D printing across medical applications, including brain models for research, academic training, and surgical planning.
A strong emphasis on innovation, along with substantial funding from both public institutions and private organizations, has accelerated the development and commercialization of advanced 3D printing solutions in the healthcare sector.
In February 2024, researchers at the University of Wisconsin successfully developed functional 3D printed brain tissue, representing a major step forward in the study of brain functionality and neurological disorders. This advancement enables more precise disease modeling for conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, enhancing research accuracy and clinical insights.
With the rising incidence of neurological disorders, North America’s continued leadership in healthcare technology and scientific research is expected to sustain strong demand for 3D printed brain models over the forecast period.
Emerging trends for 3D Printed Brain Models
Faster “scan-to-model” cycles are being operationalised in hospitals
- End-to-end workflows are being shortened using automated segmentation + cloud review + standardised printing steps.
- In one clinical platform for patient-specific 3D-printed brain tumour models, production and delivery were completed within 4 days.
Models are increasingly used to changesurgical plans (not only to “visualise” anatomy)
- In a validation with neurosurgeon reviews of 10 brain tumour cases, surgical decisions changed after inspecting the 3D model:
- Surgical posture changed in 15.6% of evaluations (10/64).
- Head rotation degree changed in 39.1% (25/64).
- Resection goal (extent) was modified in 18.8% (12/64).
Multi-material and “see-through” prints are being adopted for complex brain anatomy
- Brain tumour models are being produced with transparent materials and soft/realistic handling to better show gyri/sulci and deep structures, which supports planning and simulation.
Hybrid training ecosystems are forming (3D print + VR), with measurable learning gains
- In a skull-base training course, trainee self-ratings improved from 3.40 ± 0.70 to 4.50 ± 0.53 (5-point scale) for spatial relationships and surgical steps; usability was rated 4.70 ± 0.48.
Quality control and accuracy metrics are becoming more formal
- In an accuracy study of 35 patient-specific vascular models, mean surface deviation was about +120 μm, and both major print methods met commonly used clinical accuracy expectations of < 1 mm. This kind of measurable QC approach is being treated as a requirement before clinical use.
High-value healthcare use cases for 3D Printed Brain Models
Pre-operative planning for brain tumours (approach, craniotomy design, resection goals)
- Brain tumour models influenced key planning choices: changes were observed in posture (15.6%), head rotation (39.1%), and resection goals (18.8%) after reviewing the printed model.
Patient education and informed consent (higher understanding and satisfaction)
- In aneurysm consent support, patient understanding (5-point scale) averaged 4.7 (3.0–5.0) with a 3D printed model versus 2.5 (2.0–3.0) without it; satisfaction was 4.4 ± 0.70 vs 2.9 ± 0.57.
- In another aneurysm study, disease understanding scored 4.85 ± 0.36 vs 3.95 ± 0.99, and consultation satisfaction was 5.0 vs 4.60 ± 0.82 with vs without a 3D model.
Resident and surgeon training for complex neurovascular procedures
- Neurosurgical residents rated printed aneurysm models highly for understanding direction (4.43/5) and doctor–patient communication (4.57/5).
- A neurosurgical disease-model review notes roughly ~150 papers on neurosurgical 3D-printed disease models for planning/simulation/training, showing broad academic and clinical adoption.
Hands-on simulation for endoscopic brain procedures (ETV and related tasks)
- In a 3D printed brain + vasculature simulator study, 53% agreed and 47% strongly agreed it could help develop skills; reported production cost was ~USD 303 per simulator.
Procedure rehearsal and device technique practice for aneurysm clipping/coiling
- Printed aneurysm models supported both clipping and coiling rehearsal; patient groups and operators reported high perceived value (for example, operators often rated applicability around ~4+ / 5 in reported questionnaires).
Conclusion
The development of 3D printed brain models represents a significant advancement in medical education, research, and clinical practice. The market demonstrates strong growth potential, driven by rising neurological disease burden, rapid adoption of additive manufacturing, and increasing demand for patient-specific solutions.
Technological improvements such as faster scan-to-model workflows, multi-material printing, and integration with virtual reality are enhancing accuracy, usability, and clinical impact. Evidence indicates measurable benefits in surgical planning, training outcomes, and patient understanding.
As quality standards become more formalized and costs continue to decline, 3D printed brain models are expected to become an integral tool across healthcare and life science applications.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



