Table of Contents
- Strategic Investment Perspective
- Key Takeaways
- Top Driving Factors
- Demand Analysis
- Increasing Adoption Technologies
- Investment Opportunities
- Business Benefits
- Regional Analysis
- Use Case Analysis
- Industry Specific Adoption Insights
- Regulatory Environment Overview
- Technology Evolution Outlook
- Buyer Decision Criteria
- Key Market Segments
- Report Scope
Strategic Investment Perspective
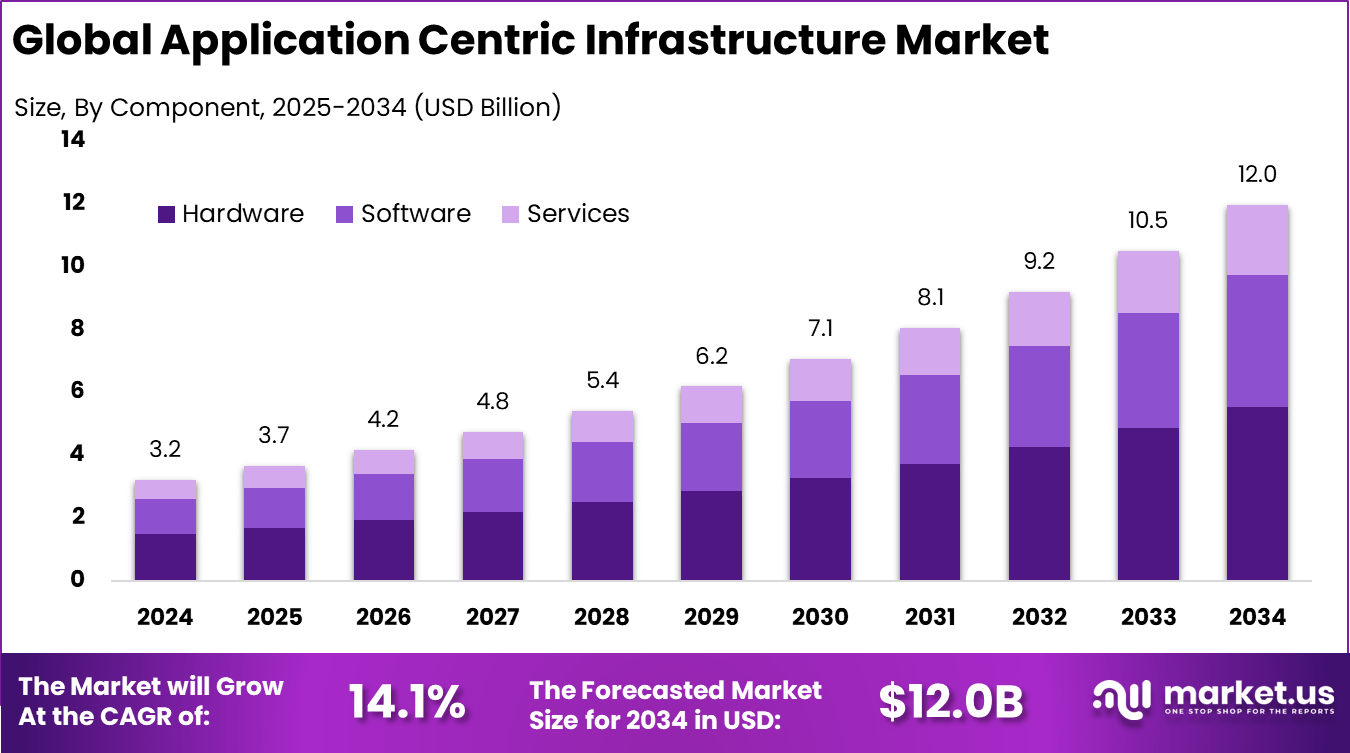
The Global Application Centric Infrastructure Market presents a compelling investment opportunity, growing from USD 3.2 billion in 2024 to nearly USD 12.0 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 14.1%. North America’s dominant position, capturing more than 42.3% share and USD 1.35 billion in revenue, underscores the region’s leadership in enterprise IT transformation and long-term growth potential for investors.
The Application Centric Infrastructure market focuses on networking architectures that are designed around application needs rather than individual network devices. This approach allows infrastructure to automatically adapt based on how applications behave, communicate, and scale across data centers and cloud environments. Policies related to security, performance, and connectivity are defined once and consistently applied across the entire network fabric. This model reduces operational complexity and aligns IT infrastructure more closely with business applications.
In modern enterprise environments, application workloads are no longer static and often span multiple locations and platforms. Application Centric Infrastructure enables centralized control while supporting distributed workloads such as virtual machines, containers, and hybrid cloud deployments. By shifting the focus from hardware configuration to application intent, organizations gain better visibility and control over how applications interact within the network. This change has made application aware infrastructure an important foundation for digital operations.
Key Takeaways
- The hardware segment led the market with 46.3% share, supported by higher demand for programmable network switches and routers used in modern application focused networks.
- Large enterprises accounted for 87.9% of adoption, as these organizations are better equipped to deploy ACI frameworks across complex data center environments.
- The IT and telecom sector represented 32.1% share, driven by wider use of cloud based and virtualized network infrastructure.
- The US market reached USD 1.21 billion in 2024 and is growing at a 12.4% CAGR, supported by ongoing digital transformation and increased use of software defined networking.
- North America held a leading 42.3% share of the global market, reflecting early technology adoption, strong enterprise IT investment, and broad use of automated infrastructure solutions.
Top Driving Factors
One of the main driving factors for the Application Centric Infrastructure market is the widespread adoption of cloud computing and virtualization. Enterprises are running a growing number of applications across private and public cloud environments, creating complexity in traditional network management. Infrastructure that can automatically respond to application requirements is increasingly preferred as it reduces manual configuration and improves consistency. This shift is supporting broader acceptance of application centric networking models.
Another important driver is the rising focus on network security and regulatory compliance. Organizations face increasing pressure to protect sensitive data and control traffic movement within complex IT environments. Application centric models allow security policies to be embedded directly into application workflows, rather than applied manually at the device level. This approach reduces configuration errors and strengthens overall security governance.
Demand Analysis
Demand for Application Centric Infrastructure is closely linked to enterprise digital transformation initiatives. Businesses modernizing their data centers require infrastructure that can support rapid application deployment and frequent changes. Traditional networks struggle to keep pace with these demands, leading organizations to seek automated and policy driven alternatives. As a result, application centric solutions are increasingly viewed as a practical requirement rather than an optional upgrade.
The demand is also influenced by the growing use of hybrid IT environments. Many enterprises operate across on premises systems and cloud platforms simultaneously, creating challenges in maintaining consistent network policies. Application Centric Infrastructure helps unify these environments through centralized control and automation. This capability is driving demand among organizations seeking operational stability across diverse application landscapes.
Increasing Adoption Technologies
Software defined networking plays a central role in the increasing adoption of Application Centric Infrastructure. By separating network control from physical hardware, software driven architectures allow policies to be managed centrally and applied dynamically. This makes it easier to adjust network behavior as application requirements change. The result is faster response times and improved alignment between infrastructure and business needs.
Automation and orchestration technologies are also supporting wider adoption. These tools enable infrastructure to respond automatically to workload changes without manual intervention. When combined with application level policies, automation improves consistency and reduces downtime. This technology combination is particularly valuable in environments where applications scale frequently or operate across multiple locations.
A key reason organizations adopt Application Centric Infrastructure is the ability to simplify network operations. Manual network configuration becomes increasingly difficult as application environments grow more complex. Application centric models reduce this burden by translating business requirements into automated network actions. This leads to faster deployments and fewer operational disruptions.
Another strong reason for adoption is improved application performance and reliability. Infrastructure decisions are based on application behavior rather than static network rules. This ensures that critical workloads receive appropriate priority and resources. As a result, organizations experience more predictable performance and improved service availability.
Investment Opportunities
Investment opportunities within the Application Centric Infrastructure market are emerging from continued enterprise infrastructure modernization. Organizations are allocating resources toward platforms that support automation, centralized management, and hybrid deployment models. These investments aim to improve operational efficiency and reduce long term infrastructure management costs. Demand for skilled integration and deployment services also creates additional opportunity areas.
Further opportunities are developing in environments that require low latency and high reliability. Industries adopting edge computing and distributed applications need infrastructure that can apply application policies closer to the data source. Application centric models support this need by extending policy control beyond traditional data centers. This creates room for investment in supporting platforms and specialized deployment solutions.
Business Benefits
One of the primary business benefits of Application Centric Infrastructure is improved operational efficiency. Automated policy enforcement reduces the time and effort required to manage network changes. IT teams can focus on higher value tasks instead of routine configuration work. This efficiency supports faster response to business requirements.
Another important benefit is enhanced visibility and control across the application environment. Centralized policy management allows organizations to monitor traffic patterns and application interactions more effectively. This visibility supports quicker issue resolution and better planning. Over time, these advantages contribute to improved service quality and stronger alignment between IT infrastructure and business goals.
Regional Analysis
North America represents a mature adoption landscape for Application Centric Infrastructure due to early cloud migration and advanced data center practices. Enterprises in this region have complex application environments that span private infrastructure and multiple cloud platforms. The focus is strongly placed on automation, security control, and application performance consistency. These factors have supported steady demand for application aware networking frameworks across large enterprises.
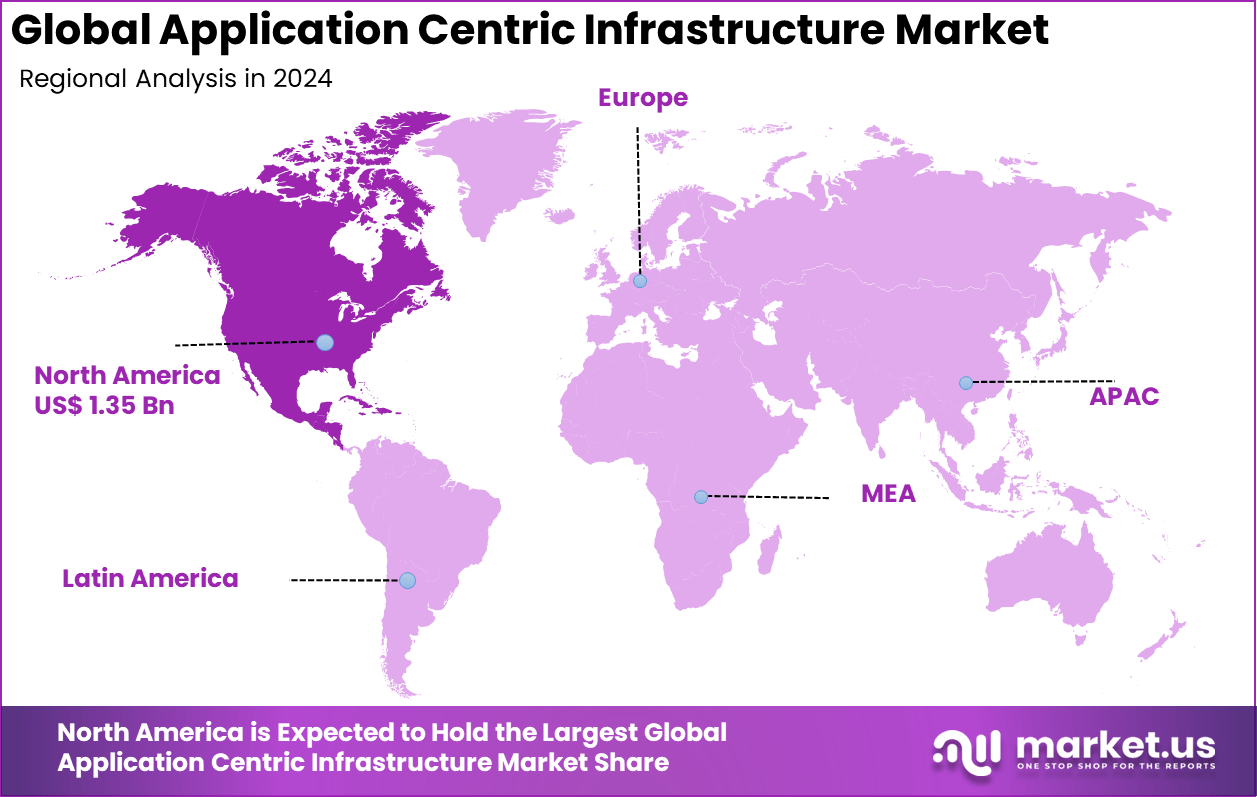
In Europe, adoption is influenced by regulatory compliance and data protection requirements. Organizations place strong emphasis on controlling data flows and enforcing application level policies across distributed environments. Application Centric Infrastructure supports this need by enabling centralized visibility and consistent rule enforcement. This has made the model attractive for enterprises operating across multiple jurisdictions and data locations.
Asia Pacific is experiencing faster adoption as enterprises modernize legacy infrastructure and expand digital services. Rapid growth in cloud usage and application driven business models is increasing the need for scalable and automated networking. Many organizations in this region are transitioning from hardware focused networking to software driven architectures. This shift is supporting broader acceptance of application centric approaches.
Use Case Analysis
One major use case for Application Centric Infrastructure is data center modernization. Organizations upgrading legacy data centers require infrastructure that can support virtualized workloads and dynamic application traffic. Application centric models allow policies to be applied consistently as workloads move or scale. This improves reliability and reduces configuration complexity.
Another important use case is hybrid cloud management. Enterprises operating across on premises systems and cloud platforms need unified network control. Application Centric Infrastructure enables centralized policy definition while supporting distributed execution. This use case helps organizations maintain performance and security consistency across multiple environments.
Application performance optimization is also a key use case. Infrastructure decisions are based on application behavior rather than static network rules. This ensures that business critical applications receive appropriate priority and resources. As a result, service quality improves and performance issues are resolved more quickly.
Industry Specific Adoption Insights
In the banking and financial services sector, Application Centric Infrastructure is adopted to support secure and compliant application environments. Financial institutions operate high volumes of sensitive transactions across complex networks. Application level policy control helps reduce risk and improve visibility. This supports stronger governance and operational stability.
The healthcare sector is also adopting application centric networking to manage diverse digital systems. Clinical applications, patient data platforms, and connected devices require reliable and secure connectivity. Application Centric Infrastructure enables segmentation and policy enforcement based on application needs. This supports data protection while improving system availability.
In the manufacturing and industrial sector, adoption is driven by automation and connected operations. Digital production systems rely on real time data exchange between applications and machines. Application centric networking helps ensure predictable performance and reduced downtime. This improves operational efficiency and supports smart manufacturing initiatives.
Risk Analysis
One key risk associated with Application Centric Infrastructure adoption is implementation complexity during the transition phase. Organizations moving from traditional network architectures often face challenges in redesigning policies and workflows around applications. If not planned carefully, this transition can lead to temporary operational disruption. Skills gaps within IT teams can further increase this risk.
Another risk relates to dependency on centralized policy management. While centralized control improves consistency, it also creates a higher impact point of failure if governance processes are weak. Inadequate testing or misconfigured policies can affect multiple applications at once. This makes disciplined change management and monitoring essential for long term stability.
Regulatory Environment Overview
The regulatory environment influencing Application Centric Infrastructure adoption is shaped by data protection, cybersecurity, and operational resilience requirements. Regulations increasingly require organizations to demonstrate control over data flows and access policies. Application centric models support this by embedding compliance rules directly into application level policies. This alignment helps organizations maintain consistent enforcement across complex environments.
In regulated industries, audit readiness and traceability are becoming more important. Application Centric Infrastructure provides visibility into how applications communicate and how policies are applied. This visibility supports reporting and compliance validation efforts. As regulatory scrutiny increases, infrastructure models that support centralized oversight are gaining relevance.
Technology Evolution Outlook
The evolution of Application Centric Infrastructure is closely linked to advances in automation and software driven networking. Infrastructure is expected to become increasingly self adjusting, responding to application behavior in near real time. This evolution reduces manual intervention and improves responsiveness. Over time, application policies are expected to become more granular and adaptive.
Another important evolution trend is deeper integration with cloud native and container based environments. As organizations deploy more distributed applications, infrastructure must support portability and consistency across platforms. Application centric models are adapting to support this requirement through improved orchestration and visibility. This progression strengthens their role in future enterprise architectures.
Buyer Decision Criteria
Buyers evaluating Application Centric Infrastructure typically focus on operational simplicity and long term scalability. Solutions are assessed based on how effectively they reduce manual configuration and support application driven policies. Ease of integration with existing systems is also a critical consideration. Buyers seek platforms that can deliver value without extensive disruption.
Security and governance capabilities also play a central role in decision making. Buyers prioritize infrastructure that supports centralized policy control and clear visibility into application traffic. The ability to enforce consistent rules across different environments is viewed as a strong advantage. These criteria reflect a broader focus on reliability, compliance, and operational control.
Key Market Segments
By Component
- Hardware
- Switches
- Controllers
- Others
- Software
- On-Premises
- Cloud-based
- Services
- Professional Services
- Support & Maintenance
By Organization Size
- Large Enterprises
- Small & Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs)
By End-Use Industry
- IT & Telecom
- BFSI
- Healthcare & Lifesciences
- Retail & eCommerce
- Government & Defense
- Manufacturing
- Energy & Utilities
- Others
Top Key Players in the Market
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- VMware, Inc.
- Juniper Networks, Inc.
- Arista Networks, Inc.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
- Dell Technologies, Inc
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Nokia Networks
- IBM Corporation
- Fujitsu Ltd.
- Extreme Networks
- Ciena Corporation
- Broadcom Inc.
- F5 Networks, Inc.
- Citrix Systems, Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Check Point Software Technologies
- Fortinet, Inc.
- Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
- NetApp, Inc.
- Others
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2024) | USD 3.2 Bn |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 12 Bn |
| CAGR(2025-2034) | 14.1% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historic Period | 2020-2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



