Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Editor’s Choice
- History of Autonomous Ships
- Autonomous Ships Market Statistics
- Container Shipping Statistics
- Global Container Fleet Statistics
- Global Merchant Ships Statistics
- Specifications of Autonomous Ships
- Benefits of Autonomous Ships
- Challenges and Concerns
- Regulations for Autonomous Ships Statistics
- Recent Developments
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Autonomous Ships Statistics: Autonomous ships are cutting-edge maritime vessels capable of operating independently without direct human control. Using a combination of advanced sensors, navigation systems, and artificial intelligence.
These ships can function in various operational modes, including fully autonomous, remotely operated, and hybrid, depending on the situation.
They promise benefits such as reduced operational costs and increased safety by minimizing human error, though they face challenges like technical reliability. Cybersecurity risks and the need for evolving regulations.
As technology advances, the integration of autonomous ships into the maritime industry is expected to progress. Aiming to enhance efficiency and safety while addressing regulatory and safety concerns.

Editor’s Choice
- The launch of Yara Birkeland, the world’s first fully electric and autonomous container ship, in 2020, represented a significant milestone.
- The global autonomous ships market revenue reached USD 6.1 billion in 2023.
- Meanwhile, fully autonomous ships are projected to contribute USD 2.22 billion in 2031, USD 2.45 billion in 2032, and USD 2.68 billion by 2033.
- In the global autonomous ships market, the hardware component holds a dominant position, accounting for 77.5% of the total market share.
- In the autonomous ships market, the commercial sector emerges as the predominant end-use segment, commanding 64.2% of the market share.
- In the autonomous ships market, ABB leads with a market share of 15%. Reflecting its strong position in providing advanced maritime automation solutions.
- The regional distribution of the autonomous ships market reveals a leading share held by the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, which commands 31.4% of the market.
- The majority of respondents believe that the presence of crew onboard vessels will remain crucial for shipboard operations in the future, with 84% affirming this view.
History of Autonomous Ships
- The history of autonomous ships has evolved significantly since the 1970s, when the first concepts of unmanned vessels emerged.
- In the 1980s and 1990s, advancements were primarily theoretical. With research focused on the potential benefits and technological feasibility of autonomous navigation systems.
- By the early 2000s, practical developments began, marked by the launch of various prototypes and pilot projects.
- One of the earliest notable projects was the European Union’s MUNIN (Maritime Unmanned Navigation through Intelligence in Networks). Which in 2016 demonstrated the potential of autonomous ships for long-distance maritime transport.
- The 2010s saw major strides, with companies like Rolls-Royce and Kongsberg unveiling plans for commercial autonomous vessels.
- The launch of Yara Birkeland, the world’s first fully electric and autonomous container ship, in 2020, represented a significant milestone.
- Regulatory frameworks have also evolved, with the International Maritime Organization (IMO) conducting extensive studies and developing guidelines to ensure the safe integration of autonomous ships into global shipping operations.
- These efforts underscore a cautious yet progressive approach to adopting autonomous maritime technology, balancing innovation with safety and regulatory compliance.
(Sources: AIP Publishing, International Maritime Organization, The Shipyard Blog)
Autonomous Ships Market Statistics
Global Autonomous Ships Market Size Statistics
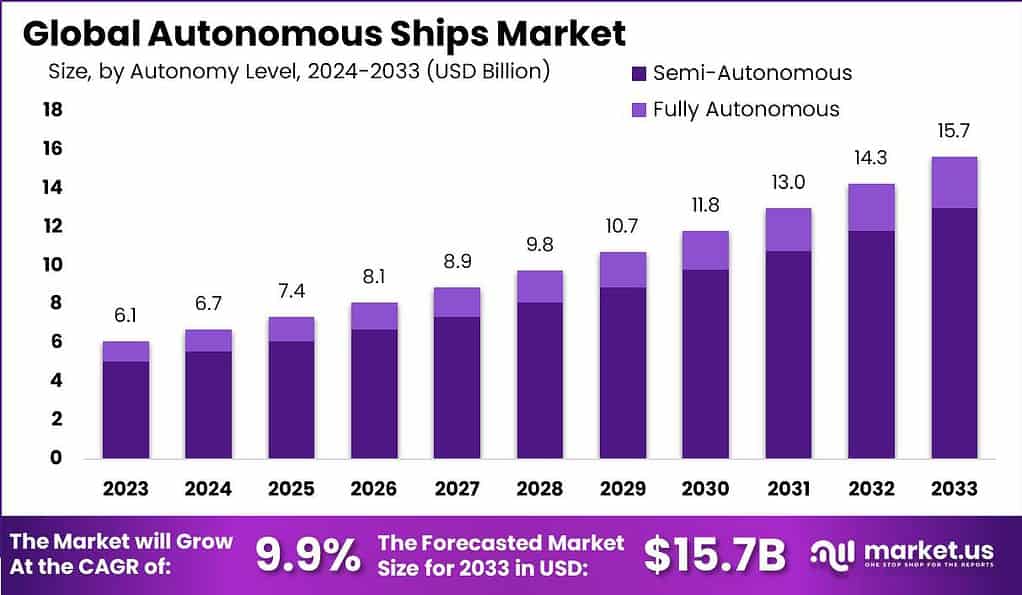
- The global autonomous ships market has exhibited a steady upward trajectory in recent years at a CAGR of 9.9%. With revenue amounting to USD 6.1 billion in 2023.
- This growth is projected to continue, reaching USD 6.7 billion in 2024 and further expanding to USD 7.4 billion by 2025.
- The market is anticipated to maintain its positive momentum. With revenues expected to hit USD 8.1 billion in 2026 and USD 8.9 billion in 2027.
- The forecast indicates a significant rise in market value. Reaching USD 9.8 billion by 2028 and USD 10.7 billion by 2029.
- The trend of growth is projected to persist into the next decade. The market is anticipated to generate USD 11.8 billion in 2030, USD 13.0 billion in 2031, USD 14.3 billion in 2032, and culminate at USD 15.7 billion by 2033.
- This consistent increase underscores the growing adoption and integration of autonomous technologies in the maritime sector. Driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, automation, and the increasing demand for efficient and cost-effective maritime operations.
(Source: market.us)

Global Autonomous Ships Market Size – By Autonomy Level Statistics
2023-2028
- The global autonomous ships market is poised for significant growth. Total revenue is projected to rise from USD 6.1 billion in 2023 to USD 15.7 billion by 2033.
- In 2023, semi-autonomous ships accounted for USD 5.06 billion, while fully autonomous ships contributed USD 1.04 billion.
- This trend is expected to continue, with semi-autonomous ships generating USD 5.55 billion in 2024 and USD 6.13 billion in 2025. While fully autonomous ships are projected to contribute USD 1.15 billion and USD 1.27 billion, respectively.
- By 2026, the market for semi-autonomous ships is anticipated to reach USD 6.71 billion. With fully autonomous ships contributing USD 1.39 billion.
- This upward trajectory continues through 2027. With revenues of USD 7.38 billion for semi-autonomous and USD 1.52 billion for fully autonomous ships.
- In 2028, semi-autonomous ships are expected to generate USD 8.12 billion, while fully autonomous ships will contribute USD 1.68 billion.
2029-2033
- By 2029, these figures are projected to rise to USD 8.87 billion and USD 1.83 billion, respectively.
- The market is forecasted to reach USD 9.78 billion for semi-autonomous ships and USD 2.02 billion for fully autonomous ships by 2030.
- In the following years, revenues from semi-autonomous ships are expected to grow to USD 10.78 billion in 2031, USD 11.85 billion in 2032, and USD 13.02 billion by 2033.
- Meanwhile, fully autonomous ships are projected to contribute USD 2.22 billion in 2031, USD 2.45 billion in 2032, and USD 2.68 billion by 2033.
- This consistent increase highlights the growing adoption of both semi-autonomous and fully autonomous technologies within the maritime industry. Driven by advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and the pursuit of more efficient maritime operations.
(Source: market.us)

Global Autonomous Ships Market Share – By Component Statistics
- In the global autonomous ships market, the hardware component holds a dominant position, accounting for 77.5% of the total market share.
- This substantial share underscores the critical role of advanced hardware systems, including sensors, navigation equipment, and communication devices, which are essential for the operation of autonomous ships.
- Meanwhile, software components constitute 22.5% of the market share, highlighting the importance of sophisticated software solutions that facilitate the integration, control, and management of autonomous functionalities.
- The interplay between these components is vital for the advancement and efficiency of autonomous maritime operations. Ensuring robust performance and safety in increasingly complex maritime environments.
(Source: market.us)

Global Autonomous Ships Market Share – By End-use Statistics
- In the autonomous ships market, the commercial sector emerges as the predominant end-use segment, commanding 64.2% of the market share.
- This significant share reflects the increasing adoption of autonomous shipping technologies in commercial applications such as cargo transport, logistics, and passenger services, driven by the need for cost efficiency, safety, and operational effectiveness.
- On the other hand, the defense sector holds 35.8% of the market share. Underscoring the strategic importance of autonomous ships in military and defense operations.
- These applications include surveillance, reconnaissance, and strategic maritime operations, where autonomous technologies enhance mission capabilities and operational precision.
- The substantial presence in both commercial and defense sectors illustrates the broad applicability and growing reliance on autonomous maritime solutions across diverse operational contexts.
(Source: market.us)

Competitive Landscape of Global Autonomous Ships Market Statistics
- In the autonomous ships market, ABB leads with a market share of 15%. Reflecting its strong position in providing advanced maritime automation solutions.
- Following closely, Wartsila holds 14% of the market, emphasizing its significant contribution to the industry’s technological advancements.
- Rolls-Royce accounts for 13% of the market share, showcasing its prominent role in developing innovative autonomous ship systems.
- Kongsberg Gruppen has a 12% market share, underscoring its expertise in integrated maritime automation.
- L3 ASV captures 11% of the market, indicating its substantial involvement in the autonomous maritime sector.
- Rh Marine follows with a 10% market share, highlighting its contributions to maritime automation technologies.
- Siemens holds 9% of the market, reflecting its pivotal role in integrating autonomous solutions within the maritime industry.
- Other key players collectively account for 16% of the market share. Demonstrating the diverse and competitive nature of the autonomous ships market.
(Source: market.us)

Regional Analysis of Global Autonomous Ships Market Statistics
- The regional distribution of the autonomous ships market reveals a leading share held by the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, which commands 31.4% of the market. This dominance is attributed to the region’s rapid technological advancements, extensive maritime activities, and significant investments in autonomous maritime technologies.
- North America follows with a 28.0% market share. Reflecting its strong focus on innovation and the early adoption of autonomous shipping solutions.
- Europe holds a close 27.7% share, driven by its robust maritime industry and supportive regulatory frameworks.
- South America accounts for 8.0% of the market, indicating a growing interest in autonomous ships, albeit at a slower pace compared to the leading regions.
- The Middle East and Africa (MEA) region holds a 4.9% market share. Highlighting emerging opportunities and gradual advancements in autonomous maritime technologies within these regions.
- This regional distribution underscores the global nature of the autonomous ships market and the varied pace of adoption across different parts of the world.
(Source: market.us)

Container Shipping Statistics
Global Container Shipping Market Volume – Growth Rate
- The global container shipping market has experienced fluctuating growth rates from 2015 to 2022.
- In 2015, the market saw a slight decline with a growth rate of –0.4%.
- This was followed by a modest recovery in 2016, achieving a growth rate of 2%.
- The market’s expansion gained momentum in 2017 with a robust growth rate of 4.7%, and this positive trend continued in 2018, albeit at a slightly reduced rate of 4.1%.
- However, in 2019, growth decelerated to 1.7%.
- The market faced another downturn in 2020, recording a negative growth rate of -0.8%, largely impacted by global disruptions.
- In 2021, the market rebounded strongly, with a growth rate of 5.7%, reflecting a significant recovery and increased demand.
- By 2022, the growth rate stabilized at 3.7%, indicating steady progress and resilience in the global container shipping market amidst varying economic conditions.
(Source: Statista)

Global Container Fleet Statistics
Growth of the Global Container Fleet
- The container fleet experienced varied growth rates from 2019 to 2022.
- In 2019, the fleet grew by 4%, reflecting a period of expansion in the container shipping industry.
- This growth slowed in 2020, with the fleet increasing by 2.9%, likely influenced by global economic challenges and disruptions.
- In 2021, the growth rate rebounded to 4.5%, indicating a strong recovery and renewed investment in fleet capacity.
- By 2022, the growth rate moderated to 3%, suggesting a stabilization in fleet expansion as the industry adjusted to ongoing market conditions and demand dynamics.
(Source: Statista)

Global Merchant Ships Statistics
Number of Merchant Ships – By Type
- As of January 1, 2022, the world merchant fleet comprised various types of ships, each serving distinct roles in global maritime operations.
- The fleet included 17,784 Ro-Ro and general cargo ships, making them the most numerous type in the fleet.
- Bulk cargo carriers followed with 12,941 ships, highlighting their critical role in transporting large volumes of raw materials.
- The fleet also included 8,258 crude oil tankers, essential for global oil distribution, and 6,122 chemical tankers, which are specialized for transporting hazardous liquids.
- Container ships numbered 5,574, reflecting their importance in global trade and goods transportation.
- Additionally, 5,369 passenger ships were catering to the travel and tourism industry.
- Lastly, the fleet contained 2,180 liquefied natural gas tankers. Underlining their role in the energy sector by transporting LNG across the globe.
- This diverse composition of the world merchant fleet underscores the complexity and specialization of maritime logistics and transportation.
(Source: Statista)

Specifications of Autonomous Ships
- Autonomous ships, such as the Yara Birkeland and those developed under the AUTOSHIP project, are equipped with advanced technologies that allow for efficient, safe, and environmentally friendly maritime operations.
- Key specifications include extensive sensor arrays capable of detecting and classifying objects up to several kilometers away. Ensuring effective situational awareness and collision avoidance.
- The Yara Birkeland, for instance, uses a fully electric propulsion system, contributing to zero emissions and reducing diesel truck journeys by 40,000 annually. Its dimensions are approximately 80 meters in length and 15 meters in width.
- Kongsberg Maritime’s systems, utilized in many autonomous ships, feature robust radar and GPS integration, supporting autonomous navigation over long distances. With operational ranges often exceeding 500 nautical miles (NM).
- These ships are also designed with substantial data storage and processing capabilities to handle complex navigational tasks and remote operations from control centers like Kongsberg’s Remote Operating Centre (ROC), which can control and monitor multiple vessels simultaneously.
- These advancements in autonomous maritime technology not only enhance operational efficiency but also significantly reduce the environmental footprint of shipping.
(Sources: Sea Machines, Kongsberg, Yara International ASA, Autoship)
Benefits of Autonomous Ships
Sectors Benefiting from Autonomous Ships Statistics
- The adoption of autonomous operations is anticipated to benefit several sectors within the shipping industry significantly.
- According to respondents, the container ships—deep sea sector shows the highest potential, with 57.58% recognizing its benefits.
- Container ships—short sea also stand to gain, with 46.19% of respondents in favor.
- The tanker sector is similarly poised for advantage, with 45.03% acknowledging its potential. Closely followed by general cargo ships at 44.87%.
- Car carriers could benefit as well, with 42.05% of respondents indicating a positive impact.
- Offshore operations, were recognized by 31.79% of respondents, and inland waterways, with 32.28%. Also presents significant opportunities for autonomous technology integration.
- Other sectors that could see benefits include specialist vessels (30.3%), ferries—short sea (30.13%), and ferries—coastal (26.66%).
- Dredging and hydraulic operations (26.32%) and ferries—international (14.07%) show more moderate potential.
- The passenger liners/cruise sector (9.93%) and yachts (10.1%) appear less likely to benefit substantially from autonomous operations, reflecting lower respondent endorsement.
- This distribution highlights the varied applicability and expected advantages of autonomous operations across different segments of the shipping industry.
(Source: Autonomous Roundtable Report)

Willingness to Support a Move to The Adoption of the Autonomous Vessel
- The willingness to support the adoption of autonomous vessels is primarily driven by their potential to enhance multiple aspects of maritime operations.
- A significant 50.83% of respondents indicated their support if autonomous vessels are proven to increase safety efficiency and reduce operating costs.
- Safety alone is a major motivator, with 25.5% of respondents expressing willingness to support adoption if it can be demonstrated to improve safety.
- Additionally, 8.94% of respondents are motivated by the potential for reduced operating costs, while efficiency gains drive 6.13%.
- Other reasons account for 8.61% of the responses, highlighting various additional factors influencing support for autonomous vessel adoption.
- This data underscores the multifaceted benefits that stakeholders are looking for in autonomous maritime technology and the strong support for its adoption. Given comprehensive improvements across safety, efficiency, and cost.
(Source: Autonomous Roundtable Report)

Challenges and Concerns
- The majority of respondents believe that the presence of crew onboard vessels will remain crucial for shipboard operations in the future, with 84% affirming this view.
- A smaller segment, comprising 10% of respondents, considers crew presence to be unessential. Indicating a minority belief in the feasibility of fully autonomous operations without a crew.
- Additionally, 6% of respondents believe that crew will be essential only in crowded areas, suggesting a conditional need for crew depending on the operational environment.
- This data highlights the prevailing sentiment within the maritime industry that human oversight and intervention will continue to play a vital role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of shipboard operations, even as autonomous technologies advance.
(Source: IMarEST Survey)

Regulations for Autonomous Ships Statistics
- The regulations for autonomous ships are evolving globally, with significant progress made in Europe and specific advancements in countries like Norway, the UK, Belgium, Denmark, and the Netherlands.
- These nations have signed an agreement to facilitate the operation of autonomous ships in the North Sea, establishing common technical standards and solutions pending international regulations by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) expected by 2025.
- The IMO has also categorized different levels of ship autonomy, ranging from remote control with crew on board to fully autonomous vessels. National regulations currently govern most autonomous shipping projects, with international guidelines still under development.
- Countries like Norway are leading in creating a framework for autonomous maritime operations, ensuring safety and operational efficiency while fostering innovation in maritime technology.
(Sources: International Maritime Organization, Shipping Telegraph, The Maritime Executive, Ship Technology, Offshore Energy)
Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- Kongsberg acquires Rolls-Royce Commercial Marine: In mid-2023, Kongsberg completed its $660 million acquisition of Rolls-Royce Commercial Marine. This acquisition aims to enhance Kongsberg’s capabilities in autonomous ship technology by integrating Rolls-Royce’s advanced marine engineering and automation systems.
- Wärtsilä acquires Transas: Wärtsilä acquired Transas, a company specializing in marine navigation solutions, for $225 million in late 2023. This merger is expected to strengthen Wärtsilä’s position in the autonomous shipping market by combining its propulsion technology with Transas’s navigation and simulation systems.
New Product Launches:
- Yara Birkeland Autonomous Container Ship: In early 2024, the Yara Birkeland, the world’s first fully electric and autonomous container ship, was launched. This vessel aims to reduce emissions and improve efficiency in short-sea shipping. Operating without a crew and using advanced navigation systems.
- Rolls-Royce’s Intelligent Awareness System: Rolls-Royce introduced its Intelligent Awareness system in mid-2023. Designed to enhance the situational awareness of autonomous ships by integrating data from multiple sensors, including radar, LIDAR, and cameras, to provide a comprehensive view of the vessel’s surroundings.
Funding:
- Ocean Infinity raises $100 million: In 2023, Ocean Infinity, a marine robotics company, raised $100 million to expand its fleet of autonomous ships and develop new technologies for ocean data collection and seabed mapping.
- Sea Machines Robotics secures $90 million: Sea Machines Robotics, a leader in autonomous control and navigation systems for ships. Secured $90 million in early 2024 to accelerate the deployment of its autonomous solutions in commercial and military vessels.
Technological Advancements:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Advances in AI and machine learning are being integrated into autonomous ships to improve navigation, collision avoidance, and operational efficiency, allowing ships to operate more safely and autonomously.
- Advanced Sensor Fusion: The development of advanced sensor fusion technologies is enhancing the capabilities of autonomous ships by combining data from multiple sensors to create a more accurate and reliable picture of the marine environment.
Market Dynamics:
- Growth in Autonomous Ships Market: The global autonomous ships market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.4% from 2023 to 2028, driven by increasing demand for efficient and sustainable shipping solutions, advancements in autonomous technologies, and regulatory support.
- Increased Adoption in Cargo Shipping: Autonomous ships are seeing increased adoption in cargo shipping due to their potential to reduce operational costs, improve safety, and enhance efficiency in long-distance and short-sea shipping.
Regulatory and Strategic Developments:
- IMO Regulatory Framework: The International Maritime Organization (IMO) updated its regulatory framework in early 2024 to include guidelines and standards for the operation of autonomous ships, focusing on safety, Maritime Security, and environmental protection.
- EU Maritime Strategy: The European Union launched a new maritime strategy in 2023 to promote the development and deployment of autonomous ships, supporting innovation, sustainability, and competitiveness in the maritime sector.
Research and Development:
- Human-Machine Collaboration: R&D efforts are focusing on improving human-machine collaboration in autonomous ships, and developing systems that allow for remote monitoring and intervention by human operators, enhancing safety and reliability.
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: Researchers are exploring new propulsion technologies and energy-efficient systems for autonomous ships to reduce emissions and improve sustainability. Including the use of renewable energy sources and hybrid propulsion systems.
Conclusion
Autonomous Ships Statistics – The adoption of autonomous ships is set to revolutionize the maritime industry. By significantly enhancing efficiency and safety and reducing operational costs.
The market is expected to grow substantially, driven by key players. Like ABB, Wartsila, and Rolls-Royce, with the Asia-Pacific region leading this expansion.
Deep-sea container ships, tankers, and general cargo vessels are anticipated to benefit the most from autonomous operations.
Despite advancements, the presence of crew onboard is still deemed crucial. Particularly in complex and crowded environments.
Overall, the integration of autonomous technologies promises to reshape maritime operations, making them more efficient, safe, and sustainable.
FAQs
Autonomous ships are vessels equipped with advanced technologies that allow them to operate with minimal or no human intervention. These technologies include sensors, navigation systems, artificial intelligence, and automation software.
The main benefits of autonomous ships include increased efficiency, enhanced safety, and reduced operating costs. They can optimize routes, reduce human error, and operate continuously without the need for rest breaks.
Deep-sea container ships, tankers, and general cargo vessels are expected to benefit the most from the adoption of autonomous operations due to their extensive use in global trade and logistics.
The market for autonomous ships is projected to grow significantly, with the Asia-Pacific region leading the expansion, followed by North America and Europe. Key players like ABB, Wartsila, and Rolls-Royce are at the forefront of this growth.
While autonomous technologies are advancing, the presence of crew onboard is still considered crucial, especially in complex and crowded environments. Human oversight remains important for ensuring optimal performance and safety.
The autonomous ships market includes various types of vessels, such as Ro-Ro/general cargo ships, bulk cargo carriers, crude oil tankers, chemical tankers, container ships, passenger ships, and liquefied natural gas tankers.
Autonomous ships enhance safety by reducing the risk of human error, enabling continuous monitoring and control, and allowing for more precise navigation and maneuvering. They can also respond to emergencies more effectively through automated systems.


