Table of Contents
Introduction
Educational Robots Statistics: Educational robots are specialized devices employed in the educational field to engage students and facilitate learning. Especially in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).
These robots possess the capability to be programmed, feature sensors, and are often mobile, allowing them to interact with their surroundings.
They are available in various forms, ranging from DIY robotic kits to pre-programmed and remotely controlled robots, serving as hands-on learning aids.
Educational robots find widespread use in STEM education, coding instruction, and problem-solving tasks. Delivering practical knowledge and preparing students for future careers in technology-related professions.
While they offer advantages such as improved learning and the development of critical skills. Challenges like cost, teacher training, and maintenance should be considered.

Editor’s Choice
- In 2023, the educational robots market generated approximately USD 1.4 billion in revenue.
- Notably, in 2028, humanoid robots’ revenue is expected to double that of non-humanoid robots.
- Among educational applications, higher education holds the largest share, accounting for 35% of the market. Reflecting the significant utilization of educational robots in tertiary institutions.
- Although the term “educational robotics” has gained prominence in recent years. The origins of such tools can be traced back to 1969 when Seymour Papert introduced the Turtle robot.
- The usage of educational robots in teaching is a topic of interest, and survey data reveals that 26.75% of respondents have affirmed the integration of educational robots into their teaching methods.
- Among primary school teachers responsible for core subjects in grades 1-4, 29.82% reported incorporating educational robots into their teaching methods. Signifying a relatively high adoption rate in this category.
- Notably, the Faculty of Teacher Education reported the highest adoption rate, with 46.93% of respondents incorporating educational robots into their teaching methods. Underscoring the strong presence of these tools in teacher education programs.
Educational Robots Market Overview
Global Educational Robots Market Size Statistics
- The global educational robots market is experiencing steady growth, with revenues projected to increase over the coming years.
- In 2022, the market generated approximately USD 1.2 billion in revenue, and this figure is expected to rise to USD 1.4 billion in 2023.
- The trend continues with an estimated revenue of USD 1.6 billion in 2024 and USD 1.9 billion in 2025.
- As we progress into the future, the market is anticipated to witness even more significant growth. Reaching approximately USD 2.3 billion in 2026 and USD 2.6 billion in 2027.
- The growth trajectory remains positive, with projections indicating revenues of USD 2.8 billion in 2028, USD 3.3 billion in 2029, and USD 3.7 billion in 2030.
- By 2031, the global educational robots market is forecasted to surpass USD 4.3 billion, with further expansion expected, reaching USD 5.1 billion in 2032.
- This upward trend underscores the increasing significance of educational robots in the modern learning landscape.
(Source: Market.us)

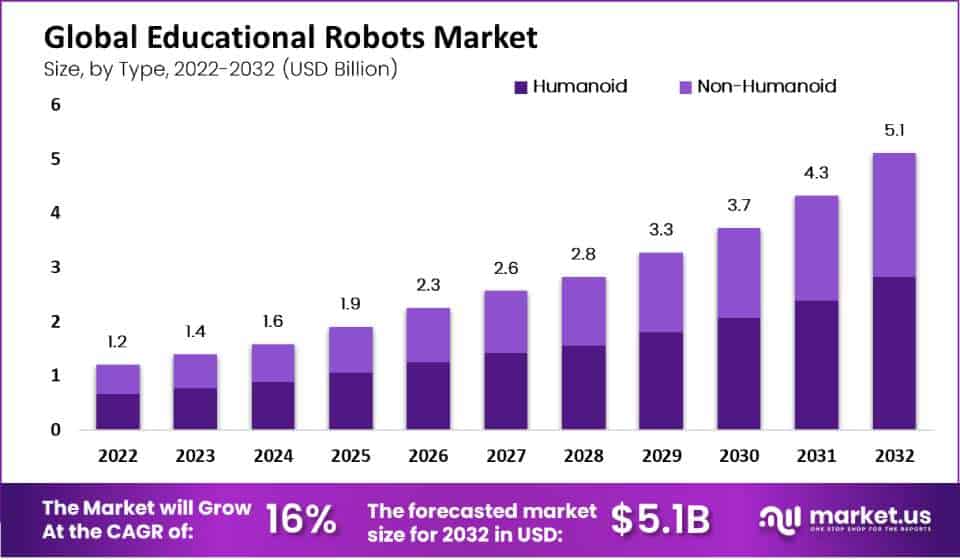
Global Educational Robots Market Size – By Type Statistics
- The global educational robots market, segmented by type into humanoid and non-humanoid robots, demonstrates a consistent upward trajectory in terms of revenue.
- In 2022, the total market revenue reached USD 1.2 billion. Evenly distributed between humanoid and non-humanoid categories, each accounting for USD 1 billion.
- This balanced growth continued in 2023, 2024, and 2025, with total revenues of USD 1.4 billion, USD 1.6 billion, and USD 1.9 billion, respectively.
- In 2026, the market expanded to USD 2.3 billion while maintaining a 1:1 ratio between humanoid and non-humanoid robot revenues.
- As we progress, the market’s growth becomes more pronounced, with a total revenue of USD 2.6 billion projected for 2027 and USD 2.8 billion for 2028.
- Notably, in 2028, humanoid robots’ revenue is expected to double that of non-humanoid robots.
- This trend continues in the following years, with total revenue reaching USD 5.1 billion in 2032, with humanoid robots contributing significantly to this growth.
- These figures underscore the increasing significance of both humanoid and non-humanoid educational robots in the global market.
(Source: Market.us)

Educational Robots Market Share – By Application Statistics
- The global educational robots market is characterized by a distribution of market share across various educational applications.
- Among these, Higher Education holds the largest share, accounting for 35% of the market. Reflecting the significant utilization of educational robots in tertiary institutions.
- Special Education follows closely with a substantial 23% market share, indicating their vital role in addressing unique learning requirements.
- Secondary Education holds a noteworthy 12% market share. Primary Education contributes 10%, underlining the use of educational robots in earlier stages of education.
- Other Applications collectively represent a substantial 20% market share. Highlighting the versatility and broad applicability of educational robots beyond traditional educational settings.
- These statistics emphasize the diverse and extensive adoption of educational robots across different educational sectors.
(Source: Market.us)

Historical Overview of Educational Robots
- Although the term “educational robotics” has gained prominence in recent years. The origins of such tools can be traced back to 1969 when Seymour Papert introduced the Turtle robot.
- This robot, programmed in the Logo programming language, marked a pioneering effort in teaching algorithmic thinking and programming. Interestingly, it also inspired the toy giant Lego, which faced financial challenges due to the expiration of its patent rights on building blocks.
- Lego ventured into dynamic and programmable blocks, building upon the foundation of the Turtle robot.
- This new product allowed children not only to build but also to program. Fostering skills that align with the demands of the modern age.
- Concurrently, the market witnessed the emergence of similar educational robotics solutions from companies like Robolink, Hanson Robotics, Modular Robotics, Primo Toys, and Engino.
- Research institutions and universities, involving scientists from various fields, also contributed by developing teaching methods geared toward specific educational objectives.
(Source: MDPI)
Usage of Educational Robots in Teaching
- The usage of educational robots in teaching is a topic of interest, and survey data reveals that 26.75% of respondents have affirmed the integration of educational robots into their teaching methods.
- This suggests that a notable portion of educators recognize the value and benefits of incorporating these specialized devices into the learning process.
- However, the majority, comprising 73.25% of respondents, have not yet adopted educational robots as a teaching tool.
- While there is a growing acknowledgment of their potential. It appears that there is still room for further adoption and exploration of how these robots can enhance the educational experience.
(Source: Researchgate)

Usage of Educational Robots in Teaching – By Subject Statistics
- The utilization of educational robots in teaching varies significantly across different subjects, as indicated by the survey results.
- Among primary school teachers responsible for core subjects in grades 1-4, 29.82% reported incorporating educational robots into their teaching methods. Signifying a relatively high adoption rate in this category.
- In contrast, technical education and mathematics recorded adoption rates of 14.04% and 5.25%, respectively.
- Other subjects, such as Croatian, chemistry and biology, history and geography, German, physics, English, and foreign languages. Each reported relatively lower adoption rates ranging from 0.88% to 3.50%.
- Furthermore, 5.70% of respondents mentioned using educational robots for various subjects or combinations of subjects.
- These findings highlight variations in the integration of educational robots across different teaching subjects, with primary school core subjects leading to adoption.
(Source: Researchgate)

Usage of Educational Robots According to Demographics
According to Age
- The usage of educational robots appears to be associated with the age of respondents, as reflected in the survey data.
- Among respondents aged 23 to 29 years, 25.00% reported incorporating educational robots in their teaching methods.
- The adoption rate increased significantly among respondents aged 30 to 39, with 33.33% utilizing educational robots.
- In the age group of 40 to 49, 24.10% of respondents reported using educational robots for teaching purposes.
- A lower but still notable adoption rate of 16.23% was observed among those aged 50 to 59.
- However, respondents aged 60 and above showed a relatively lower adoption rate of 1.32%.
- These findings suggest that younger educators, particularly those in their 30s. This has a higher tendency to integrate educational robots into their teaching practices. While the adoption gradually decreases with increasing age.
(Source: Researchgate)

According to the Graduated Faculty
- The utilization of educational robots in teaching varies significantly across different faculties and departments within educational institutions, as indicated by the survey results.
- Notably, the Faculty of Teacher Education reported the highest adoption rate, with 46.93% of respondents incorporating educational robots into their teaching methods. Underscoring the strong presence of these tools in teacher education programs.
- In contrast, the Faculty of Science and the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences recorded adoption rates of 14.04% and 12.28%, respectively. Reflecting a lower but still substantial integration of educational robots in these areas.
- Other faculties and departments, including Organization and Informatics, Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, Electrical Engineering and Computing, and others, reported adoption rates ranging from 0.88% to 6.14%.
- These findings highlight the varying degrees of adoption of educational robots across different faculties and departments within educational institutions, with teacher education programs leading in utilization.
(Source: Researchgate)

Popular Educational Robots Statistics
Wonder Workshop
- Wonder Workshop enhances the classroom experience through its STEM learning robots, Dash and Cue. Dash appeals to younger children with its singing and dancing abilities and can respond to voice commands.
- On the other hand, Cue offers similar features but is designed for older kids, focusing on more advanced interactions.
- Both robots provide teachers with an immersive way to teach children about robotics, coding, engineering, and various STEM-related subjects.
(Source: Wonder Workshop)
The LEGO Group
- In 1984, a professor from MIT created a programming language tailored for children. Enabling them to control robot “turtles,” making them move, turn, and draw.
- This innovative experiment caught the attention of Lego CEO Kjeld Kirk Kristiansen. Who saw the potential to integrate this technology with Lego Bricks
- This collaboration between Lego and MIT led to the development of Lego Mindstorms. A range of programmable Lego robots aimed at inspiring kids to explore STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math) and computer programming.
- Programmable Robots for Education are automated machines that can be programmed to perform various tasks
- Lego envisions applications for both homes and classrooms, and this initiative has even given rise to international Lego robotics tournaments as part of the First Lego League.
(Source: LEGO Group)
Kaspar
- The University of Hertfordshire initiated the Kaspar project, which stands for Kinesics and Synchronization in Personal Assistant Robotics.
- Kaspar, resembling a doll-like humanoid, serves as a valuable tool for educators and parents in assisting children with autism or communication challenges.
- Kaspar’s design is deliberately minimal in its facial expressions, prioritizing the specific requirements of children with autism.
(Source: University of Hertfordshire)
BeatBots
- BeatBots is the company responsible for creating Keepon. A small yellow robot that gained internet recognition for its fondness for the band Spoon.
- Originally conceived by Hideki Kozima, Keepon was designed to foster social interaction and enhance communication abilities in children facing developmental challenges.
- While the commercial version of Keepon is utilized in educational settings and by therapists. There’s also a consumer version known as MyKeepon, which is accessible to a wider audience.
(Source: BeatBots)
VEX Robotics
- Vex Robotics has a mission to engage students in STEM fields by instructing them in the construction and programming of robots.
- The company provides a range of robotic products tailored to various age groups of students. Along with a curriculum that serves as a valuable resource for educators.
- Additionally, they organize annual competitions that draw participants from elementary school to high school levels globally.
- These competitions offer students the opportunity to compete and excel in subjects related to robotics, including research, mathematics, and science.
(Source: VEX Robotics)
Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- LEGO Education acquires Modrobotics: In 2023, LEGO Education, a leading provider of educational robotics kits, acquired Modrobotics. A company specializing in modular robotic systems, for $50 million. This acquisition aims to expand LEGO’s robotics offerings for K-12 education by integrating Modrobotics’ modular systems into their STEM-focused educational products.
- SoftBank Robotics acquires Aldebaran Robotics: In early 2023, SoftBank Robotics acquired Aldebaran Robotics. A French company known for developing the NAO robot, for $100 million. This move strengthens SoftBank’s portfolio of educational robots, with plans to enhance learning experiences through AI-driven interactive robots.
New Product Launches:
- VEX Robotics launches VEX GO for early learners: In late 2023, VEX Robotics launched VEX GO. A robotics system designed for young learners aged 7-10. The product is aimed at introducing STEM concepts to children through hands-on building and coding challenges. Fostering an early interest in robotics and engineering.
- UBTECH introduces the JIMU Robot AstroBot Series: In mid-2024, UBTECH Robotics launched its new JIMU Robot AstroBot Series. A robotics kit that teaches children how to program robots using block-based coding. The product is designed for middle school students, helping them build and program interactive robots for educational purposes.
Funding:
- Robokind raises $30 million for robot-assisted learning: In 2023, Robokind, a company specializing in educational robots for children with autism, raised $30 million in funding. The investment will be used to expand Robokind’s product line and bring its robot-assisted learning solutions to more schools and therapy centers.
- Wonder Workshop secures $40 million for coding robots: In early 2024, Wonder Workshop, known for its Dash and Dot coding robots. Secured $40 million in Series C funding to develop new AI-driven educational robots. The funding will be used to scale production and enhance coding curriculums for elementary and middle schools worldwide.
Technological Advancements:
- AI-powered interactive robots: By 2025, it is expected that 45% of educational robots will feature AI capabilities, enabling more personalized learning experiences. These robots will be able to adapt to student learning speeds and provide real-time feedback, significantly enhancing STEM education.
- Integration of AR/VR with educational robots: Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are becoming integrated with educational robots. By 2026, 30% of robots in educational settings are projected to have AR/VR functionalities, allowing students to interact with virtual environments while programming and controlling robots.
Conclusion
Educational Robots Statistics – In summary, educational robots hold a crucial role in contemporary education, enriching the learning process across diverse subjects.
Their versatility, programmability, and interactive capabilities make them invaluable tools for nurturing essential skills and preparing students for forthcoming careers in technology-related fields.
From early education to higher levels, the incorporation of educational robots is reshaping the methodologies of teaching and learning.
As the market continues to progress, it is evident that these robots will persist as integral components of educational approaches, catering to a broad spectrum of subjects and age groups.
The future holds the promise of further innovations in educational robotics, expanding the horizons of knowledge and skills for the students of the future.
FAQs
Educational robots are specialized devices designed for teaching and learning purposes. They are often used in classrooms to engage students and promote learning, particularly in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) subjects.
Educational robots can vary in complexity, but they are generally programmed to perform specific tasks or activities. They may have sensors and motors that allow them to interact with the environment or respond to commands, making them effective tools for hands-on learning.
Educational robots are designed for a wide range of age groups, from young children in primary education to students in higher education and even beyond. There are age-appropriate robots and curricula available to cater to different educational levels.
Students can learn a variety of skills from educational robots, including programming, problem-solving, critical thinking, and teamwork. Educational robots can also help students understand complex concepts in subjects like mathematics, science, and engineering.
Teachers can integrate educational robots into their lessons by using robot-specific curricula or designing their activities. Robots can be used to teach a wide range of subjects, from coding and mathematics to science experiments and creative projects.


