Table of Contents
Overview
New York, NY – Feb 13, 2026 – Global Image-Guided And Robot-Assisted Surgical Procedures Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 13.9 Billion by 2034 from US$ 3.6 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 14.3% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2023, North America led the market, achieving over 46.40% share with a revenue of US$ 1.67 Billion.
Image-guided and robot-assisted surgical procedures are redefining precision, safety, and efficiency in modern healthcare systems. These advanced technologies integrate real-time imaging, navigation systems, and robotic platforms to support surgeons in performing minimally invasive and highly accurate interventions across multiple specialties, including orthopedics, neurology, cardiology, and oncology.
The adoption of image-guided and robotic-assisted systems has increased steadily due to the rising demand for minimally invasive procedures and improved patient outcomes. Enhanced visualization through high-resolution imaging enables accurate targeting of affected tissues while minimizing damage to surrounding structures. Robotic platforms provide greater dexterity, stability, and control, resulting in reduced surgical variability and improved procedural consistency.
Clinical evidence indicates that these procedures are associated with shorter hospital stays, reduced blood loss, lower complication rates, and faster recovery times compared to conventional open surgeries. Hospitals and surgical centers are increasingly investing in robotic systems to strengthen surgical capabilities and maintain competitive positioning in advanced care delivery.
The growth of this segment can be attributed to continuous technological advancements, rising healthcare expenditure, and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases requiring surgical intervention. As innovation continues, image-guided and robot-assisted procedures are expected to play a central role in advancing patient-centric, precision-driven surgical care worldwide.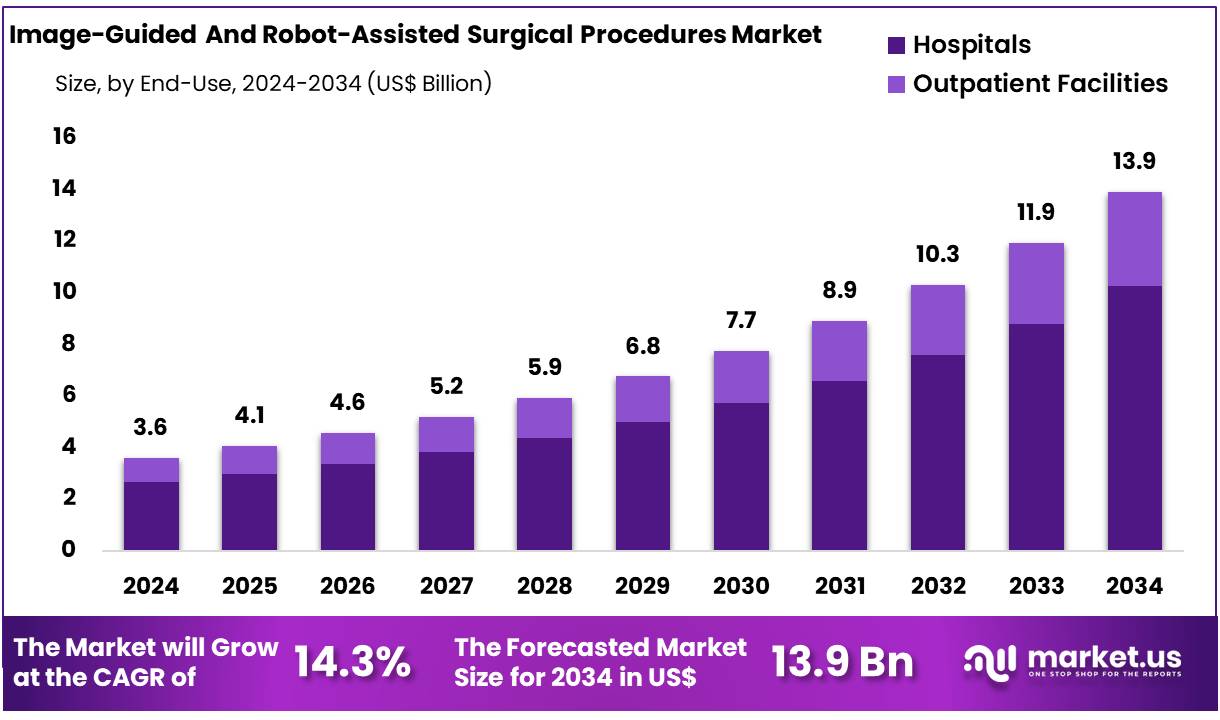
Key Takeaways
- The Image-Guided and Robot-Assisted Surgical Procedures market generated revenue of US$ 3.60 billion and is projected to reach US$ 13.90 billion, registering a CAGR of 14.3% during the forecast period.
- By specialty, the Orthopedic Surgery segment accounted for the highest revenue share, contributing 27.2% of the total market.
- By end-use, the Hospitals segment dominated the market, holding a substantial 73.8% revenue share.
- On a regional basis, North America led the global market, capturing the largest share at 46.40%.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America accounted for the largest share of the global Image-Guided and Robot-Assisted Surgical Procedures market, representing 46.40% of total revenue. Market leadership in the region has been supported by continuous technological advancements in surgical systems and a well-established healthcare infrastructure backed by a strong economic framework.
The increasing volume of complex surgical interventions, including trauma and critical care procedures, has contributed significantly to market growth. The demand for image-guided and robot-assisted techniques has expanded due to their high precision, enhanced surgical accuracy, and improved clinical outcomes. Healthcare institutions across the region have shown strong preference for these advanced platforms to optimize procedural efficiency and patient recovery.
As a result, North America continues to play a central role in influencing innovation, adoption trends, and overall market development within the global landscape.
Emerging trends in Image-Guided And Robot-Assisted Surgical Procedures
Procedure volumes are scaling, and new robot generations are entering routine care
- Clinical usage has been expanding because minimally invasive pathways are being preferred for many common operations.
- Intuitive reported ~2.7 million da Vinci procedures in 2024 (about +17% YoY) and 1,430 multiport system placements in 2024, with cumulative experience reaching nearly 17 million procedures.
- New platform cycles are being enabled by regulatory clearance; for example, FDA 510(k) K232610 covers the da Vinci Surgical System Model IS5000.
“More imaging inside the operation” is becoming the standard for precision
- Intraoperative imaging (such as CT / cone-beam CT and MRI) is being used to confirm anatomy and results *duringthe case, not only before/after.
- In glioma surgery, randomized evidence has shown higher complete resection with intraoperative MRI (96% vs 68% in one trial).
- In practice, this trend supports fewer “surprises” after surgery and helps standardize complex steps (tumor margins, implant placement, and vascular flow checks).
Navigation + robotics in bone/spine is shifting from “optional” to “expected”
- Accuracy gains are a key driver because small placement errors can cause large clinical problems.
- A meta-analysis summary reported median lumbar pedicle screw accuracy of 96.1% with navigation vs 79% without navigation.
- Recent clinical series using intraoperative CT navigation have reported very low perforation (example: 1.4% in one 70-screw series).
Fluorescence image guidance (ICG) is moving from “nice to have” to evidence-supported use in select steps
- ICG fluorescence is being used to assess perfusion and lymphatic mapping in real time, using simple visual signals rather than indirect judgment alone.
- A major society evidence review pooling 7 randomized trials reported reduced colorectal anastomotic leak risk with ICG (OR 0.58; 95% CI 0.44–0.75) and also reported ~6.32 more lymph nodes retrieved on average in GI cancer procedures.
- At the same time, mixed results have been reported in some trials/subgroups, so targeted adoption (right patient + right operation type) is increasingly being used.
Safety oversight is tightening as AI features expand (navigation, automation, and decision support)
- As AI-enabled guidance tools are added to surgical workflows, more attention is being placed on post-market surveillance, adverse event reporting, and “human-in-the-loop” controls.
- Recent reporting has described at least 10 patient injuries linked to an AI-enhanced sinus navigation system across late-2021 to 2025, alongside 100+ adverse event reports after AI integration (causality debated), highlighting why safety governance is becoming a key buying and adoption criterion.
- The market direction is being shaped by this: adoption is increasingly being tied to training, credentialing, and real-world outcome tracking, not only device capabilities.
High-value use cases
Spine instrumentation (pedicle screws) with CT navigation and/or robots
- Used for: pedicle screw planning, trajectory guidance, and verification before closure.
- Why it is adopted: placement accuracy is improved; navigation median accuracy has been reported at 96.1% vs 79% without navigation in lumbar in-vivo subgroup reporting.
- Practical impact: revision and neurologic risk can be reduced when misplacement rates are lowered; low perforation examples (e.g., 1.4%) have been reported in intraoperative CT navigation series.
Colorectal surgery perfusion checks (ICG fluorescence) to reduce leak risk
- Used for: perfusion assessment before creating the bowel connection (anastomosis) and for deciding where to cut.
- Numeric support: pooled randomized evidence has shown leak reduction with ICG (OR 0.58) and a very large increase in “change of plan” events (transection point changes reported with OR 35.15 in pooled RCTs), meaning the imaging frequently alters intraoperative decisions.
- Reality check: some trials show mixed benefit by subgroup, so use is often focused on higher-risk anastomoses rather than applied blindly to all cases.
Brain tumor surgery (glioma) with intraoperative MRI guidance
- Used for: verifying residual tumor and enabling “further resection” safely in the same operation.
- Numeric support: higher complete resection has been reported with iMRI (96% vs 68% in a randomized comparison).
- Operational note: iMRI workflows are typically used in high-complexity centers because they require infrastructure, shielding, and standardized safety steps.
Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (urology) as a high-volume robotic pathway
- Used for: prostate removal with fine dissection around nerves and continence structures.
- Adoption signal: literature summaries report that almost 90% of radical prostatectomies in the United States are robot-assisted.
- Long-term outcomes are actively studied; for example, a large comparative dataset reported 75% of patients receiving robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy in that cohort.
Orthopedic joint replacement (example: total hip arthroplasty) with robotic assistance
- Used for: component positioning and alignment consistency in hip replacement.
- Adoption trend: a nationwide analysis reported robotic-assisted THA rising from 1.2% (2016) to ~6.7% (2022).
- Implication: this is still a minority share, but the growth curve indicates expanding hospital investment where consistency and revision avoidance are strategic goals.
Conclusion
Image-guided and robot-assisted surgical procedures are transforming modern surgical care through improved precision, consistency, and patient safety. Procedure volumes are increasing steadily, supported by regulatory approvals, technological advancements, and expanding clinical evidence.
Higher accuracy rates, such as 96% pedicle screw precision with navigation and improved tumor resection outcomes with intraoperative MRI, demonstrate measurable clinical value. Reduced complication risks, including lower anastomotic leak rates with fluorescence guidance, further strengthen adoption. Hospitals continue to invest heavily, particularly in North America, which holds 46.40% market share. Overall, strong clinical performance and sustained innovation are expected to support long-term market expansion.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



