Table of Contents
Introduction
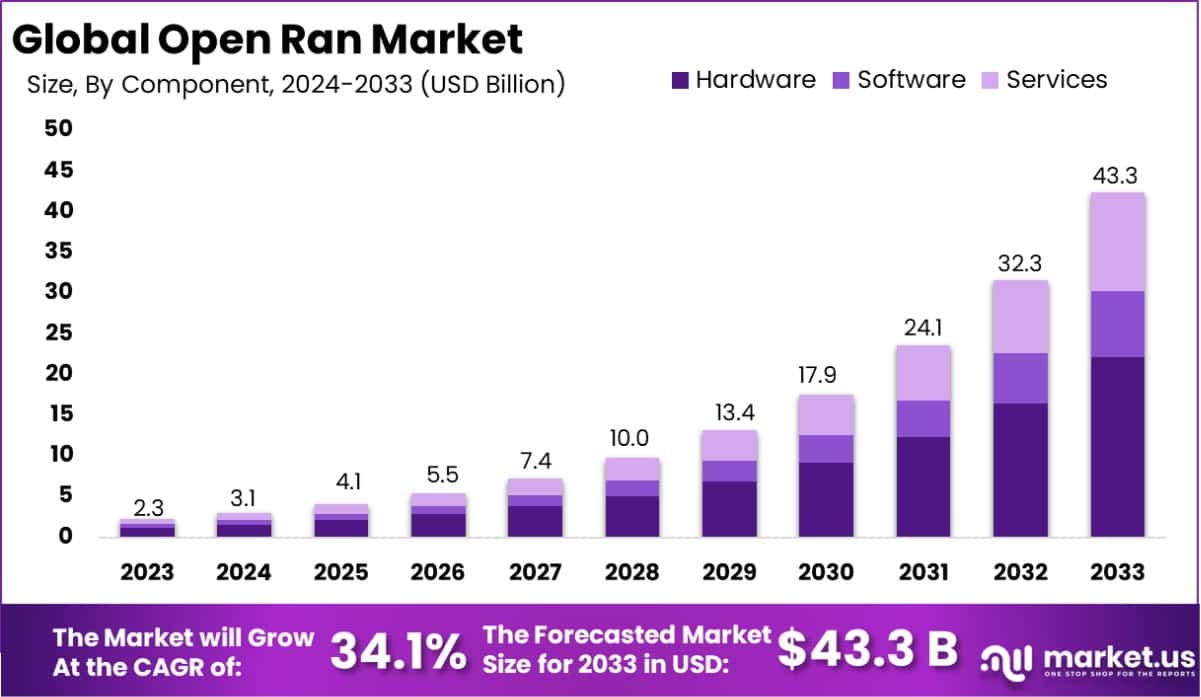
According to the findings from Market.us, The Global Open RAN Market is on a rapid growth trajectory. By 2033, the market size is forecasted to reach USD 43.3 Billion, up from USD 2.3 Billion in 2023. This represents a significant Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 34.1% over the next decade, from 2024 to 2033.
In 2023, North America emerged as a dominant force in the Open RAN landscape, capturing a substantial 42.3% market share. This translates to revenue of approximately USD 0.97 Billion from this region alone. The robust market share underscores North America’s leading role in adopting and implementing Open RAN technologies, reflecting a strong investment and innovation landscape in this sector.
Open RAN stands for Open Radio Access Network. It’s a new way to build mobile networks where the different parts of the network can talk to each other using standard, open interfaces. This means that any company can make equipment that works together without needing to rely on the same manufacturer for all parts. It opens up the market to more competition and innovation, making it easier and possibly cheaper to set up and upgrade mobile networks.
The Open RAN market is growing as more mobile network operators adopt this technology. Operators see Open RAN as a way to reduce costs and increase flexibility in their networks. As they can choose from more suppliers, they aren’t stuck with one vendor, which can help them negotiate better prices and access the latest technology more quickly.
The growth of the Open RAN market is driven by the need for more flexible and cost-effective network solutions. Telecommunication companies are eager to reduce their reliance on single vendors, which can lower costs and spur innovation. Additionally, government policies in several countries support the use of Open RAN to promote competition and security in the network technology industry.
There’s a strong demand for Open RAN because it allows for more customized and efficient network operations. Operators can better manage their networks to meet the increasing data demands without significant increases in cost. This demand is further boosted by the rollout of 5G networks, where Open RAN can play a crucial role in ensuring widespread and cost-effective deployment.
The shift towards Open RAN offers substantial opportunities for new players in the market, particularly in software development for network management and optimization. There’s also potential for established companies to innovate their offerings for compatibility with Open RAN specifications, tapping into a growing market eager for modular and interchangeable network solutions.
The expansion of the Open RAN market is expected to accelerate with advancements in technology and further standardization of network components. As more telecom operators recognize the benefits of Open RAN in reducing operational costs and enhancing network capabilities, the adoption rate is likely to increase, leading to a broader market expansion globally. This expansion is supported by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the performance and reliability of Open RAN systems.
Open RAN Statistics
- The Open RAN Market is on an impressive growth trajectory. It’s set to expand from USD 2.3 billion in 2023 to USD 43.3 billion by 2033. This rapid growth is projected at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 34.1% over the next decade.
- Looking at the components within this market, Hardware leads the way, claiming over 51.1% of the market share in 2023. This segment is pivotal due to its essential role in building out open RAN infrastructure.
- In terms of network technology, 4G Networks are the cornerstone in 2023, holding more than 38.9% of the market. This dominance underscores the current reliance on 4G as the backbone for communications infrastructure, even as newer technologies begin to emerge.
- Focusing on specific units within the market, the Radio Unit stands out with more than 40.5% market share. This unit is crucial for signal transmission and reception, highlighting its integral function in the network setup.
- The market also shows a strong preference for Sub-6 GHz frequencies, which accounted for more than 76.4% of the segment in 2023. This frequency band is favored for its balance between coverage and bandwidth, proving essential for widespread network deployment.
- Geographically, North America is at the forefront, with a commanding 42.3% market share, translating to USD 0.97 billion in revenue. This region leads due to its rapid adoption of advanced technologies and substantial investments in infrastructure development.
- In a recent report by New Street Research, analysts explored Rakuten Mobile’s claim that Open RAN technology provides a more cost-effective alternative for mobile network operators. The analysis demonstrated that on a per-site basis, the capital costs associated with deploying Open RAN are 40% lower than traditional network setups. This significant reduction suggests that Open RAN can offer substantial upfront savings for operators looking to expand or upgrade their networks.
- Furthermore, the operational costs, which include the ongoing expenses for managing and maintaining network infrastructure, were found to be 30% lower with Open RAN. This decrease in operational expenses can lead to long-term cost efficiencies for operators, potentially enhancing profitability and investment capacity.
Growth Factors
- Diverse Vendor Ecosystem: Open RAN promotes a more competitive landscape by enabling telecommunications operators to select from a wider array of vendors. This reduces dependency on specific suppliers and fosters innovation and agility within the network infrastructure.
- Governmental Support: Investments in Open RAN are significantly supported by government initiatives, which recognize the potential of Open RAN to advance national telecommunications capabilities, thus driving growth.
- Cost Effectiveness: By transitioning to Open RAN, operators can realize substantial cost savings. This approach reduces capital expenditures and operational costs by allowing more flexible and competitive pricing in network deployments.
- Technological Advancements: The push towards 5G and the need for more scalable and flexible network solutions have made Open RAN an attractive option for modernizing existing network infrastructures.
- Increased Deployment in Private Networks: Open RAN’s adaptability makes it suitable for private networks, which are tailored to specific organizational needs. This flexibility is increasingly demanded by enterprises and governments alike.
Technological Innovations
- Virtualization and Software-Centric Networks: Open RAN facilitates the shift toward virtualized network functions, reducing the reliance on physical hardware and allowing easier updates and maintenance.
- Enhanced Network Functionality with AI and Machine Learning: Incorporating AI helps in optimizing network traffic and predictive maintenance, thus improving overall efficiency and performance.
- Advanced Component Integration: The adoption of components like Radio Units and Centralized Units in Open RAN architectures enhances the capability to manage complex networks efficiently, particularly in densely populated areas or regions with high data traffic.
- Support for a Wide Range of Frequencies: Open RAN supports various frequency bands, including Sub-6GHz for broader coverage, which is crucial for extensive network deployment across diverse geographical locations.
- Interoperability and Standardization: Open RAN promotes standardization across different vendor equipment, which is vital for ensuring compatibility and seamless integration of new technologies into existing infrastructures.
Emerging Trends
- Commercial Deployments Gain Traction: Open RAN has transitioned from trial stages to small-scale commercial deployments, with significant activity from mobile operators and vendors globally. Companies like DISH Wireless and Verizon in the USA have embarked on extensive Open RAN implementations to enhance network flexibility and interoperability.
- Shift Towards Cloud-Native Networks: There is a growing emphasis on cloud-native network functions within the Open RAN ecosystem, allowing for greater scalability and flexibility in network management and operations. This trend is critical for adapting to the increasing data demands and complex network management tasks.
- Enhanced Multi-Vendor Interoperability: Open RAN fosters a multivendor environment which reduces supply chain and operational risks by diversifying sources and limiting the impact of issues with specific vendors. This is increasingly becoming a key focus area to ensure robust and resilient network architectures.
- Increased Government Interest and Investment: Governments are showing heightened interest in Open RAN, viewing it as a pivotal area for growth and innovation within the telecom sector. This support is expected to drive further research and development, accelerating Open RAN adoption.
- Energy Efficiency Initiatives: Major telecom operators like Deutsche Telekom and Vodafone are prioritizing energy-saving frameworks within their Open RAN strategies. These initiatives are crucial for reducing the environmental impact and operational costs associated with running extensive mobile networks.
Top Use Cases
- Urban 5G Rollouts: Open RAN is being employed in urban settings to facilitate the rollout of 5G networks. Vodafone’s deployment of a commercial 5G Open RAN pilot in Italy exemplifies this application, leveraging Open RAN’s flexibility for faster and more cost-effective network upgrades.
- Rural Network Expansion: Operators like Verizon are using Open RAN to expand network coverage in rural areas. This approach allows for more cost-effective network setups and easier maintenance, ensuring broader and more reliable connectivity.
- Network Modernization: Open RAN enables legacy networks to transition smoothly to more advanced network technologies like 5G, without the need for significant upfront investment in new hardware. This use case is particularly prevalent in regions with existing extensive 4G infrastructure that needs upgrading.
- Disaster Recovery: The inherent flexibility and interoperability of Open RAN facilitate quicker recovery and adaptation in disaster-prone areas. By using a diversified vendor pool, networks can ensure faster restoration of services and resilience against future disruptions.
- Innovative Customer Services: Open RAN allows for the implementation of advanced network features such as real-time analytics and network slicing. These technologies enable telecom operators to offer customized and innovative services tailored to the specific needs of different customer segments.
Major Challenges
- Interoperability and Standardization: The evolution of Open RAN requires more refined and universally accepted standards to ensure seamless interoperability among the diverse hardware and software from different vendors. This lack of standardization can slow down deployment and integration processes.
- Security Concerns: Open RAN networks involve multiple vendors, which can lead to complex security challenges. Maintaining robust security protocols across various components and ensuring they meet stringent standards is critical but challenging.
- Economic Pressures: The initial investment for setting up Open RAN infrastructure can be high due to the costs associated with developing new technologies and training personnel. Additionally, macroeconomic factors such as funding and market stability impact the pace at which Open RAN can be adopted.
- Vendor Diversity: While Open RAN aims to break the monopoly of traditional single-vendor setups, achieving a healthy vendor ecosystem is challenging. There’s a need for more collaboration between new and established players to foster a competitive yet cooperative market environment.
- Technical Complexity: Integrating and managing a multi-vendor RAN setup is technically demanding. Operators must handle complex configurations and updates that require sophisticated network management and orchestration tools, making the deployment and ongoing operations challenging.
Business Benefits
- Flexibility in Network Management: Operators can upgrade and scale their networks more flexibly and cost-effectively, adapting quickly to changing market demands or technological advancements.
- Reduced Operational Costs: The shift to Open RAN helps in lowering operational expenses through less reliance on physical infrastructure and manual interventions, which translates to reduced costs and enhanced network management.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: By improving network capabilities and performance, Open RAN enables operators to offer better service quality, thus enhancing user satisfaction and loyalty.
- Faster Deployment of New Technologies: Open RAN accelerates the deployment of new services and technologies, such as 5G, by simplifying the integration process and reducing dependencies on specific hardware or software vendors.
- Increased Security and Compliance: The diverse vendor environment in Open RAN networks improves security by mitigating risks associated with vendor lock-in and enhances compliance with global standards and regulations.
Top Opportunities
- Cost Efficiency: Open RAN reduces reliance on single vendors, potentially lowering the cost of network components and maintenance due to competitive pricing from multiple suppliers.
- Innovation and Flexibility: The open architecture of Open RAN fosters innovation by allowing operators to mix and match components from different vendors, leading to more tailored and advanced network solutions.
- Enhanced Network Capabilities: Open RAN architectures are designed to be agile and scalable, supporting advanced network features like network slicing and edge computing, which are crucial for future technologies like 5G and IoT.
- Market Diversification: Open RAN opens up opportunities for new vendors to enter the market, which can lead to more innovation and competitive pricing. This diversification also reduces the risk associated with dependency on specific vendors.
- Improved Service Delivery: With its inherent flexibility, Open RAN can improve the speed and efficiency of service deployment. Operators can leverage automated operations and AI-driven insights to enhance performance and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
In summary, Open RAN is reshaping how mobile networks are built and operated by promoting more flexibility and cost-efficiency. Its adoption marks a significant shift towards open standards in a market traditionally dominated by a few large vendors. As the technology matures and more telecom operators adopt Open RAN, we can expect a more competitive and innovative marketplace, which could lead to better services for consumers and more robust growth in the telecom industry. The future of Open RAN looks promising, with ample opportunities for both established companies and new entrants to innovate and thrive in the evolving landscape of network technologies.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



