Table of Contents
Remittance Market Size
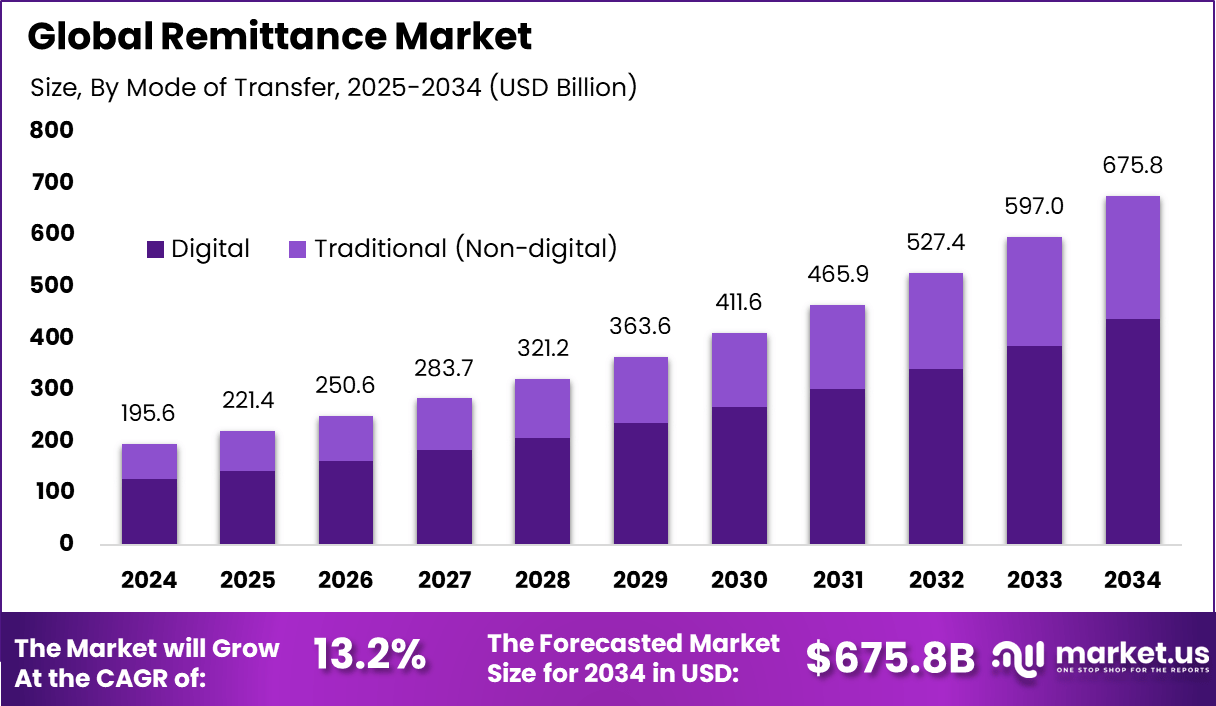
The global remittance market was valued at USD 221.4 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach approximately USD 675.8 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 13.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant position with more than 34.3% market share, generating around USD 67.0 billion in revenue.

The remittance market refers to cross border money transfers sent by individuals to family members or others, most often from migrant workers to households in their home countries. These transfers are typically used for essential spending such as food, rent, education fees, and healthcare, which makes remittances a stable flow even during economic stress. Remittance services are delivered through banks, money transfer operators, mobile wallets, and digital platforms that connect the sender, payment networks, and the receiver.
Top Market Takeaways
- Digital transfer channels account for 64.7%, as speed, mobile access, and lower fees continue to shape user preference.
- Inward remittances represent 58.9%, highlighting strong and consistent flows from overseas workers to home economies.
- Banks lead distribution with 42.6%, supported by regulatory trust, compliance strength, and established international networks.
- Migrant labor drives 47.3% of end-use demand, confirming remittances as a critical source of household income.
- North America holds 34.3% share, backed by a large migrant base and advanced financial systems.
- The U.S. market reached USD 57.71 billion and is expanding at a 10.2% CAGR, supported by digital adoption and steady immigration-led transfers.
Global and India-Specific Remittance Insights
- India received USD 135.46 billion in remittance inflows in FY2024–25, recording 14% annual growth.
- India has remained the world’s largest remittance recipient for over 10 years, reflecting sustained overseas employment.
- Remittances now contribute more than 10% of India’s current account inflows and support nearly half of the trade deficit.
- Growth is increasingly led by highly skilled professionals in developed economies, reducing reliance on traditional GCC corridors.
- The U.S. is the largest source of remittances to India with a 27.7% share, followed by the UAE, UK, Saudi Arabia, and Singapore.
- Remittance flows to developing countries reached USD 401 billion as early as 2012, with India, China, the Philippines, and Mexico as key beneficiaries.
- For recipient households, remittances often contribute close to 60% of total income, supporting essential needs such as food, healthcare, and education.
Demand Analysis
Demand is shaped by the size of migrant communities, wage levels in host countries, and the cost of sending money along each corridor. Price sensitivity is high, so users often compare providers and shift quickly when fees fall or exchange rate spreads improve. Reliability matters because remittances are closely tied to household budgets, so failed or delayed transfers can have direct social impact.
On the receiving side, demand is influenced by cash needs, wallet acceptance, and the ability to use funds for bills or merchant payments. Where cash pickup remains common, demand tends to favor wide agent networks and extended service hours. Where digital wallets are widely accepted, demand shifts toward instant credit and low cost transfers to accounts or wallets. Seasonal patterns also appear around holidays, school admissions, and emergency periods, when transfer volumes can rise.
Increasing Adoption Technologies
Real time payment rails and faster cross border settlement are improving transfer speed and reducing uncertainty for users. Wallet to wallet and account to wallet transfers are expanding as providers integrate with local payment systems and national ID frameworks. Digital onboarding, eKYC, and risk based verification are also making it easier for customers to start using regulated services without heavy paperwork.
API based connectivity is enabling remittance platforms to plug into multiple banking partners, payout networks, and compliance tools. Cloud infrastructure and modern fraud detection systems are improving uptime and transaction monitoring at scale. Some corridors are adopting ISO 20022 style messaging and richer payment data, which supports better reconciliation and fewer transfer errors. Agent networks are also being digitized through smart devices that simplify cash payout and reporting.
Customers adopt digital remittance options mainly for convenience, as transfers can be initiated anytime without visiting a branch or agent location. Faster delivery builds confidence, especially when funds are needed for urgent household expenses. Transparent fees and real time tracking reduce confusion and help users choose providers based on clear total cost.
Providers adopt these technologies to lower operating costs, reduce manual handling, and improve compliance consistency across corridors. Automated screening and transaction monitoring can reduce false alerts while still meeting regulatory expectations. Better system integration also helps providers launch new corridors faster and offer multiple payout options without rebuilding core systems. Over time, improved service quality supports higher retention in a market where switching costs are low.
Investment Opportunities
Opportunities are being created in digital first corridors where mobile wallet usage is rising and customers prefer instant settlement. Investment can be directed toward payout infrastructure, including partnerships with local banks, wallet providers, and retail agents that expand reach. There is also room to build specialized products for small business cross border payments that sit adjacent to consumer remittances but share similar rails.
Risk and compliance tooling remains an attractive area because regulators expect stronger controls as volumes move to digital channels. Platforms that improve pricing transparency, foreign exchange management, and liquidity routing can also create durable value for providers. In receiving markets, merchant acceptance and bill payment ecosystems can be strengthened so remittance funds stay digital and become easier to spend. Cross border payroll solutions for migrant workers are another pathway, linking salary disbursement directly with remittance flows.
AI Led Growth Outlook
AI is increasingly used to improve fraud detection by identifying unusual transaction patterns, device signals, and behavioral changes that rule based systems may miss. It can also support smarter compliance workflows by prioritizing alerts and reducing manual reviews for low risk transactions. These capabilities can reduce losses and improve approval rates, which directly affects customer experience.
AI also supports service quality by improving customer support through automated chat, multilingual assistance, and faster dispute handling. In pricing and routing, AI assisted optimization can help providers choose efficient corridors, manage liquidity, and reduce settlement delays. Over time, these improvements can support broader access by lowering costs for smaller value transfers. The growth outlook is positive where AI is applied in a controlled way with clear governance and explainable outcomes.
Emerging Trends
In the remittance market, a significant trend is the increasing adoption of digital money transfer platforms that allow customers to send funds using mobile apps, web portals, and digital wallets instead of relying solely on traditional agent networks and bank branches. This digital shift is driven by the convenience of instant transfers, lower transaction costs, and wider accessibility, particularly in regions with high smartphone penetration. As digital infrastructure improves, more individuals and small businesses are preferring online remittance channels for cross-border payments.
Another emerging trend is the integration of real time tracking and transparency features within remittance services. Senders and receivers now expect clear visibility into transfer status, fees, and delivery timelines. Providers are embedding live tracking dashboards and automated notifications that keep users informed from fund initiation to payout. This trend enhances trust and user satisfaction, as it reduces uncertainty about where and when funds will arrive.
Growth Factors
A key growth factor in the remittance market is the expanding global diaspora and migrant workforce. Millions of individuals work outside their home countries and regularly send money to support families, education, healthcare, and living expenses. This persistent demand for cross-border transfers underpins sustained growth in remittance volumes and drives innovation in service delivery mechanisms that can reduce cost and increase speed.
Another important growth factor is the enhancement of cross-border payment infrastructure. Financial institutions, payment service providers, and fintech innovators are investing in systems that improve interoperability, reduce settlement times, and streamline compliance. These infrastructure improvements make it easier for remittance providers to scale services globally while complying with regulatory requirements such as anti-money laundering and know-your-customer standards.
Driver
A principal driver of the remittance market is the demand for affordable and efficient money transfer services. Traditional transfer methods have historically carried high fees and slow delivery times, which motivates senders to seek alternatives that minimise costs and deliver funds quickly. Service models that offer competitive pricing, digital access, and faster transaction processing attract both individual customers and small enterprises engaged in frequent cross-border exchanges.
Another driver is the growing integration of mobile money services with remittance networks. In many regions, especially in parts of Africa, Latin America, and Asia, mobile wallets are widely used for everyday transactions. Linking remittance services directly to these wallets enables receivers to access funds instantly, bypassing the need for bank accounts or physical agent visits. This connectivity expands reach and supports inclusion of unbanked and underbanked populations.
Restraint
A significant restraint in the remittance market is the complexity of regulatory compliance across jurisdictions. Providers must navigate diverse legal frameworks, reporting requirements, and sanctions regimes when facilitating cross-border transfers. Ensuring adherence to anti-money laundering, counter-terrorist financing, and customer identity verification standards adds operational cost and complexity, particularly for smaller providers.
Another restraint stems from the variability in financial infrastructure across countries. Some regions lack robust digital payment ecosystems or reliable banking channels, which can limit the efficiency and reach of remittance services. Providers may need to maintain hybrid distribution networks that combine digital platforms with agent locations, which increases logistical challenges and expense.
Opportunity
A strong opportunity in the remittance market lies in the expansion of blockchain and distributed ledger technologies for cross-border payments. These technologies have the potential to simplify settlement processes, reduce intermediary fees, and provide transparent audit trails. By enabling near-real-time settlement with lower operational overhead, distributed ledger based remittance solutions can open new pathways for competitive service offerings.
Another opportunity exists in partnering with local financial ecosystems to enhance payout options. By integrating with banks, mobile money providers, and agent networks, remittance services can offer receivers greater choice for fund access, including direct wallet deposits, bank transfers, cash pickup, or bill payment services. This flexibility improves user experience and broadens market reach.
Challenge
A core challenge for the remittance market is balancing security and user convenience. Strong authentication, fraud detection, and compliance checks are critical to protect users and prevent misuse. However, overly burdensome verification processes can slow transfers and deter users seeking fast and simple services. Designing systems that safeguard transactions while maintaining smooth user journeys remains complex.
Another challenge involves managing foreign exchange volatility and pricing transparency. Exchange rates can fluctuate rapidly, and fees embedded in currency conversion affect the total cost of transfers. Providing clear, competitive, and predictable pricing that accounts for exchange rate movement is essential to retain customer trust and encourage repeat use.
You May also Read
Robot Mission Replay Tools Market
Robotics Red Team Services Market
Key Market Segments
By Mode of Transfer
- Digital
- Traditional (Non-digital)
By Type
- Inward Remittance
- Outward Remittance
By Channel
- Banks
- Money Transfer Operators
- Online Platforms (Wallets)
By End-use
- Migrant Labor Workforce
- Personal
- Small Businesses
- Others
Top Key Players in the Market
- Bank of America Corporation
- ZEPZ
- Citigroup, Inc.
- Ria Financial Services, Inc.
- OFX
- Wells Fargo
- Western Union Holdings, Inc.
- PayPal
- MoneyGram International, Inc.
- Wise US, Inc.
- Others
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2024) | USD 195.6 Bn |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 675.8 Bn |
| CAGR(2025-2034) | 13.2% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historic Period | 2020-2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends |
| Segments Covered | By Mode of Transfer (Digital, Traditional (Non-digital)), By Type (Inward Remittance, Outward Remittance), By Channel (Banks, Money Transfer Operators, Online Platforms (Wallets)), By End-use (Migrant Labor Workforce, Personal, Small Businesses, Others) |
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



