Table of Contents
According to Market.us’s research, The global smart glass market is projected to reach a value of USD 13.2 billion by 2032, increasing from USD 6.0 billion in 2024, with an anticipated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.5% during the period from 2023 to 2032.
Smart glass is an innovative technology that revolutionizes the transparency and functionality of glass surfaces. It allows users to adjust the opacity of glass to control light and heat transmission, enhancing privacy and energy efficiency. Various types of smart glass include electrochromic, thermochromic, photochromic, and polymer dispersed liquid crystal (PDLC) glasses, each suited for specific applications such as windows, skylights, and even automotive glass.
The major driving factors for the smart glass market include the need for energy efficiency and enhanced privacy. Smart glass reduces reliance on artificial lighting and HVAC systems, which significantly lowers energy costs and supports sustainable building practices. Its ability to switch from transparent to opaque also offers instant privacy in settings like offices and healthcare facilities, contributing to its increasing adoption.
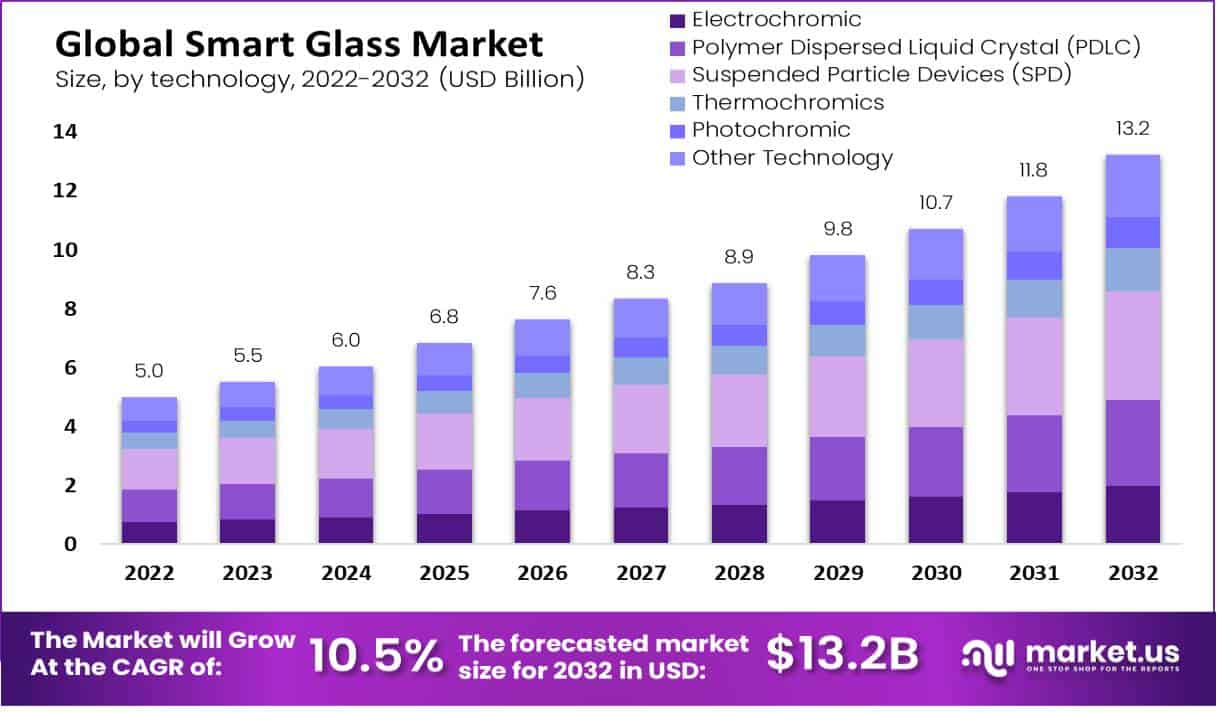
Market demand for smart glass is fueled by its diverse applications and the benefits it provides, such as energy savings and aesthetic versatility. Its integration into smart home systems allows for automated or remote control, aligning with modern trends towards more connected and responsive living and working environments.
There are significant opportunities in the smart glass market due to the ongoing technological advancements and increasing interest in green building solutions. Smart glass is integral in obtaining LEED certification and is increasingly favored in new construction and retrofitting projects for its environmental benefits and compliance with energy efficiency standards.
Technological advancements in smart glass focus on enhancing its functionality and durability. Innovations include improved switchable films that offer quicker transitions and better performance in a wider range of environmental conditions. Moreover, advancements are making smart glass more accessible and cost-effective, which could expand its usage beyond luxury markets into more mainstream applications.
Analysts’ Viewpoint
Investment Opportunities & Risks
The Smart Glass market presents substantial investment opportunities, particularly driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient and smart technology solutions in construction and automotive sectors. Key growth drivers include the adoption of green building initiatives and advancements in technologies such as electrochromic and suspended particle devices (SPD) that enhance the functional attributes of glass
However, investors should be wary of the inherent risks associated with the fluctuating costs of raw materials and the technical challenges that could impede the aesthetic appeal of smart glass products. Additionally, the competitive landscape is intense, with major players continuously innovating and expanding their market presence, which could pose challenges for new entrants.
Consumer Insights
Consumer preferences in the smart glass market are increasingly shifting towards products that offer not only functional efficiency but also environmental sustainability. There is a growing inclination towards products that can integrate seamlessly into personal and public vehicles, as well as into smart building designs, to reduce carbon emissions and enhance energy conservation. Moreover, the integration of smart glass with solar panel technologies provides dual benefits of energy generation and efficient light control, making these products more appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Technological Impact and Regulatory Environment
Technologically, the market is advancing with the development of SPD and Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal (PDLC) technologies that allow users to control the light transmission through glass, which is essential for applications in automotive and architectural industries. The regulatory environment is also supportive, with various regions offering incentives for energy-efficient renovations and constructions, further propelling the market growth.
Regional Analysis
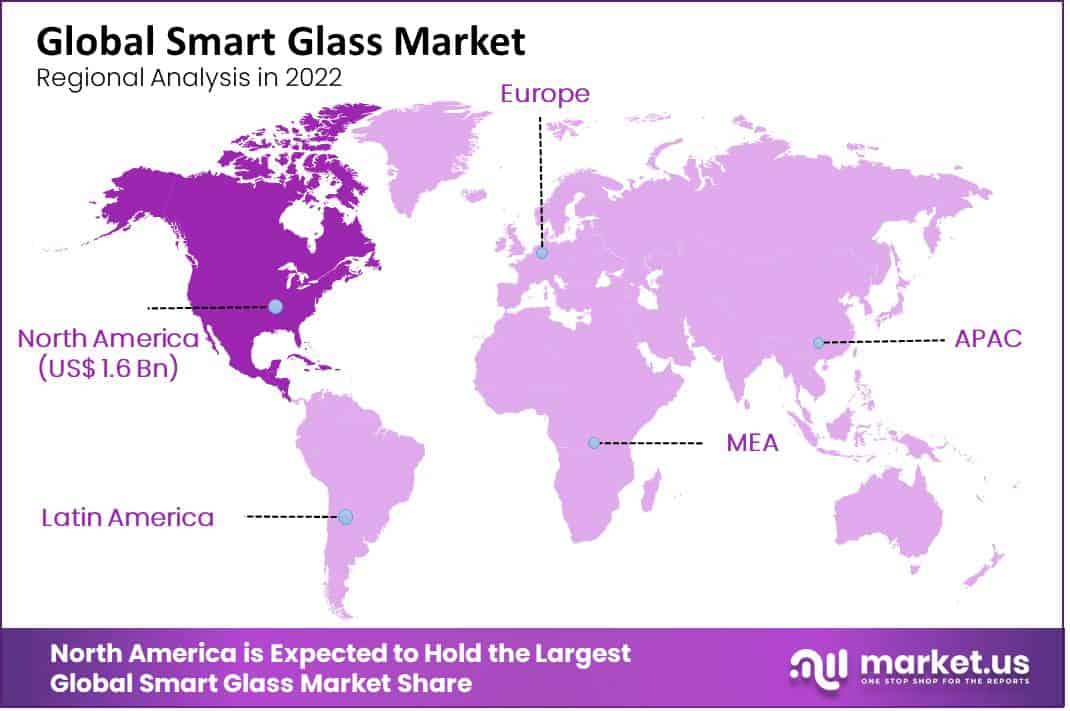
North America, particularly the United States, holds a prominent position in the smart glass market, accounting for 32.0% of the global share. This dominance can be attributed to several key factors that collectively foster innovation and adoption in this region.
Firstly, North America benefits from a robust technological infrastructure, which supports the development and integration of advanced materials like smart glass across various industries, including automotive, construction, and aerospace. The region’s emphasis on sustainable and energy-efficient building solutions has also propelled the adoption of smart glass, which contributes to energy conservation by regulating light and heat transfer.
Moreover, the presence of leading technology firms and startups focused on material science and IoT (Internet of Things) applications has accelerated research and innovation within the smart glass sector. These companies are supported by significant investment from venture capital, which is eager to fund the next wave of technological advancements. For example, significant investments in research have led to developments in electrochromic technologies, which allow glass to change its light transmission properties in response to electrical signals.
Finally, regulatory support from government bodies in North America further enhances the market’s growth. Incentives for green building initiatives, alongside stringent energy codes, push both commercial and residential construction sectors towards smart glass solutions. This regulatory environment, combined with high consumer awareness regarding the benefits of energy efficiency, continues to drive demand in this region.
Driver
Integration with Smart Home Systems
The smart glass market is driven significantly by its integration with smart home systems, enhancing the functionality and appeal of residential and commercial spaces. This technology aligns perfectly with the increasing demand for home automation, where everything from lighting to security is interconnected and can be controlled remotely.
Smart glass offers convenience and energy efficiency, adjusting its opacity based on time of day or lighting conditions to optimize indoor comfort and reduce reliance on HVAC systems. The integration not only appeals to energy-conscious consumers but also adds a modern aesthetic that is highly valued in contemporary architecture. As home automation becomes more mainstream, the role of smart glass is expected to expand, further propelling market growth.
Restraint
High Initial Cost
One of the primary restraints in the smart glass market is the high initial cost associated with its adoption. The advanced technology behind smart glass, which includes materials such as electrochromic and thermochromic elements, necessitates a substantial upfront investment in both materials and installation.
This cost barrier can deter potential users, particularly in residential sectors and emerging markets where budget constraints are tighter. Despite the long-term savings on energy and maintenance, the initial expense remains a significant hurdle, impacting the rate of adoption across global markets.
Opportunity
Expansion in Automotive and Aerospace Industries
There is a growing opportunity for smart glass within the automotive and aerospace industries. These sectors are increasingly adopting smart glass to enhance passenger comfort and energy efficiency. In automotive, smart glass is used for sunroofs and windows, offering dynamic light management that improves driving comfort and reduces energy consumption by minimizing the need for air conditioning.
In aerospace, larger smart glass windows are being developed to provide passengers control over their environment, improving their experience and reducing glare during flights. This trend is expected to continue as both industries seek to integrate more advanced technologies into their consumer offerings.
Challenge
Technical Limitations and Durability Concerns
Technical limitations and durability concerns present ongoing challenges in the smart glass market. While the technology has advanced, issues such as the speed of transition between states and long-term reliability in extreme weather conditions remain problematic. These technical challenges can affect the performance and lifespan of smart glass installations, making potential customers hesitant to invest.
Continuous research and development are crucial to overcoming these obstacles and improving the quality and functionality of smart glass to meet market expectations and consumer demands.
Key Market Segments
Based on Technology
- Electrochromic
- Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal (PDLC)
- Suspended Particle Devices (SPD)
- Thermochromics
- Photochromic
- Other Technology
Based on Application
- Architectural
- Transportation
- Automotive
- Aircraft
- Marine
- Consumer Electronics
- Power Generation
- Other Applications
Market Key Players
- Saint-Gobain S.A.
- Corning Incorporated
- Guardian Industries
- Nippon Sheet Glass Co., Ltd.
- Kinestral Technologies, Inc.
- Research Frontiers Inc.
- VELUX Group
- SPD Control Systems Corporation
- AGC Inc.
- RavenWindow
- Polytronix, Inc.
- Gentex Corporation
- Other Key Players
Emerging Trends
- Integration with IoT and Connectivity: The integration of smart glass with the Internet of Things (IoT) and other connectivity technologies like 5G is emerging as a significant trend. This allows for advanced automation in building and vehicle systems, enhancing user control and energy management.
- Augmented Reality Enhancements: Smart glass is increasingly being used to support augmented reality (AR) applications. This trend is particularly evident in the automotive and aerospace sectors, where AR can be used for heads-up displays and other interactive features.
- Sustainable Energy Solutions: There is a growing trend towards using smart glass in conjunction with solar power technologies to create energy-efficient solutions in buildings and transportation.
- Advanced Privacy and Security Features: The development of smart glass that offers adjustable opacity settings provides enhanced privacy and security for users in both residential and commercial settings.
- Customization and Personalization: Increasing consumer demand for customized and personalized options is driving innovation in smart glass technologies, allowing users to tailor the functionality of their glass based on specific needs and preferences.
Top Use Cases for Smart Glass
- Automotive Applications: Smart glass is extensively used in the automotive industry for applications such as sunroofs, rearview mirrors, and windows that offer dynamic light control and enhanced privacy.
- Architectural Design: In the construction sector, smart glass is used for exterior windows, skylights, and façades to manage solar gain and improve building energy efficiency.
- Consumer Electronics: Smart glass is used in consumer electronics for display screens that adjust their transparency based on external conditions and user preferences.
- Healthcare Facilities: Utilization of smart glass in healthcare settings for privacy in wards and operation theaters while maintaining a sterile environment.
- Retail and Hospitality: In retail and hospitality, smart glass is used to transform storefronts and hotel rooms, offering instant privacy and dynamic space utilization.
Major Challenges
- High Cost of Implementation: The initial installation cost of smart glass technology is high, which can be a significant barrier to widespread adoption.
- Technical Limitations: Some smart glass technologies still face challenges such as slower response times, limited durability, and issues with visual clarity under certain conditions.
- Material and Manufacturing Complexity: The complexity of materials and the manufacturing process for smart glass can lead to higher production costs and complexities in supply chain management.
- Regulatory and Standardization Issues: Navigating the regulatory landscape and the lack of standardization across different regions can impede market growth and innovation.
- Consumer Awareness and Acceptance: There is a need to increase consumer awareness and acceptance of smart glass technologies, which are often perceived as novel and untested.
Attractive Opportunities
- Expansion into Emerging Markets: There are significant opportunities for growth in emerging markets, especially in Asia-Pacific, where urbanization and construction activities are increasing.
- Energy Conservation Initiatives: Governments and organizations focusing on energy conservation present opportunities for the deployment of smart glass as part of green building initiatives.
- Innovative Product Development: Opportunities exist for companies that innovate with new and improved smart glass products that offer better functionality and cost-effectiveness.
- Partnerships with Technology Companies: Collaborations with technology companies to integrate advanced features like AI and IoT can open new avenues for smart glass applications.
- Health and Safety Applications: The ongoing global health crisis highlights the potential for smart glass to be used in public and private spaces to maintain health, safety, and privacy without sacrificing aesthetic and environmental control.
Conclusion
The smart glass market showcases remarkable growth potential, characterized by its diverse applications and the ongoing technological advancements that are enhancing its functionality and accessibility. As global emphasis on energy efficiency and privacy continues to rise, smart glass is positioned as a pivotal technology in both existing and emerging markets. Its ability to integrate with smart home systems and contribute to sustainable building practices further cements its role in modern architectural, automotive, and device manufacturing industries.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



