Table of Contents
Introduction
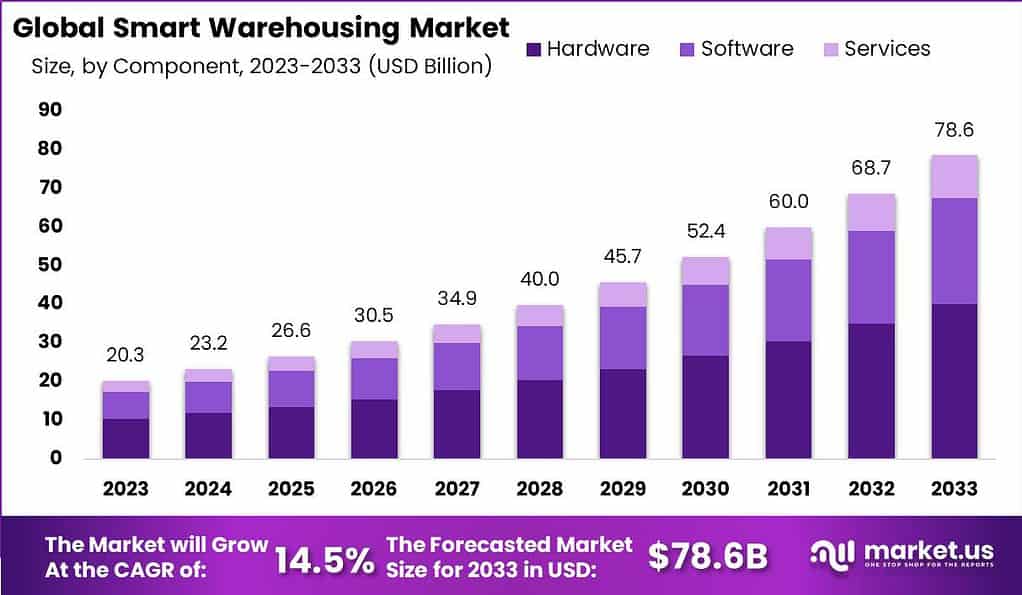
The Smart Warehousing Market plays a crucial role in modern logistics and is expected to experience significant growth. The market is projected to evolve from USD 20.3 billion in 2023 to an estimated USD 78.6 billion by 2033, representing a CAGR of 14.5%. The expansion can be attributed to the advancements in automation, robotics, and the continuous surge in e-commerce demand, which has made it imperative to have efficient and automated supply chain solutions.
North America is currently a leader in smart warehousing adoption, thanks to its advanced technological infrastructure and the presence of major e-commerce and retail companies. Amazon’s recent introduction of autonomous mobile robots in their fulfillment centers is a testament to this trend. On the other hand, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to experience the highest growth rate. This is due to the rapid adoption of automation and robotics in supply chain operations, driven by the booming e-commerce landscape.
Recent developments in the Smart Warehousing sector reflect a dynamic landscape of mergers, acquisitions, and funding rounds that highlight the industry’s ongoing evolution towards more technology-driven operations. For instance, Ryder System, a logistics giant, expanded its e-commerce and omnichannel fulfillment capabilities through strategic acquisitions, including Dotcom Distribution in November 2022, Whiplash in January 2022 for $480 million, and Midwest Warehouse & Distribution System in November 2021 for $135 million. These moves underscore the shift towards integrating direct-to-consumer offerings alongside traditional business-to-business services, aiming to meet the burgeoning demands of e-commerce transformation within the logistics ecosystem.
January 2024 witnessed significant financial activities across various sectors, including smart warehousing and logistics. Noteworthy transactions include Keystone Agency Partners securing an additional $330 million, elevating its total raised capital to over $1 billion, and Sunbit raising a $310 million debt warehouse facility led by Citi and Ares Management. Another standout development was Quantinuum’s $300 million equity fundraising at a pre-money valuation of $5 billion, led by JPMorgan Chase. These examples of substantial funding rounds reflect a vibrant investment landscape for startups and established companies alike, underscoring the critical role of innovative logistics and warehousing solutions in driving efficiency and scalability across industries.
These developments reflect a broader trend towards consolidation, technological advancement, and enhanced funding in the smart warehousing and broader logistics sectors. This signals a robust appetite for innovation and growth among investors and industry players alike.
Key Takeaways
- The Smart Warehousing market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.5% from 2023 to 2033, reaching a value of approximately USD 78.6 billion by 2033, up from USD 20.3 billion in 2023.
- In 2023, hardware components accounted for over 51% of the market share, emphasizing their pivotal role in enabling real-time data capture and automation.
- On-premises solutions dominated the market with over 56% share in 2023, driven by the benefits of enhanced control, customization, and reliability.
- Robotics and automation held more than 32% of the market share in 2023, offering efficiency gains and addressing labor shortages.
- The order fulfillment segment captured over 34% of the market share in 2023, fueled by the need for rapid and accurate order processing, particularly in e-commerce.
- Large warehouses held the largest market share at more than 48% in 2023, leveraging advanced technologies to manage complex operations efficiently.
- Transportation & Logistics accounted for over 19.5% of the market share in 2023, benefitting from optimized supply chain operations.
- North America dominated the Smart Warehousing market in 2023, capturing over 31.5% of the market share.
Smart Warehousing Statistics
- Digital warehouse technology adoption has doubled over the last decade.
- 99% of warehouse operators plan to use Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) within the next five years.
- 5G connectivity in smart warehousing can be up to 100 times faster than 4G.
- Radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology is increasingly used for inventory tracking.
- 62% of companies report a lack of clarity in their supply chains.
- Mobility solutions optimize worker movements and inventory management.
- Machine learning algorithms help predict demand based on historical data.
- The number of warehouses worldwide is expected to increase significantly by 2025.
- The average number of Stock Keeping Units (SKUs) handled by automated warehouses is 13,985.
- Labor costs comprise 50-70% of warehousing budgets.
- The injury rate in warehousing is about 5.1 out of every 100 workers.
- Hourly wages in warehousing increased by over 20% from 2008 to 2017.
- Temporary workers account for over 13% of the warehouse workforce.
- Only 10% of warehouses used advanced automation technology in 2016.
- 96% of industry leaders see innovation as crucial for growth.
- More than 30% of warehouses are currently using or considering robotics.
- Global robot shipments are expected to grow to 620,000 units annually by 2021.
- The adoption of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) exceeded 90% for the first time in 2018.
- Less than 30% of commercial transportation companies use advanced digitization.
Use Cases
- Automated Picking: Robotics technology can triple the speed of order picking compared to traditional methods. Drones improve inventory visibility by performing audits and locating items autonomously.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI analyzes supply chain data to predict and mitigate potential crises, optimizing operations. For instance, AI can alert you to upcoming storage space shortages, allowing for proactive adjustments.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): WMS solutions offer real-time data tracking and visual reports, uncovering inefficiencies in warehouse operations. This enables the quick resolution of issues, maintaining smooth operations.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs enhance the efficiency of warehouse processes such as storage, loading, and stocktaking, without necessitating a complete layout redesign.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT connects various devices to streamline operations. For example, RFID tags help manage inventory by communicating with a WMS to indicate where items should be stored, significantly reducing manual input and errors. The global IoT in warehouse market is expected to reach USD ~18 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of approximately ~21%.
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): Modern AS/RS enhance throughput and accuracy while addressing previous criticisms of high cost and inflexibility.
Companies across industries are adopting smart warehousing technologies. For example, Amazon uses Kiva robots for efficient goods movement, DHL leverages IoT for inventory management, and Alibaba’s Cainiao Network optimizes operations with AI and AGVs.
The Benefits of Smart Warehousing
- Improved Accuracy: Digital tags like RFID and automated inventory control systems minimize human error, ensuring precise inventory tracking.
- Increased Efficiency: Automation technologies like robots and AGVs speed up shipping and warehouse operations, allowing businesses to respond quickly to demand changes.
- Reduced Costs: Smart warehouses can significantly lower labor costs and optimize space, leading to reduced operational expenses and potentially lower product prices for consumers.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Real-time inventory control and faster order fulfillment improve customer satisfaction, helping businesses build stronger relationships.
- Better Transparency: Advanced technologies provide real-time insights into inventory flow and warehouse processes, improving decision-making and stakeholder communication.
Recent Developments
- In 2023, Microsoft partnered with Honeywell to integrate Azure IoT and Dynamics 365 with Honeywell’s warehouse solutions.
- IBM enhanced its Supply Chain Optimization suite with new AI-powered tools and launched its Sterling Warehouse. Management System on IBM Cloud for scalable and flexible WMS deployment.
- SAP launched its Logistics Cloud Warehouse Management, a cloud-based WMS offering improved analytics and integration with other SAP solutions, and enhanced its Intelligent Robotic Warehouse Manager with machine learning.
Key Players Analysis
- Honeywell International Inc. has been a key player in the smart warehousing industry for over three decades. They offer a comprehensive range of automation, software, and labor productivity tools that have revolutionized logistics and warehousing operations worldwide. With technologies employed in over 10,000 warehouses and distribution centers, Honeywell has enhanced material handling through automation and improved order fulfillment accuracy to 99%. Their handheld RFID readers also achieve a 99% inventory tracking accuracy rate, demonstrating the significant impact of their technologies on warehouse operations’ efficiency and reliability.
- Siemens believes that smart warehousing is not only about automation through robots but also entails the effective use of data for predictive maintenance, reduced downtime, and energy cost savings. Siemens advocates for Totally Integrated Automation combined with digitalization to enhance operational efficiency and productivity in the warehousing sector.
- Zebra Technologies Corporation is pushing the smart warehousing sector forward by planning to deploy RFID technology in 58% of warehouses by 2028 to improve inventory visibility and manage out-of-stocks efficiently. Their 2023 Global Warehousing Study highlights the need for modernization, with a focus on accelerating project timelines to manage the growing challenge of returns. This reflects the necessity to modernize operations with technological solutions for increased agility and better real-time decision-making.
- IBM Corporation is utilizing AI and automation to revolutionize smart warehousing by integrating these technologies into existing workflows and systems. This approach aims to simplify operations, increase operational efficiency, and improve customer experiences. IBM’s focus on automating essential processes across business and IT sectors is geared towards growth and cost reduction, showcasing their commitment to driving higher productivity and better decision-making at lower costs and greater speeds.
- Oracle Corporation is enhancing smart warehousing through its warehouse management solution, which leverages cloud advantages and enterprise-grade functionality. This solution is designed to help warehouses meet the challenges of today’s demand-driven marketplace by managing complex fulfillment operations and achieving total inventory visibility, from the distribution center to the store shelf. Oracle’s approach emphasizes preparing warehouses for future demands, ensuring they are equipped to handle new growth efficiently.
- SAP Extended Warehouse Management (SAP EWM) helps manage high-volume goods movements and integrates complex supply chain logistics with warehouse processes, offering improved visibility and control. This solution supports the management of large-scale warehouse operations, enabling businesses to respond quickly to changing conditions and maintain sustainable operations.
- The KION Group is shaping the future of intralogistics with its innovative approach to smart warehousing. Their vision focuses on a warehouse ecosystem driven by artificial intelligence, digitalization, and automation, including the development of autonomous mobile robots like the LoadRunner. These robots, part of a “smart vehicle swarm,” exemplify the use of AI in intralogistics, aiming to revolutionize warehouse operations with their speed and intelligence. KION’s research efforts, in collaboration with institutions like the Fraunhofer Institute, signify a significant leap towards highly automated, efficient, and sustainable warehouse solutions.
- Cognex Corporation offers advanced vision systems and image-based barcode readers that enhance the efficiency, speed, and productivity of warehousing and distribution operations. These technologies streamline packing, sorting, palletizing, and inventory management, meeting the growing demands for performance and customer satisfaction in the food and beverage sector.
- ABB Robotics provides robotic solutions to automate logistics processes, helping modern distribution and fulfillment centers balance volume, flexibility, speed, and accuracy. They offer a comprehensive portfolio that includes various types of industrial robots, AMRs, Cobots, and functional packages, backed by extensive expertise from their Global Solution Centers. Their technology seamlessly transitions from robots to software-enabled hardware, marking a significant innovation in logistics automation.
- Tecsys, Inc. specializes in providing comprehensive supply chain management solutions, including warehousing management systems. Their platforms, like Elite™ Healthcare and Omni™ Retail, offer advanced management capabilities to various industries, focusing on efficiency, accuracy, and integration. They aim to transform supply chains into highly efficient operations, enhancing customer satisfaction through streamlined processes.
- Manhattan Associates is a leading provider of Manhattan Active® Warehouse Management system, a cloud-native, comprehensive solution designed to optimize warehouse operations. This system is scalable and integrated, aiming to enhance efficiency, productivity, and decision-making across supply chains.
Conclusion
The growth of the Smart Warehousing Market is influenced by the intersection of technological progress, the rapidly growing e-commerce sector, and strategic initiatives within the industry. This growth demonstrates the crucial role of smart warehousing solutions in improving supply chain efficiency and adapting to the changing demands of the digital economy.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



