Table of Contents
Report Overview
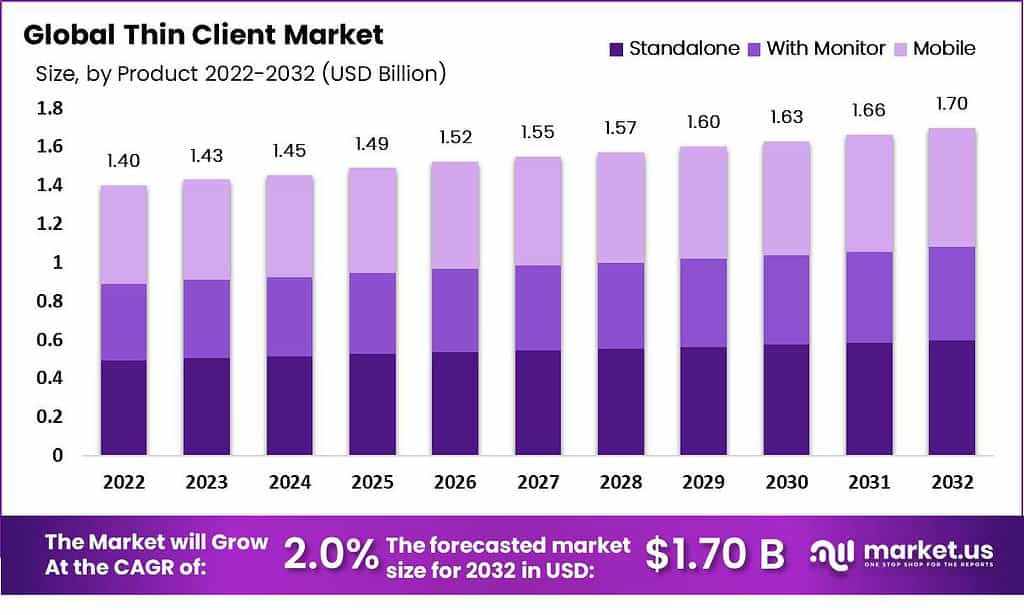
According to Market.us, The global thin client market is projected to reach a valuation of USD 1.7 billion by 2032, growing from an estimated USD 1.45 billion in 2024. This steady growth reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.0% over the forecast period from 2023 to 2032. The market’s expansion is driven by the increasing adoption of cost-efficient computing solutions and the rising demand for secure, centralized systems in enterprise environments. This growth trajectory also highlights the growing preference for virtualization and cloud-based infrastructures, which align well with the operational strengths of thin client systems.
A thin client is a lightweight computing device that depends on a central server for processing and data storage. Unlike traditional personal computers, which handle applications and data locally, thin clients serve primarily as interfaces, transmitting user inputs to the server and displaying the resulting outputs. This architecture centralizes computing resources, facilitating easier management and enhanced security.
The demand for thin clients is bolstered by their cost-effectiveness and energy efficiency. By centralizing processing tasks, organizations can reduce hardware expenditures and lower energy consumption, contributing to overall operational savings. Additionally, the simplified management of software updates and security protocols enhances organizational efficiency.
Technological advancements have significantly enhanced the functionality of thin clients. Modern devices now support complex applications and multimedia content, thanks to improved processing power and efficient data compression techniques. These developments have broadened the applicability of thin clients beyond traditional settings, making them suitable for sectors requiring robust graphical performance.
The business benefits of adopting thin client technology are substantial. Organizations can achieve lower total cost of ownership due to reduced hardware and maintenance expenses. Enhanced security is another critical advantage, as centralized data storage minimizes the risk of data breaches associated with lost or stolen devices. Moreover, the scalability of thin client solutions allows businesses to efficiently accommodate growth without significant additional investments in infrastructure.
Analysts’ Viewpoint
Investment opportunities in this market are bolstered by the increasing demand for centralized and energy-efficient computing systems. However, potential investors should be cognizant of associated risks, such as the reliance on stable network connectivity and limited processing capabilities compared to traditional PCs. Consumer insights reveal a preference for devices that offer simplified management and reduced hardware costs, aligning with the benefits provided by thin clients.
Technological advancements, including integration with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, are expected to further influence market dynamics. The regulatory environment also plays a crucial role, as compliance with data protection and privacy laws is essential, especially in sectors handling sensitive information.
Emerging Trends
- Cloud and Edge Integration: Thin clients are increasingly leveraging cloud and edge computing, enhancing their capability to manage data-intensive applications without the need for local storage or processing power. This trend facilitates more robust, scalable, and efficient computing environments, especially valuable in sectors like healthcare and finance where data security and availability are paramount.
- Adoption of AI and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and machine learning in thin client solutions is advancing. These technologies enable smarter, automated operations that can predict user behavior and optimize system performance, thereby enhancing the overall user experience and system efficiency.
- Enhanced Security Measures: As cybersecurity threats evolve, thin clients are incorporating more sophisticated security protocols to safeguard sensitive information. Features like biometric authentication and advanced encryption are becoming standard to ensure data integrity and privacy.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Thin clients already consume less energy than traditional PCs, but new models are pushing even further with energy-efficient designs that minimize carbon footprints. This is in line with broader industry trends emphasizing environmental responsibility.
- Expansion into New Markets and Applications: As the technology matures, thin clients are being tailored for more diverse applications, penetrating sectors such as education and remote work infrastructures. This diversification is aided by enhancements in performance and compatibility with a wider range of software and peripherals.
Top Use Cases
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI): Thin clients are extensively used in VDI setups where they serve as endpoints for users to access their desktop environments hosted on central servers. This setup is ideal for organizations looking to enhance data security and simplify IT management.
- Remote Work and Hybrid Environments: With the shift towards hybrid work models, thin clients offer a secure and cost-effective way for employees to access corporate networks and resources remotely. This adaptability makes them suitable for organizations with flexible workplace policies.
- Educational Institutions: In education, thin clients provide a cost-efficient solution for computer labs and classroom settings. They allow easy management and maintenance of multiple devices, supporting an environment conducive to learning with minimal IT overhead.
- Healthcare Facilities: In healthcare, thin clients help maintain privacy and security of patient data by enabling access to applications and databases through centrally managed servers. Their use reduces the risk of data breaches and supports compliance with strict regulatory requirements.
- Manufacturing and Warehousing: Thin clients are used in manufacturing and warehousing operations to streamline processes and reduce the risk of data loss. Their robustness and ability to operate in demanding environments make them ideal for these sectors.
Major Challenges
- Network Dependency and Server Bottlenecks: One significant challenge is the reliance of thin clients on constant network connectivity and server availability. Any downtime or performance issues with the server can drastically impact the effectiveness of thin clients, causing disruptions in user sessions and potential data loss.
- Performance Limitations: Thin clients often struggle with high-demand tasks such as multimedia applications, advanced graphical processing, or intensive local computations. This limitation can be a major drawback in environments requiring such capabilities.
- Network Congestion Issues: Common occurrences like login storms, where multiple users log in simultaneously (e.g., at the beginning of a workday), can overload the network, leading to significant slowdowns and reduced user experience. Managing network traffic effectively remains a critical challenge.
- High Initial Setup Costs: Although thin clients themselves may be less expensive than traditional PCs, the total cost of ownership can be high due to the need for robust server infrastructure, licensing fees, and the software needed to run these environments effectively.
- Limited Offline Functionality: Thin clients require a network connection to access most of their functions since they rely on servers to run applications and store data. This makes them unsuitable for scenarios where offline access is necessary.
Attractive Opportunities
- Integration with Advanced Cloud and Edge Computing: As cloud and edge computing technologies advance, thin clients stand to benefit significantly. They can serve as efficient endpoints in distributed computing architectures, enhancing their utility in diverse sectors.
- Adoption in Expanding Remote Work Environments: The shift towards remote and hybrid work models presents a significant opportunity for thin clients. They offer a secure, manageable, and cost-effective way for businesses to extend their operations beyond traditional office environments.
- Growth in Education and Healthcare Sectors: Thin clients are particularly suitable for the education and healthcare sectors where cost-effective, centrally managed, and secure computing solutions are crucial. Their adoption can lead to reduced IT overhead and enhanced data security.
- Enhancements in Security Features: With increasing cyber threats, the inherent security advantages of thin clients – such as centralized data storage and minimal local data presence – make them an attractive option for industries with stringent security requirements.
- Environmental Sustainability: The low power consumption and reduced electronic waste associated with thin clients align with global sustainability goals. This environmental advantage presents a compelling case for businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint while maintaining effective IT operations.
Market Taxonomy
| By Form Factor | By Application |
|---|---|
| Standalone With Monitor Mobile | ITS Education BFSI Industrial Government Healthcare Retail Other Applications |
Top Key Players
- Dell
- HP Inc.
- IGEL Technology
- NComputing
- Fujitsu
- Lenovo
- Stratodesk Corporation
- VXL Technology
- ClearCube Technology
- Centerm Information Co. Ltd.
- Other Key Players
Conclusion
In conclusion, the thin client market is evolving dynamically, propelled by ongoing technological advancements and shifts in organizational needs. The increasing integration with cloud computing, the expanding possibilities offered by remote and hybrid work environments, and the emphasis on environmental sustainability are key factors driving this evolution. Thin clients offer significant opportunities for organizations looking to enhance security, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency through centralized management.
However, they also face challenges such as reliance on robust network infrastructures, limited offline functionality, and initial setup costs. As the market continues to grow, driven by advancements in technologies like 5G and Wi-Fi 7, thin clients are expected to become more versatile and integral to modern IT strategies, aligning with broader trends such as enhanced security measures and the push towards sustainability.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



