Table of Contents
Introduction
According to Educational Robots Statistics, Educational robots are specialized devices employed in the educational field to engage students and facilitate learning, especially in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). These robots possess the capability to be programmed, feature sensors, and are often mobile, allowing them to interact with their surroundings.
They are available in various forms, ranging from DIY robotic kits to pre-programmed and remotely controlled robots, serving as hands-on learning aids. Educational robot finds widespread use in STEM education, coding instruction, and problem-solving tasks, delivering practical knowledge and preparing students for future careers in technology-related professions.
While they offer advantages such as improved learning and the development of critical skills, challenges like cost, teacher training, and maintenance should be considered.
Editor’s Choice
- In 2023, the educational robots market generated approximately USD 1.4 billion in revenue.
- Notably, in 2028, humanoid robots’ revenue is expected to double that of non-humanoid robots.
- Among educational applications, higher education holds the largest share, accounting for 35% of the market, reflecting the significant utilization of robots in tertiary institutions.
- Although the term “educational robotics” has gained prominence in recent years, the origins of such tools can be traced back to 1969 when Seymour Papert introduced the Turtle robot.
- The usage of educational robots in teaching is a topic of interest, and survey data reveals that 26.75% of respondents have affirmed the integration of robots into their teaching methods.
- Among primary school teachers responsible for core subjects in grades 1-4, 29.82% reported incorporating educational robots into their teaching methods, signifying a relatively high adoption rate in this category.
- Notably, the Faculty of Teacher Education reported the highest adoption rate, with 46.93% of respondents incorporating robots into their teaching methods, underscoring the strong presence of these tools in teacher education programs.
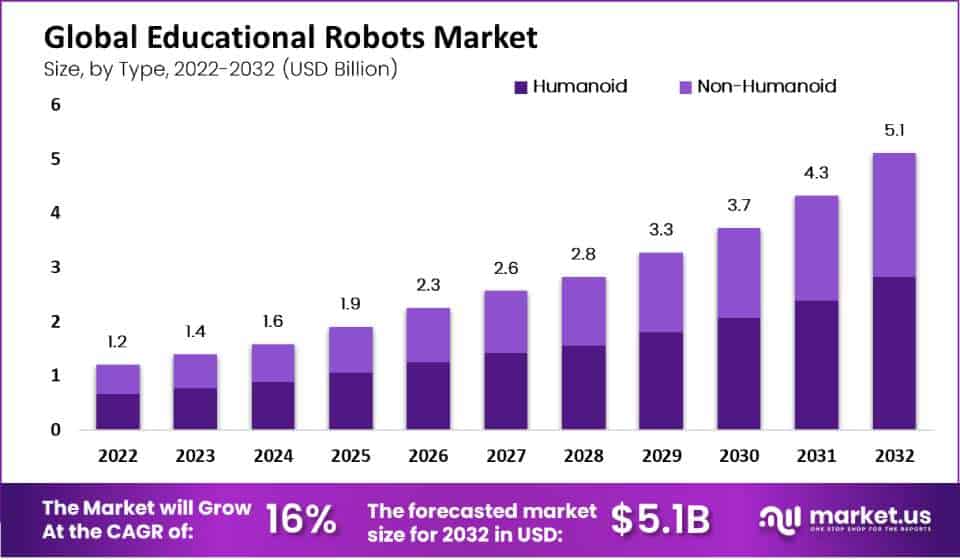
Global Educational Robots Market Overview
Global Educational Robots Market Size
- The global educational robots market is experiencing steady growth, with revenues projected to increase over the coming years.
- In 2022, the market generated approximately USD 1.2 billion in revenue, and this figure is
- The growth trajectory remains positive, with projections indicating revenues of USD 2.8 billion in 2028, USD 3.3 billion in 2029, and USD 3.7 billion in 2030.
- By 2031, the global educational robots market is forecasted to surpass USD 4.3 billion, with further expansion expected, reaching USD 5.1 billion in 2032.

Educational Robots Market Size – By Type
- The global educational robots market, segmented by type into humanoid and non-humanoid robots, demonstrates a consistent upward trajectory in terms of revenue.
- In 2022, the total market revenue reached USD 1.2 billion, evenly distributed between humanoid and non-humanoid categories, each accounting for USD 1 billion.
- In 2026, the market expanded to USD 2.3 billion while maintaining a 1:1 ratio between humanoid and non-humanoid robot revenues.
- Notably, in 2028, humanoid robots’ revenue is expected to double that of non-humanoid robots.
- This trend continues in the following years, with total revenue reaching USD 5.1 billion in 2032, with humanoid robots contributing significantly to this growth.

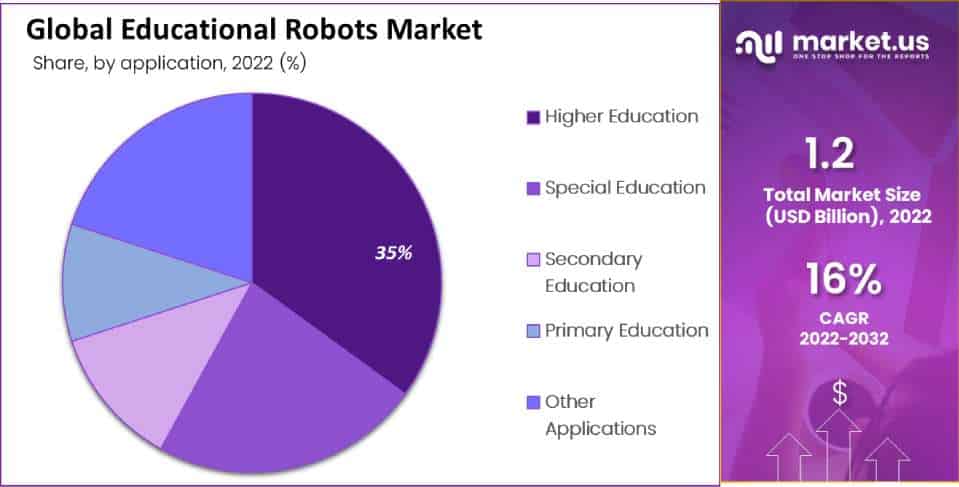
Global Educational Robots Market Share – By Application
- The global educational robots market is characterized by a distribution of market share across various educational applications.
- Among these, Higher Education holds the largest share, accounting for 35% of the market, reflecting the significant utilization of robots in tertiary institutions.
- Special Education follows closely with a substantial 23% market share, indicating their vital role in addressing unique learning requirements.
- Secondary Education holds a noteworthy 12% market share, while Primary Education contributes 10%, underlining the use of educational robots in earlier stages of education.
Historical Overview of Educational Robots
- Although the term “educational robotics” has gained prominence in recent years, the origins of such tools can be traced back to 1969 when Seymour Papert introduced the Turtle robot.
- This robot, programmed in the Logo programming language, marked a pioneering effort in teaching algorithmic thinking and programming. Interestingly, it also inspired the toy giant Lego, which faced financial challenges due to the expiration of its patent rights on building blocks.
- Lego ventured into dynamic and programmable blocks, building upon the foundation of the Turtle robot.
- Concurrently, the market witnessed the emergence of similar educational robotics solutions from companies like Robolink, Hanson Robotics, Modular Robotics, Primo Toys, and Engino.
Usage of Educational Robots in Teaching
- The usage of educational robots in teaching is a topic of interest, and survey data reveals that 26.75% of respondents have affirmed the integration of robots into their teaching methods.
- This suggests that a notable portion of educators recognize the value and benefits of incorporating these specialized devices into the learning process.
- However, the majority, comprising 73.25% of respondents, have not yet adopted educational robots as a teaching tool.

Educational Robots in Teaching Usage – By Subject
- The utilization of educational robots in teaching varies significantly across different subjects, as indicated by the survey results.
- Among primary school teachers responsible for core subjects in grades 1-4, 29.82% reported incorporating educational robots into their teaching methods, signifying a relatively high adoption rate in this category.
- In contrast, technical education and mathematics recorded adoption rates of 14.04% and 5.25%, respectively.
- Other subjects, such as Croatian, chemistry and biology, history and geography, German, physics, English, and foreign languages, each reported relatively lower adoption rates ranging from 0.88% to 3.50%.

Usage of Educational Robots According to Demographics
According to Age
- The usage of educational robots appears to be associated with the age of respondents, as reflected in the survey data.
- Among respondents aged 23 to 29 years, 25.00% reported incorporating robots in their teaching methods.
- The adoption rate increased significantly among respondents aged 30 to 39, with 33.33% utilizing educational robots.
- In the age group of 40 to 49, 24.10% of respondents reported using educational robots for teaching purposes.
- A lower but still notable adoption rate of 16.23% was observed among those aged 50 to 59.
- However, respondents aged 60 and above showed a relatively lower adoption rate of 1.32%.

According to the Graduated Faculty
- The utilization of educational robots in teaching varies significantly across different faculties and departments within educational institutions, as indicated by the survey results.
- Notably, the Faculty of Teacher Education reported the highest adoption rate, with 46.93% of respondents incorporating educational robots into their teaching methods, underscoring the strong presence of these tools in teacher education programs.
- In contrast, the Faculty of Science and the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences recorded adoption rates of 14.04% and 12.28%, respectively, reflecting a lower but still substantial integration of educational robots in these areas.
- Other faculties and departments, including Organization and Informatics, Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, Electrical Engineering and Computing, and others, reported adoption rates ranging from 0.88% to 6.14%.

Popular Educational Robots
Wonder Workshop
- Wonder Workshop enhances the classroom experience through its STEM learning robots, Dash and Cue. Dash appeals to younger children with its singing and dancing abilities and can respond to voice commands.
- On the other hand, Cue offers similar features but is designed for older kids, focusing on more advanced interactions.
- Both robots provide teachers with an immersive way to teach children about robotics, coding, engineering, and various STEM-related subjects.
The LEGO Group
- In 1984, a professor from MIT created a programming language tailored for children, enabling them to control robot “turtles,” making them move, turn, and draw.
- This innovative experiment caught the attention of Lego CEO Kjeld Kirk Kristiansen, who saw the potential to integrate this technology with Lego bricks.
- This collaboration between Lego and MIT led to the development of Lego Mindstorms, a range of programmable Lego robots aimed at inspiring kids to explore STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math) and computer programming.
Kaspar
- The University of Hertfordshire initiated the Kaspar project, which stands for Kinesics and Synchronization in Personal Assistant Robotics.
- Kaspar, resembling a doll-like humanoid, serves as a valuable tool for educators and parents in assisting children with autism or communication challenges.
- Kaspar’s design is deliberately minimal in its facial expressions, prioritizing the specific requirements of children with autism.
BeatBots
- BeatBots is the company responsible for creating Keepon, a small yellow robot that gained internet recognition for its fondness for the band Spoon.
- Originally conceived by Hideki Kozima, Keepon was designed to foster social interaction and enhance communication abilities in children facing developmental challenges.
- While the commercial version of Keepon is utilized in educational settings and by therapists, there’s also a consumer version known as MyKeepon, which is accessible to a wider audience.
VEX Robotics
- Vex Robotics has a mission to engage students in STEM fields by instructing them in the construction and programming of robots.
- The company provides a range of robotic products tailored to various age groups of students, along with a curriculum that serves as a valuable resource for educators.


