Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Editor’s Choice
- Google Bard Statistics Overview
- Bard Statistics by Timeline
- Bard Statistics by Google User
- Google Bard Statistics by Visits
- Bard Audience Demographics
- Regional Variations in Bard Usage
- Bard Marketing Channels
- Engagement of Social Media Platforms
- Training Dataset of Bard Statistics
- Bard Statistics by Referral Traffic
- Outgoing Links from Bard Google.com Statistics
- Google Bard Statistics by Estimated Costs
- Google Bard vs. ChatGPT Statistics
- Recent Developments
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Bard Statistics: Google Bard is a chatbot developed by Google to facilitate natural conversations through cutting-edge technology like natural language processing and machine learning.
It goes beyond enhancing Google search by seamlessly integrating into websites, messaging apps, or applications, delivering responses that mimic human interaction.
Bard aims to improve the search experience by enabling users to ask questions in everyday language, eliminating the need for specific keywords.
It’s trained on real conversations, ensuring its responses are relatable and natural, with added context for more meaningful information. One standout feature is its ability to handle follow-up questions, a unique aspect of search tools.

Editor’s Choice
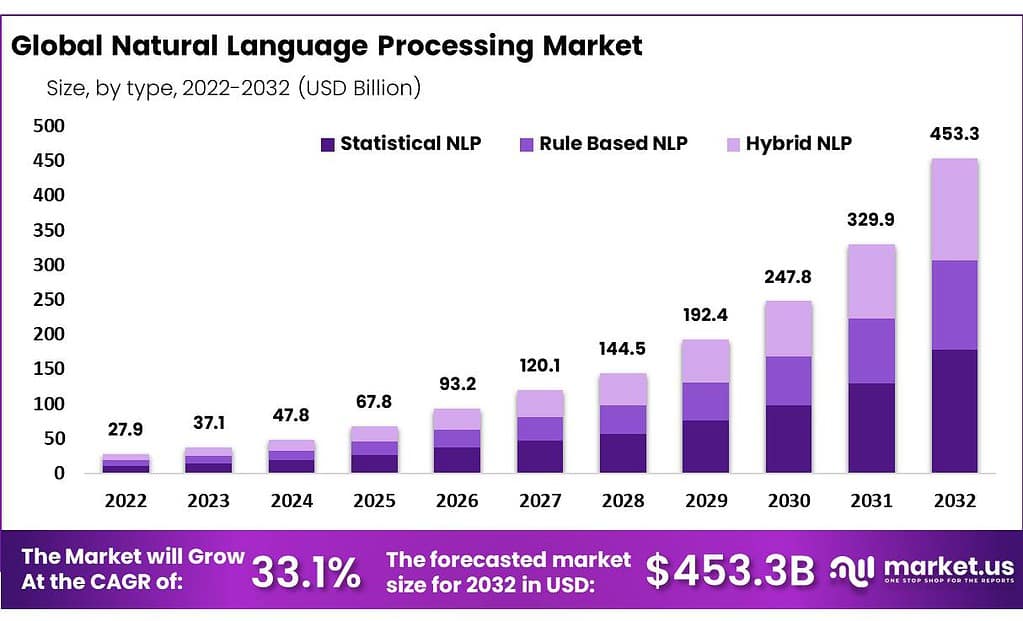
- The Global Natural Language Processing Market in terms of revenue was estimated to be worth USD 37.1 Bn in 2023 and is poised to reach USD 453.3 Bn by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 33.1% from 2023 to 2032.
- Google Bard is on track to surpass 1 billion users by the end of 2023, with over 140.6 million monthly visitors.
- People from more than 230 countries and territories have access to this chatbot.
- Bard is available in over 43 languages, including Chinese, Korean, Arabic, Hindi, and Spanish.
- Demographically, 60% of Bard’s users are male, and 40% are female.
- The largest user group, comprising 34.20%, falls in the 25 to 34 age range, followed closely by the 18 to 24 age group.
- In terms of global traffic, the United States leads with 37.24%, followed by India.
- It’s estimated that each search query on Bard costs between $0.006 and $0.031 to run.
- Regarding traffic sources, more than 76% come directly, while 16.77% are organic.
Google Bard Statistics Overview
- Google Bard was officially launched on March 21, 2023, following its foundation on February 8, 2023, under the umbrella of its parent company, Google, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc.
- With a substantial user base, Bard attracts around 140.6 million monthly visitors across 230 countries and territories.
- It boasts language support in 43 languages, underpinned by the powerful LaMDA (Language Models for Dialog Applications).
- The extensive training dataset powering Bard encompasses a staggering 750 GB of data, equivalent to 1.56 trillion words.
- Notably, the cost per query for this sophisticated AI chatbot ranges from $0.003 to $0.028, reflecting its resource-intensive capabilities.
(Source: Google Bard)
Bard Statistics by Timeline
- Google Bard’s journey has seen a series of significant updates and enhancements since its launch on February 6, 2023.
- Access was opened to the public on March 21, welcoming a broader user base. Subsequent updates in April included adding an experiment updates page and introducing the ‘Google it’ option, enhancing user convenience.
- The evolution continued in April with Bard’s expanded support for 20 programming languages and the introduction of various drafts on April 21.
- May 2023 marked enhancements in Bard’s summarization capabilities and source attribution for its responses on May 15. In late May, Bard further enhanced its utility by enabling the display of help images alongside relevant responses.
- June 2023 ushered in improvements, making Bard’s responses location-relevant and enabling coding assistance, particularly in math and data analysis. Users could also export Bard tables to Google Sheets, enhancing data management capabilities.
- July marked a significant expansion, as Bard became available in 40 additional languages and 27 more countries, broadening its global reach.
(Source: Google Bard)
Bard Statistics by Google User
- Google Bard is anticipated to reach a user base of over 1 billion, although specific user figures are currently unavailable.
- This projection is bolstered by the robust monthly traffic, exceeding 140.6 million visitors.
- Regarding user purposes, 40% utilize Google Bard to research topics of interest, while 30% employ the chatbot for creative endeavors such as crafting poems, scripts, and stories.
- Additionally, 20% seek assistance with work or educational tasks, leaving the remaining 10% to use Bard for entertainment purposes like gaming, video searches, and music exploration.
(Source: mylearning.org)

Google Bard Statistics by Visits
- In the summer months of June, July, and August 2023, two distinct platforms, bard.google.com and bardai.io, witnessed varying levels of visitor traffic.
- Bard.google.com, the largest of the two, experienced substantial user engagement with 140.6 million visits in June, which increased to 189.2 million in July and remained strong at 183.5 million in August.
- In contrast, bardai.io, a more specialized platform, saw comparatively lower visitor numbers.
- It recorded 160.7 thousand visits in June, 104.5 thousand in July, and 96.3 thousand in August. These statistics highlight the fluctuations in user activity across these platforms during the specified summer months.
- The top keyword, simply “bard,” garners significant attention with 2.4 million searches, indicating a strong user interest.
- “Google Bard” closely follows with 2.1 million searches, suggesting a specific interest in this AI-powered chatbot.
- “Bard AI” receives substantial attention with 751,000 searches, while “Bard Google” records 483.9 thousand searches, reflecting curiosity about AI in the context of Google.
- “Google Bard AI” rounds out the list with 127.9 thousand searches, highlighting a more specific query.
- The collective impact of these search terms provides a comprehensive view of user engagement with Bard-related keywords, with a few other queries contributing 8.5 thousand searches.
(Source: Similarweb)
Bard Audience Demographics
Age-wise Distribution of Bard
- The usage of Bard across different age groups varies significantly. The highest user percentage falls within the 25-34 age bracket, accounting for 34.20% of Bard’s user base.
- The 18-24 age group follows closely behind, representing 22.21% of users.
- Users aged 35-44 comprise 19.68% of Bard’s users, while the 45-54 age group constitutes 12.86% of the user base.
- In the older age demographics, Bard sees progressively fewer users, with 7.03% in the 55-64 age group and 4.02% among users aged 65 and above. This distribution of users across age groups provides valuable insights into Bard’s user community demographics.
(Source: Similarweb)

Gender Distribution of Bard Users
- Bard’s user base displays a noticeable gender distribution, with 62.55% male users, while female users account for 37.45%.
- This gender split sheds light on the demographic composition of Bard’s users, with a higher prevalence of male engagement than female users.
(Source: Similarweb)

Regional Variations in Bard Usage
- Google Bard draws its traffic from a global audience, with a predominant share originating from the United States, contributing to 37.24% of the total traffic.
- India follows as the second-largest source of traffic, accounting for 9.56%.
- Japan and the United Kingdom also play substantial roles, with 6.67% and 5.44% of the traffic, respectively.
- Australia adds to the international presence, providing 2.53% of the traffic.
- The remaining 38.56% of the traffic comprises visitors from various other countries, showcasing the diverse and widespread user base of Google Bard on a global scale.
(Source: Similarweb)

Bard Marketing Channels
- Google Bard’s traffic sources are diversified across various marketing channels. The largest share of traffic, amounting to 79.61%, comes directly, indicating that many users access Bard without intermediaries.
- Referrals contribute a smaller yet notable 2.45% of the traffic, suggesting that some users discover Bard through external websites or sources.
- Organic search constitutes 13.84% of the traffic, highlighting the significance of users finding Bard through search engines without paid promotions.
- Paid search and social media channels contribute a modest portion, with 1.98% and 1.9%, respectively, indicating some level of paid advertising and social media engagement.
- Email marketing and display ads represent a smaller fraction, with 0.18% and 0.04% of the traffic, respectively. This comprehensive distribution of traffic sources demonstrates Bard’s multi-faceted approach to user acquisition and engagement.
(Source: Similarweb)

Engagement of Social Media Platforms
- Google Bard receives traffic from various social media platforms, with YouTube being the most significant source, contributing 52.19% of the total traffic.
- Twitter is the second-largest contributor, directing 14.16% of users to Bard.
- Facebook and WhatsApp also play substantial roles, accounting for 8.82% and 8.58% of the traffic, respectively.
- LinkedIn adds to the mix, with 5.61% of the traffic from this professional network.
- Other social media platforms collectively contribute 10.64% of the traffic, showcasing the diverse sources through which users discover and engage with Google Bard.
(Source: Similarweb)

Training Dataset of Bard Statistics
- Google Bard’s training dataset comprises diverse sources, each contributing a distinct percentage. Most of the dataset, 50%, is derived from dialog data sourced from forums, reflecting real-world conversational interactions.
- A substantial portion, 12.5%, is based on C-4 data, likely to provide a wide range of textual content for training.
- The inclusion of English Wikipedia data, also at 12.5%, underscores the significance of this reputable knowledge source.
- Code documents contribute 12.5%, focusing on technical and programming-related content.
- The dataset also encompasses 6.3% of English and non-English web documents, balancing language-specific and multilingual content sources. This diverse compilation of training data sources ensures that Google Bard has a broad understanding of language and knowledge.
(Source: MeetanshI)

Bard Statistics by Referral Traffic
- Referral traffic to bard.google.com is diverse, originating from various categories. Notably, a significant portion, 33.61%, comes from Search Engines, indicating that users often discover bard.google.com through web searches.
- The Computers, Electronics, and Technology category also contributes substantially, with 26.33% of the referral traffic, showcasing the relevance of bard.google.com to tech-related content.
- Email referrals account for 16.07%, indicating that email communications also play a role in directing users to the platform.
- The programming and developer software category contributes 12.4% of the traffic, underscoring the technical nature of some content hosted on bard.google.com.
- Additionally, a small fraction, 1.99%, stems from File Sharing and Hosting, while 9.6% falls into the ‘Other’ category, representing a mix of miscellaneous sources that bring traffic to bard.google.com. This data provides insights into the diverse referral sources contributing to the platform’s traffic.
(Source: Similarweb)

Outgoing Links from Bard Google.com Statistics
- Bard.google.com features a range of outgoing links across different categories, reflecting its engagement with various online resources. A significant proportion of these outgoing links, at 49.11%, belong to the Programming and Developer Software category, highlighting the platform’s relevance to technical content.
- The Computers, Electronics, and Technology categories contribute notably, accounting for 31.06% of the outgoing links, underscoring its connection to tech-related resources.
- Search Engines also play a role, contributing 8.31% of the links, suggesting connections to external search results or tools.
- Email-related links constitute 7.53%, reflecting interactions with email services.
- A smaller percentage, 1.55%, relates to File Sharing and Hosting links.
- The ‘Other’ category encompasses 9.6% of outgoing links, representing a diverse mix of connections to various online destinations. This data illuminates the diverse resources accessed through outgoing links from bard.google.com.
(Source: Similarweb)

Google Bard Statistics by Estimated Costs
- Each search on Google Bard incurs a base cost of $0.003 per inquiry, along with an extra charge ranging from $0.003 to $0.028, added to the standard search cost.
- Consequently, the total expense for each Bard search can fall between $0.006 to $0.031.
- Google Bard’s responses, generated with different word counts, correlate with the percentage of Google queries handled by AI. For instance, when 25 words are generated per query, with AI handling 10% of Google queries, it amounts to an estimated cost of $0.6 billion.
- As the word count per query increases to 50 words, the cost escalates proportionally, reaching $1.2 billion for the same query percentage.
- This pattern continues with 75 words generated per query and 100 words generated per query, with the estimated costs doubling and tripling accordingly.
- According to Bard Statistics, For instance, when AI handles 30% of Google queries and generates 75 words per response, the projected cost is $5.4 billion. These figures illustrate the varying costs associated with Google Bard’s responses based on word count and query percentage, providing insights into the financial dynamics of AI-generated content.
(Source: Reuters)
Google Bard vs. ChatGPT Statistics
- User engagement differs between the two, with Google Bard recording an average session duration of 3.19 minutes, while ChatGPT boasts a longer average session duration of 8.44 minutes.
- Additionally, their pre-training data cut-off points vary, with Google Bard’s data cut-off in 2019, while ChatGPT’s data extends up to 2021.
- Cost-wise, the incremental expense per query ranges from $0.003 to $0.028 for Google Bard, while ChatGPT has a more fixed cost of $0.0036 per query.
- Regarding subscription models, Google Bard currently offers its services for free. In contrast, ChatGPT provides both a free tier and a subscription-based Plus plan at $20 per month, offering additional features and benefits to users.
- The scale of their training datasets is another differentiator, with ChatGPT trained on a vast 300 billion words. In contrast, Google Bard boasts an even more extensive dataset, incorporating a whopping 1.56 trillion words. This substantial dataset contributes to both platforms’ language understanding capabilities.
- In terms of parameters, ChatGPT utilizes 175 billion parameters, while Google Bard employs 137 billion parameters. These parameters are crucial for fine-tuning model performance and enhancing language comprehension.
- The pre-training data cut-off points also diverge, with ChatGPT’s data being current up to 2021, while Google Bard’s pre-training data is based on information available up to 2019.
- Finally, when it comes to data storage size, ChatGPT requires 570 GB, whereas Google Bard demands a slightly larger storage capacity of 750 GB.
- Read more about ChatGPT statistics.
(Source: Similarweb)
Recent Developments
Acquisitions and Mergers:
- Google acquires Bard Inc: In early 2024, Google completed the acquisition of Bard Inc., an AI-powered content generation company, for $1.5 billion. This acquisition aims to enhance Google’s capabilities in AI-driven content creation and natural language processing.
- Microsoft acquires AI Text Solutions: Microsoft finalized its acquisition of AI Text Solutions, a competitor in the AI-generated content space, for $900 million in late 2023. This merger strengthens Microsoft’s position in AI and machine learning for content generation.
New Product Launches:
- Bard AI 2.0: Bard Inc. launched Bard AI 2.0 in January 2024, featuring advanced natural language generation capabilities, improved contextual understanding, and enhanced content creation tools for businesses and individual users.
- Google Cloud Bard API: Google introduced the Google Cloud Bard API in mid-2023, allowing developers to integrate Bard’s AI-driven text generation into their applications and services, offering scalable and customizable content solutions.
Funding:
- Bard Inc. raises $500 million: Bard Inc. secured $500 million in a Series C funding round in 2023 to expand its AI research and development efforts and increase its market presence in the content generation industry.
- AI Content Solutions secures $200 million: AI Content Solutions, a startup focused on AI-driven writing tools, raised $200 million in early 2024 to enhance its product offerings and scale its operations.
Technological Advancements:
- Contextual AI Models: Recent advancements in contextual AI models have significantly improved Bard’s ability to generate coherent and contextually relevant text, making it more suitable for diverse applications such as marketing, customer service, and creative writing.
- Multilingual Capabilities: Bard has expanded its multilingual capabilities, supporting over 50 languages by leveraging advanced translation and language modeling technologies, making it accessible to a global audience.
Market Dynamics:
- Growing Demand for AI Content Generation: The market for AI-driven content generation tools is expected to grow at a CAGR of 20% from 2023 to 2028, driven by the increasing need for scalable content solutions in digital marketing, e-commerce, and media industries.
- Adoption in Enterprises: Large enterprises are adopting Bard’s AI technology to automate content creation processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs associated with human writers, particularly in areas like customer support and content marketing.
Regulatory and Strategic Developments:
- Ethical AI Guidelines: Bard Inc. has implemented stringent ethical AI guidelines to ensure responsible use of its technology, focusing on transparency, bias mitigation, and user privacy, aligning with global standards and regulations.
- Partnership with Educational Institutions: Bard Inc. has partnered with several universities and educational institutions to integrate its AI-driven content generation tools into their curricula, promoting the use of AI in academic research and learning.
Research and Development:
- Enhanced AI Training Data: Bard’s R&D efforts are focused on improving the quality and diversity of training data, ensuring that its AI models can generate more accurate and contextually relevant content across different domains.
- Collaboration with AI Research Labs: Bard Inc. is collaborating with leading AI research labs to explore new applications of its technology and advance the state-of-the-art in natural language processing and generation.
Conclusion
Bard Statistics – Google Bard has emerged as a significant player in the chatbot industry, presenting a formidable competition to ChatGPT.
This conversational AI chatbot, Google Bard, is engineered to comprehend and engage in human conversations using a highly natural approach.
Its impact in the field has been noteworthy, drawing in millions of users and achieving impressive metrics. Powered by the robust LaMDA model, Bard is well-positioned for ongoing expansion and enhancement, promising continued growth and refinement in its capabilities.
FAQs
Bard serves as a versatile tool, offering benefits in several areas. It excels at providing quick answers, fostering creativity, and boosting productivity. It functions as a valuable collaborator, simplifying various tasks and projects.
Regarding citation, when Bard incorporates content from other sources, it references the originating page. It typically selects the most popular source if multiple websites have similar content.
Bard can assist with coding and explaining coding-related topics, though it’s essential to thoroughly review and test the code it generates due to its experimental nature.
Regarding accessibility, anyone aged 18 or older with a personal Google Account or a Google Workspace account can use Bard. It’s important to note that it’s not compatible with Google Accounts managed by Family Link or Google Workspace for Education, designed for users under 18.
As for languages, Bard currently operates in English, Japanese, and Korean. However, it’s actively working on learning 40 more languages to cater to a broader global audience.
Regarding data collection, Google collects various information through Bard, including conversations, location, feedback, and usage data. This data aids in improving products, services, and machine-learning technologies like Bard. It’s crucial to note that conversations with Bard are not used for advertising or sold to third parties. Additionally, automated tools are employed to remove personally identifiable information, ensuring user privacy.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)



